pleural effusion 2015
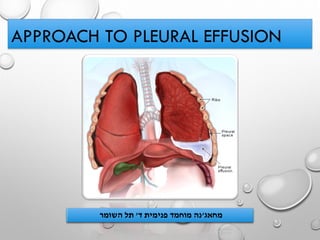
- 1. APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSION מחאג'ד פנימית מוחמד נה'השומר תל
- 2. בת צעירה אישה מגיעה מיון בחדר תורנים אתם34בימים החמרה עם נשימה קוצר על שמתלוננת האחרונים,אמתית וצמרמורת בחום מלווה,ימין בצד בעיקר בחזה כאבים,לה יש שלאחרונה מדווחת פרודוקטיבי ושיעול לילה הזעות.ברקע:מעשנת,לאלכוהול מכורה,גלולות נוטלת. בקבלתה: יציבההימודנאמיתאוושות ללא סדירים לב קולות,דם לחץ140/80,חום38.6,דיספנייתעם סטורציה93חדר באוויר,לגב קלה הקרנה עם עליונה בבטן קלה רגישות למעט רכה בטן. סימטרית לא חזה בית התפשטות,מימין מופחתת אוויר כניסת,פרימיטוסירוד,בניקוש עמימות עם ימין מצד צלוליטיס סימני ללא בצקות ללא תקינות גפיים. בנשימה מתגברים חזה מכאבי סובלת חודש שמזה מדווחת,קבלה בקהילה:קודיקאל,אזיניל ,טאריביד,ואיטופאן.משמעותי שיפור ללא.
- 5. • Definition and overview • Pathophysiology • Etiology • Clinical manifestation • Complications • Lab tests and diagnosis • Treatment and management
- 6. Definition and overview • Up to 25 ml of pleural fluid is normally present ,not detectable on conventional chest radiographs. • Pleural fluid arise from systemic pleural vessels and exit through lymphatic • About 100-200ml of fluid circulates though the pleural space Within a 24-hour period • Has an alkaline pH of about 7.64 • A pleural effusion is present when there is an excess quantity of fluid in the pleural space.
- 8. Increased pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) Decreased intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) Increased capillary permeability (Pneumonia) Decreased plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia) Increased pleural membrane permeability (malignancy) lymphatic obstruction (malignancy) , rupture [chylothorax] diaphragmatic defect , cirrhosis (hepatic hydrothorax)
- 9. PLEURAL EFFUSION TYPES • THE 5 MAJOR TYPES OF PLEURAL EFFUSION ARE: 1) TRANSUDATE 2) EXUDATE 3) EMPYEMA 4) HEMORRHAGIC PLEURAL EFFUSION OR HEMOTHORAX 5) CHYLOUS OR CHYLIFORM EFFUSION.
- 10. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, 18th edition. Fauci, Braunwald, Kasper, Hauser, Longo, Jameson, Loscalzo.
- 12. LEADING CAUSES OF PLEURAL EFFUSION IN USA IN DECREASING ORDER OF INCIDENCE 1. CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE 2. PNEUMONIA 3. CANCER 4. PULMONARY EMBOLISM 5. VIRAL DISEASE 6. CABG 7. CIRRHOSIS WITH ASCITES
- 13. EXUDATIVE PLEURAL EFFUSIONS Drug-induced pleural disease 1) Nitrofurantoin 2) Dantrolene 3) Methysergide 4) Bromocriptine 5) Procarbazine 6) Amiodarone
- 15. • HISTORY: • DYSPNEA , ORTHOPNEA • PLEURITIC CHEST PAIN • COUGH • FEVER • HEMOPTYSIS • ARTHRALGIA , MYALGIA, ARTHRITIS, OTHER AUTOIMMUNE RELATED HISTORY • WT. LOSS • TRAUMA • HISTORY OF CANCER • SMOKING • ORAL CONTRACEPTIVE • CARDIAC SURGERY [E.G CABG] • OCCUPATIONS • PHYSICAL: • DULLNESS TO PERCUSSION • DECREASED BREATH SOUNDS • ABSENT TACTILE FREMITUS • OTHER FINDINGS: ASCITES, JVP, PERIPHERAL EDEMA, FRICTION RUB, UNILATERAL LEG SWELLING
- 16. CLUES IN THE PHYSICAL TO THE COMMON ETIOLOGIES
- 17. 1. CHF : Distended neck veins, an S3 gallop, or peripheral edema 2. PE : A right ventricular heave or thrombophlebitis and sinus tachycardia . 3. neoplastic disease :The presence of lymphadenopathy or hepatosplenomegaly suggests. 4. Ascites may suggest a hepatic cause. 5. Para pneumonic effusion :Signs of consolidation above the level of the fluid in a febrile patient suggests.
- 18. • Mainly Asymptomatic as isolated condition . • Symptoms are more likely when a pleural effusion is moderate or large-sized >400-500ml • if inflammation is present. • Symptoms of pleural effusions may include: A. Shortness of breath B. Chest pain, especially on breathing in deeply (pleurisy, or pleuritic pain) C. Fever D. Cough E. Because pleural effusions are usually caused by underlying medical conditions, symptoms of these conditions are also often present Symptoms of Pleural Effusions
- 19. DIAGNOSIS
- 21. LIGHT’S CRITERIA • SENSITIVITY 99%, SPECIFICITY 98%
- 22. Exceptions These are processes that typically cause exudative effusions, but may cause transudative effusions. •Amyloidosis •Chylothorax •Constrictive pericarditis •Hypothyroid pleural effusion •Malignancy •Pulmonary embolism •Sarcoidosis •Superior vena cava obstruction •Trapped lung
- 23. SERUM • Serology for autoimmune disorders : RF factor , Anti CCP , ANA , ANTI dDNA …. • Routine : RBC , hemoglobin , WBC , PMN ….. • Infectious : CRP , ESR , WBC , PMN , leukocytosis , acute phase proteins , LDH • Albumin , total protein • Renal function • Liver enzymes , ALT , AST , GGT , ALP • PT , PTT , INR* , PLT
- 24. RADIOLOGY Effusions of more than 175 mL are usually apparent as blunting of the costophrenic angle. • Location : TB Vs CHF Vs cirrhosis • Mediastinal shift • Heart enlargement [ CHF] • Amount • Recent Vs previous • Reccurent [ malignancy e.g. mesothelioma] A. CXR [ PA , AP , lateral decubitus ] B. Ultrasound C. CT
- 25. LOCATION AMOUNT CORRELATION 75 mL barley detectable 175 mL obscure the lateral cost phrenic sulcus on an PA 500 mL obscure the diaphragmatic contour on an PA 1000 ml reaches the level of the 4th anterior rib, On decubitus radiographs and CT scans, less than 10 mL can be identified PORCEL et al. AFP 2006; 73: 1212
- 26. QUANTITATION OF EFFUSION Based on the decubitus films 1. small effusions <1.5 cm 2. moderate =1.5 to 4.5 cm 3. large effusions >4.5 cm. Effusions thicker than one 1cm are usually large enough for sampling by thoracentesis, since at least 200 mL of liquid are already present
- 28. CT Scan
- 29. Thoracentesis for both diagnosis and treatment Pleural Fluid Analysis
- 30. INDICATIONS FOR THORACENTESIS LIKELY INDICATED IN MOST PATIENTS! > 1 CM LAYERING ON LATERAL DECUBITUS CHF IS HIGHLY UNLIKELY [ E.GLARGE EFFUSION RECURRENT PLEURAL EFFUSION , MALIGNANCY PLEURAL EFFUSION AND FEVER: EMPYEMA THERAPEUTIC THORACENTESIS: DYSPNEA, CHEST PAIN … UNCLEAR ETIOLOGY OR OBVIOUS CAUSE WITH ATYPICAL PRESENTATION CHF WITH ATYPICAL PRESENTATION [E.G. UNEQUAL BILATERAL EFFUSION]
- 31. CONTRAINDICATIONS There are no absolute contraindications to thoracentesis Benefit Vs risks Caution if : A. PTT , PT B. Cr >6 mg/dL C. decisions to reverse the coagulopathy or correct the thrombocytopenia should be individualized D. Anticoagulation or a bleeding diathesis
- 32. complications
- 33. • PAIN AT THE PUNCTURE SITE • BLEEDING (HEMATOMA, HEMOTHORAX (1%) , OR HEMOPERITONEUM) • PNEUMOTHORAX ( 2-6%) • SOFT TISSUE INFECTION • SPLEEN OR LIVER PUNCTURE • VASOVAGAL EVENTS • SEEDING THE NEEDLE TRACT WITH TUMOR • ADVERSE REACTIONS TO THE ANESTHETIC
- 34. Pleural fluid glucose, lactate, amylase, triglyceride, and/or tumor markers Microscopic examination –(WBCs) or (RBCs) or microorganisms. WBC differential—determination of percentages of different types of WBCs High PMN bacterial infection High lymphocytes TB Gram stain –Bacterial culture and susceptibility testing Less commonly ordered tests for infectious diseases, such as tests for viruses, mycobacteria (AFB smear and culture), and parasites. Ph RF factor Cytology Appearance : cloudy , milky , bloody . . . . Pleural Fluid Analysis
- 35. PORCEL et al. AFP 2006; 73: 1212 Pleural Fluid Tests
- 36. PORCEL et al. AFP 2006; 73: 1212 Pleural Fluid Tests
- 37. PORCEL et al. AFP 2006; 73: 1212 Pleural Fluid Tests
- 38. PORCEL et al. AFP 2006; 73: 1212 Pleural Fluid Tests
- 39. EXUDATIVE EFFUSION Cell count :- 1. Neutrophil acute pleural process (pneumonia, PE) 2. Lymphocytic chronic process (Cancer, TB, CABG) Culture/stain- infected fluid Glucose- low level (<60mg/dl) (pneumonia, CA) Cytology- malignancy pH- Para pneumonic <7.2 -must drain fluid indicates poor prognosis Bloody – Hematocrit compared to the blood <1% is no significant 1-20% indicates either cancer, PE or trauma >50% indicates hemothorax.
- 40. EXUDATIVE EFFUSIONS OTHER TESTS • SUSPECTED TB • ADENOSINE DEAMINASE (> 50 IU/L) • B2 - MICROGLOBULIN • PCR (SENS 100%, SPEC 95%) • PPD • SUSPECTED RHEUMATOID • PLEURAL RF • LOW GLUCOSE • SUSPECTED SLE • SERUM COMPLEMENT • PLEURAL ANA • SUSPECTED PNEUMONIA • PH • SUSPECTED PANCREATITIS • PLEURAL AMYLASE
- 41. • LYMPHOCYTIC (> 50%) • CA (30-35%) • TB (15-20%) • SARCOIDOSIS • PMNS • EMPYEMA • PARA PNEUMONIC • RHEUMATOID • PULMONARY INFARCTION • PMN OR LYMPHOCYTIC • PE • POST-CARDIAC INJURY • EOSINOPHILIC (> 10%) • TRAUMA • PTX • CA • ASBESTOS, PARASITES • PNEUMONIA • RBC > 100,000/MM • CA • TRAUMA • PULMONARY INFARCTION
- 43. Clinical features suggestive of malignancy: 1. Symptoms > one month 2. Absence of fever 3. Bloody tinged fluid 4. CT very suggestive for malignancy 5. Persistent pneumonia 6. Pts history : smoking , asbestosis , malignancy history Pleural fluid: A. Appearance : Mostly bloody B. WBC differential : mainly lymphocytic C. Glucose : mostly decreased <60 mgdL , or normal D. Elevated lactate >2/3 X serum lactate E. PH < 7.2 typically F. Cytology and tumor markers are positive**
- 44. Lung >breast > lymphoma/leukemia metastatic adenocarcinoma positive cytology 70% Lymphoma 25-50% Mesothelioma 10% Squamous Cell Carcinoma 20% Sarcoma within pleura 25% Epidemiology
- 45. EMPYEMA PYOTHORAX OR PURULENT PLEURITIS
- 46. Typical symptoms include : cough, chest pain, shortness of breath and fever , persistent pneumonia** an accumulation of pus in the plural cavity along with : a. Pleural PH < 7.2 with normal blood PH. b. Pleural gluc< 60 mgdl c. Pleural lactate >2/3 serum lactate d. Purulent , cloudy , yellow-brownish fluid Treatment and management : 1. Thoracentesis 2. Chest tube 3. Antibiotics for 1-4 weeks or until improvement 4. Cipro , Flagyl , Penicillin's , clindamycin , vancomycin , gentamycin Consider streptokinase , urokinase for fibrinolysis
- 48. CLINICAL SYMPTOMS Shortness of breath, cough , chest pain-- common to pneumonia. Febrile respiratory illness, accentuation, prolongation the symptoms in pneumonia-- alert the possibility of empyema. Aerobic empyema-- acute febrile illness. Anaerobic empyema-- more indolent, usually 10 days.
- 49. DRAINAGE
- 51. • 15-20% of effusions • Careful review of history, PE, meds, risk factors • Consider occult abdominal process • Consider PE Meigs' syndrome : triad of ascites pleural effusion benign ovarian tumor . It resolves after the resection of the tumor.
- 52. JOSÉ M. PORCEL, M.D., Arnau de Vilanova University Hospital, Lleida, Spain RICHARD W. LIGHT, M.D., Saint Thomas Hospital, Nashville, Tennessee Am Fam Physician. 2006 Apr 1;73(7):1211-1220.
- 56. RESOURCES 1. REDUCING IATROGENIC RISK IN THORACENTESIS: ESTABLISHING BEST PRACTICE VIA EXPERIENTIAL TRAINING IN A ZERO-RISK ENVIRONMENT. DUNCAN DR, MORGENTHALER TI, RYU JH, DANIELS CHEST. 2009;135(5): 1315 2. PNEUMOTHORAX FOLLOWING THORACENTESIS: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS. GORDON CE, FELLER-KOPMAN D, BALK EM, SMETANA GW ARCH INTERN MED. 2010;170(4):332 3. COMPLICATIONS ASSOCIATED WITH THORACENTESIS. SENEFF MG, CORWIN RW, GOLD LH CHEST 1986; 90:97-100 4. THORACENTESIS: COMPLICATONS, PATIENT EXPERIENCE AND DIAGNOSTIC VALUE. COLLINS TR, SAHN SA. AM REVIEW RESPIRATORY DISEASE 1983; 127:A114 5. HARRISON’S PRINCIPLES OF INTERNAL MEDICINE, 18TH EDITION. FAUCI, BRAUNWALD, KASPER, HAUSER, LONGO, JAMESON, LOSCALZO. 6. UPTODATE ONLINE. WWW.UPTODATE.COM. 7. PORCEL ET AL. AFP 2006; 73: 1212 8.
- 58. Thanks Docs
