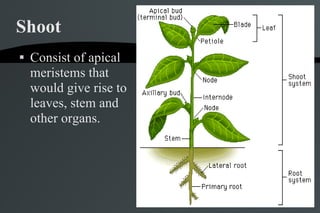
The document summarizes the major plant organs and structures. It discusses roots, shoots, stems, leaves, buds, and reproductive organs. It also defines different plant habits including annual, biennial, perennial, herb, vine, liana, shrub, tree, and describes different environments plants can grow in such as terrestrial, aquatic, floating, emergent and epiphytic.