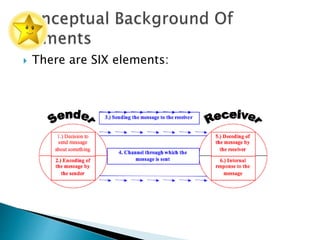
This document discusses communication styles and skills. It begins by outlining seven major conversational styles: dominant, interruptive, manipulative, polite, creative, sarcastic, and passive. It then describes the six elements of the communication process. Several factors that can negatively influence communication are identified, including a sender's past experiences and lack of encoding skills. Nonverbal communication such as body language, proxemics, and paralanguage are also discussed. The importance of listening skills is emphasized. Finally, the document provides steps to enhance communication skills and resolve conflicts, including using positive language and focusing on understanding others' perspectives.