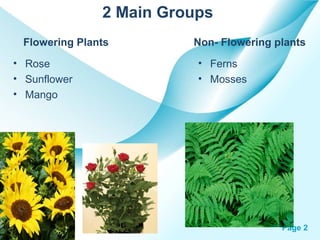
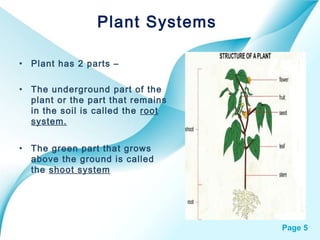
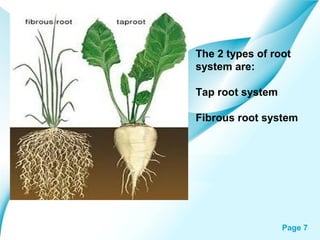
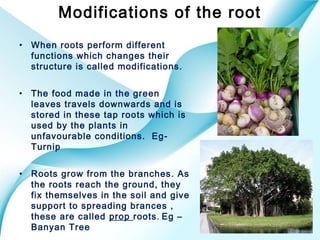
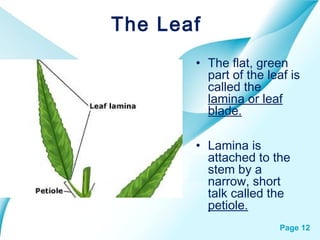
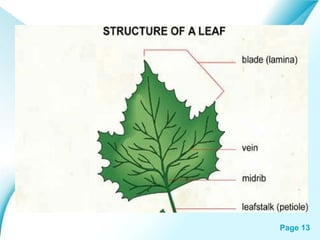
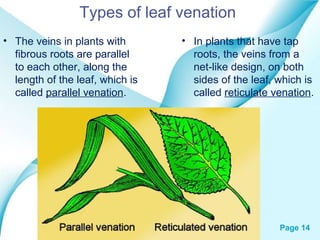
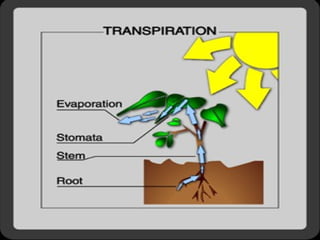
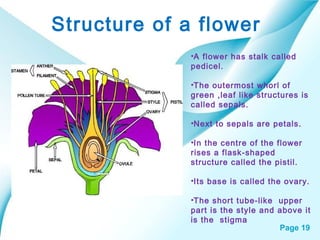
The document provides an overview of plant classification, including flowering and non-flowering plants, and various plant systems such as roots, stems, and leaves. It details the functions of these systems and their modifications, alongside processes like photosynthesis and pollination. Additionally, it mentions resources for further learning about plant life cycles.