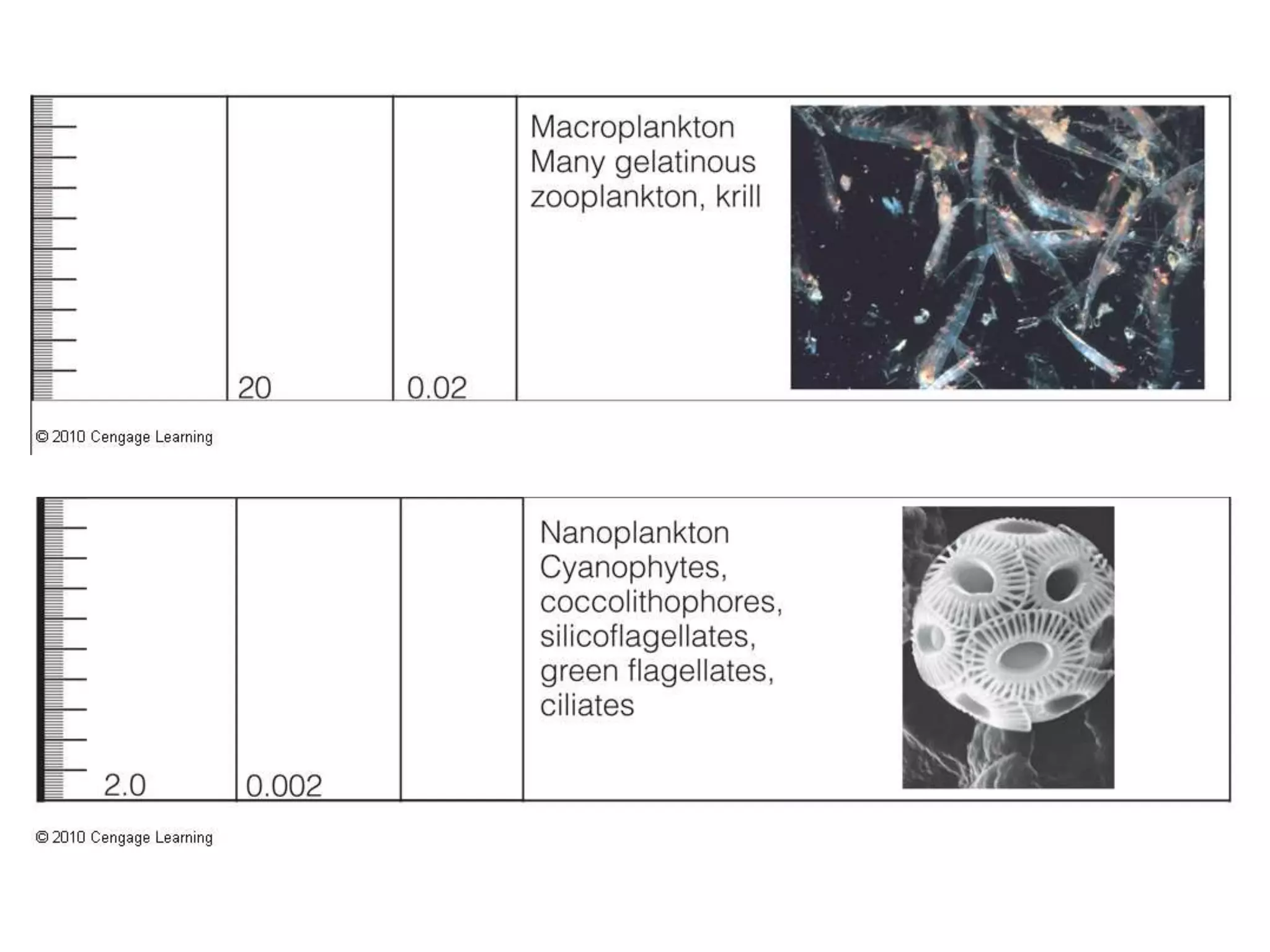
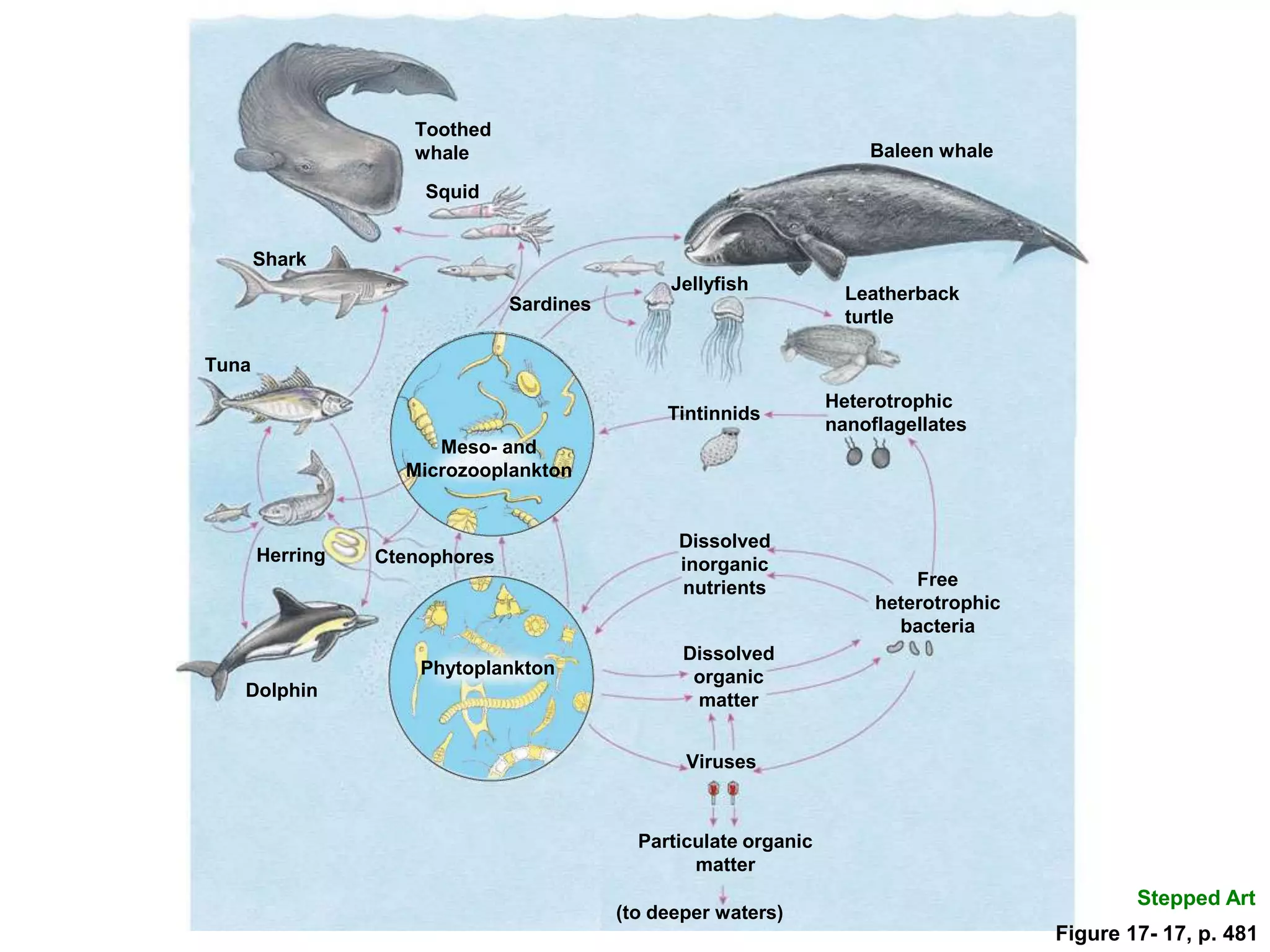
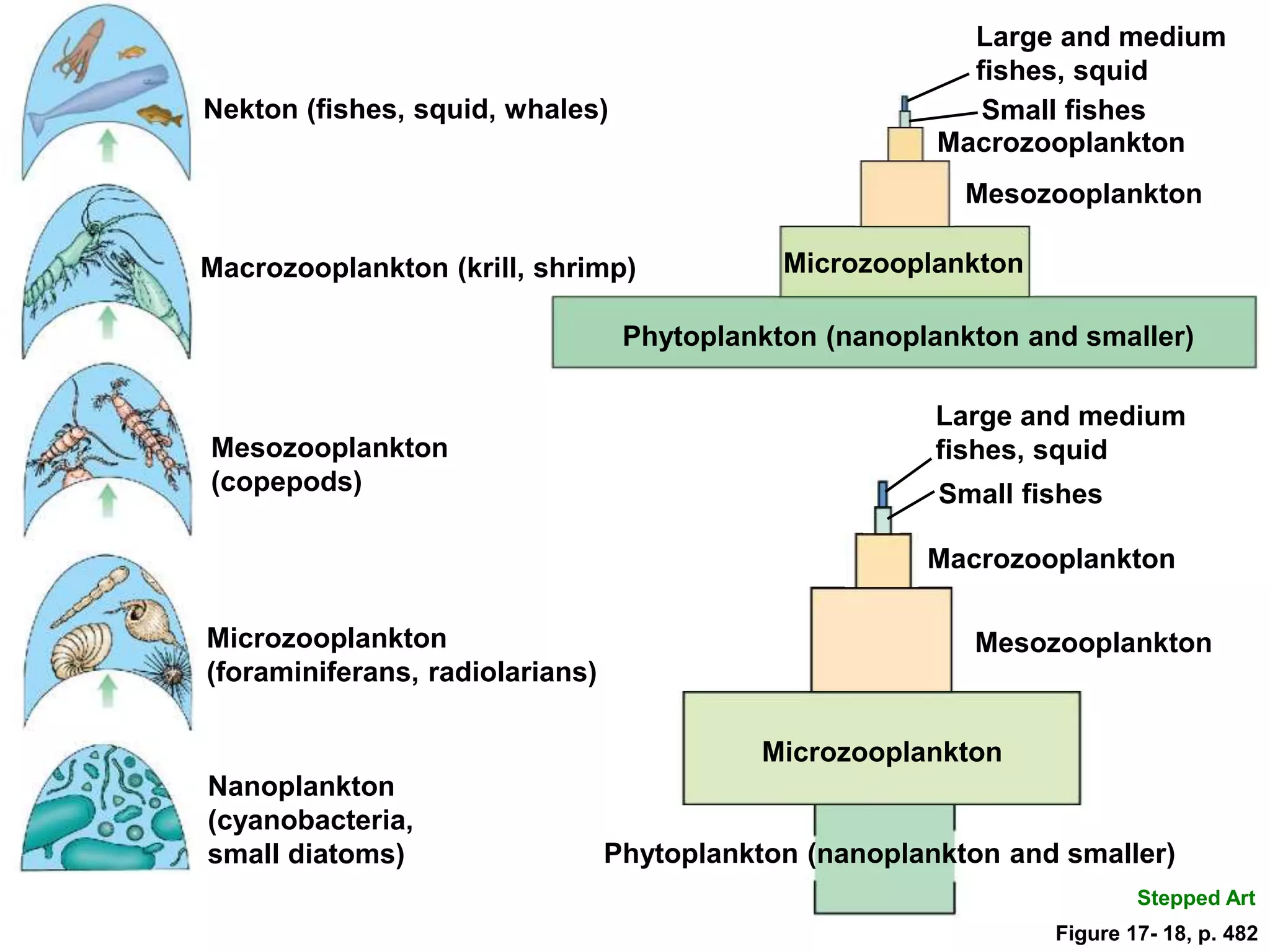
The document discusses the diversity and productivity of plankton, classified into various groups such as phytoplankton, zooplankton, and bacterioplankton, which are crucial for marine food webs. It highlights the role of plankton in aquatic ecosystems, detailing their life history, motility, size, and spatial distribution, alongside explaining the ecological importance of these organisms in nutrient cycling and food production. Additionally, it explores mechanisms behind the patchiness of plankton distribution and the efficiency of open-ocean food webs, emphasizing the foundational role of phytoplankton in marine environments.