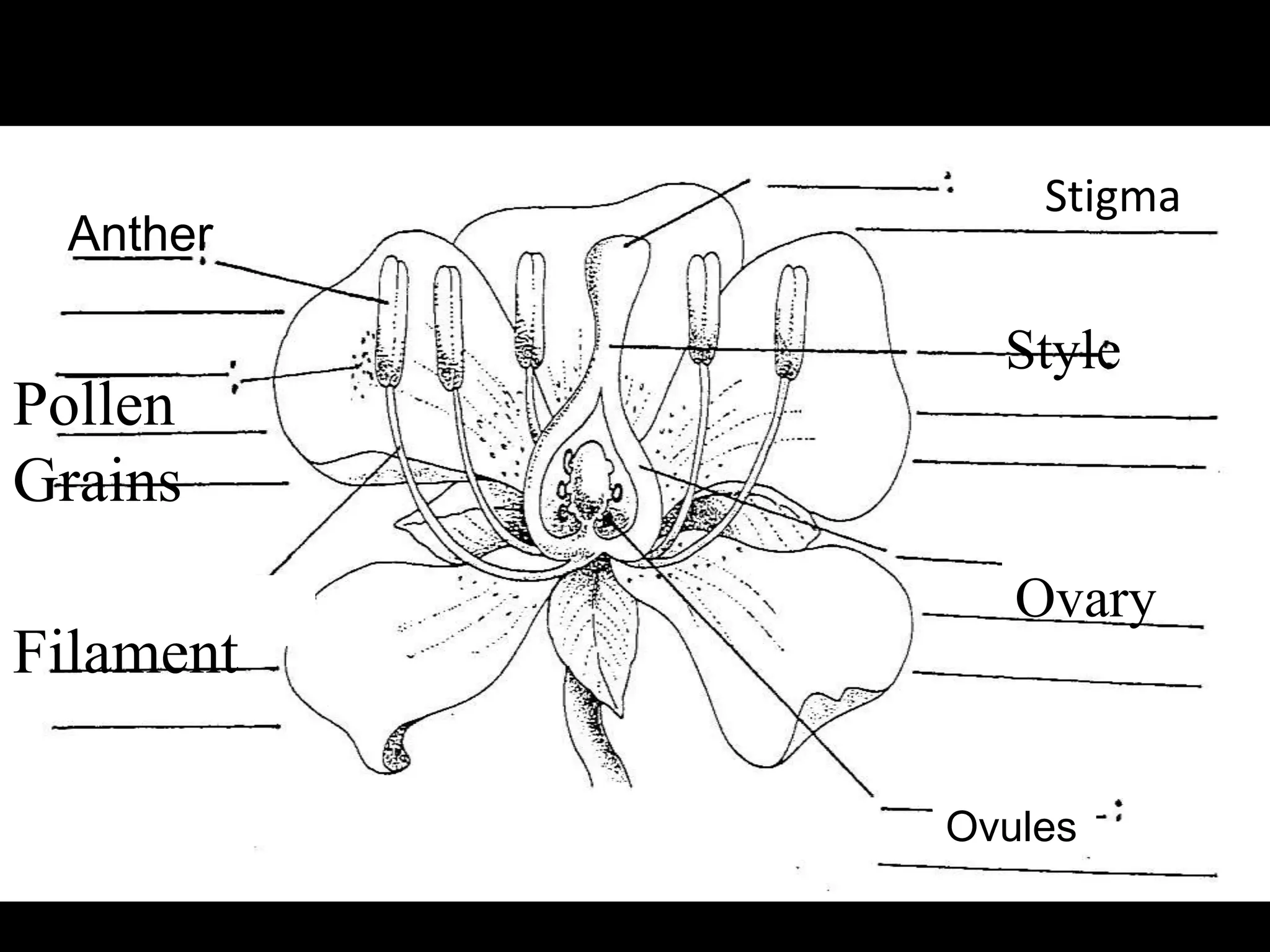
Plants reproduce both sexually and asexually. Sexual reproduction involves a male and female parent producing offspring that are genetically different, while asexual reproduction involves one parent producing offspring that are genetically identical clones. There are advantages to each type of reproduction depending on the environment and situation. Asexual reproduction is simpler and requires less energy, making it preferable when colonizing new areas or in harsh environments where sexual reproduction may not be successful.