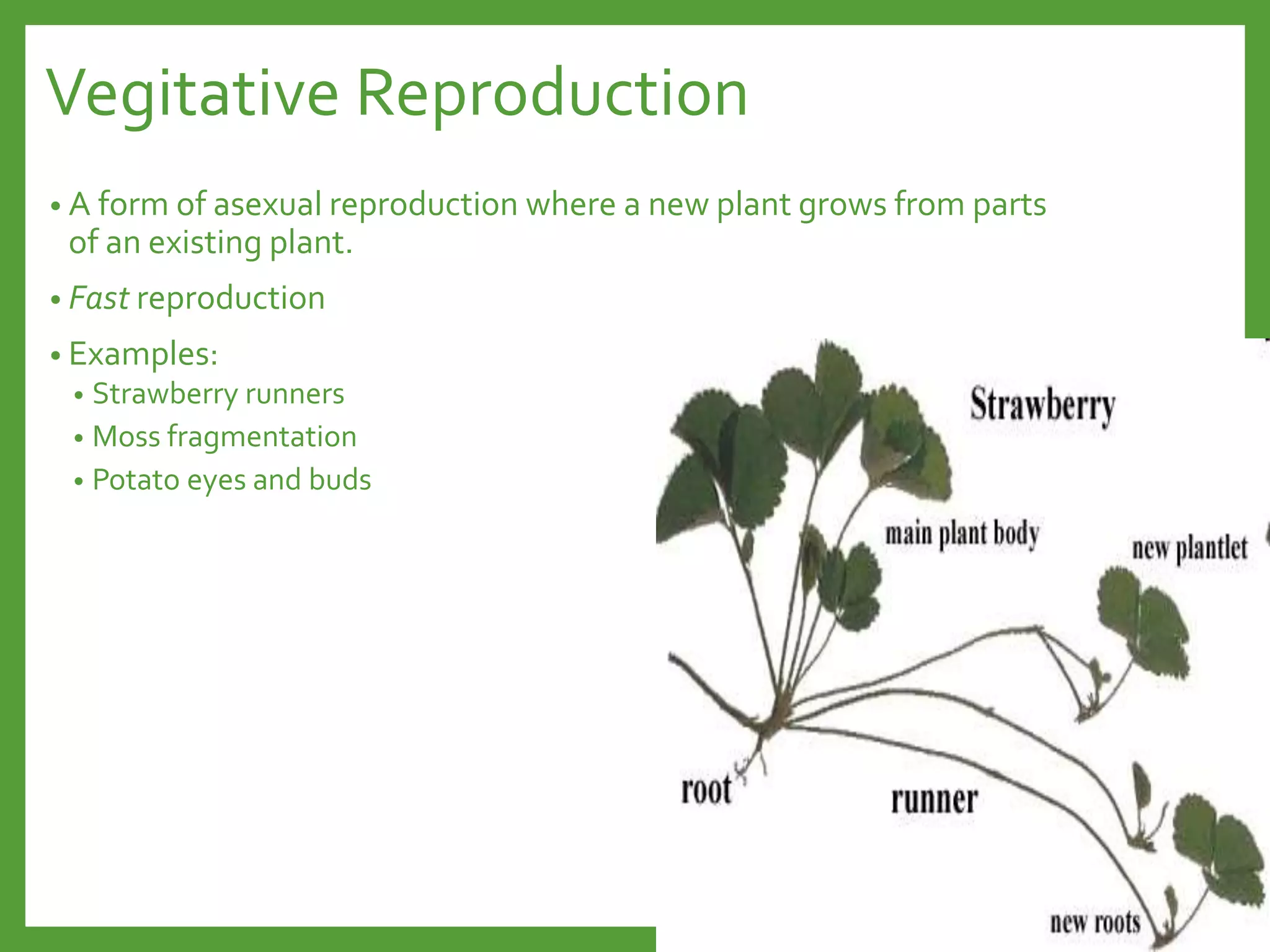
Plant reproduction can occur sexually through the fusion of egg and sperm cells, or asexually through cloning. Sexual reproduction involves flowers with sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels that attract pollinators. Asexual reproduction methods for plants include vegetative propagation through stems, roots, leaves, bulbs, or artificial techniques like cuttings, grafting, layering, and tissue culture. Both sexual and asexual reproduction have advantages and disadvantages for plant survival and dispersal. The relationship between a flower's structure and its function aids in pollination and fruit/seed production and dispersal.