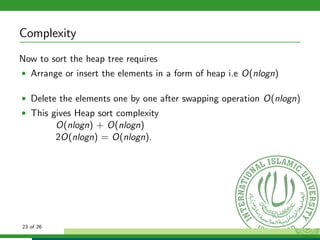
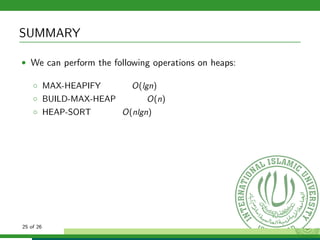
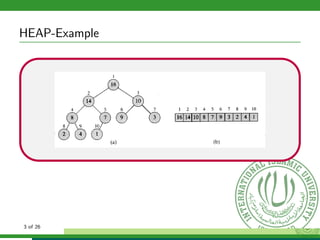
The document provides a comprehensive overview of heap sort, a sorting algorithm that combines attributes of both merge sort and insertion sort, emphasizing its in-place sorting and O(n log n) running time. It explains the concepts of full and complete binary trees, heap properties, and the heap structure, along with detailed procedures for maintaining heap properties and sorting elements. Additionally, it covers the complexities of various heap operations and concludes with an overview of the performance of the heap sort algorithm.





![What is Heap-Properties
• Properties of Heap is
◦ Completeness Property
◦ Order Proprty
• Types of Heap is
◦ Max Heap
A[PARENT(i)] A[i]
◦ Min Heap
A[PARENT(i)] ≤ A[i]
4 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heapsort-160101105129/85/Heap-sort-9-320.jpg)
![What is Heap-Properties
• Properties of Heap is
◦ Completeness Property
◦ Order Proprty
• Types of Heap is
◦ Max Heap
A[PARENT(i)] A[i]
◦ Min Heap
A[PARENT(i)] ≤ A[i]
4 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heapsort-160101105129/85/Heap-sort-10-320.jpg)




![Heap Representations
• Heap can Be Represented As
◦ Root of tree is A[1]
7 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heapsort-160101105129/85/Heap-sort-15-320.jpg)
![Heap Representations
• Heap can Be Represented As
◦ Root of tree is A[1]
◦ Left
A[i] = A[2i]
7 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heapsort-160101105129/85/Heap-sort-16-320.jpg)
![Heap Representations
• Heap can Be Represented As
◦ Root of tree is A[1]
◦ Left
A[i] = A[2i]
◦ Right
A[i] = A[2i + 1]
7 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heapsort-160101105129/85/Heap-sort-17-320.jpg)
![Heap Representations
• Heap can Be Represented As
◦ Root of tree is A[1]
◦ Left
A[i] = A[2i]
◦ Right
A[i] = A[2i + 1]
◦ Parent
A[i] = A[ i/2 ]
7 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heapsort-160101105129/85/Heap-sort-18-320.jpg)
![Heap Representations
• Heap can Be Represented As
◦ Root of tree is A[1]
◦ Left
A[i] = A[2i]
◦ Right
A[i] = A[2i + 1]
◦ Parent
A[i] = A[ i/2 ]
◦ Heapsize[A] ≤ Length[A]
7 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heapsort-160101105129/85/Heap-sort-19-320.jpg)

![Maintaining The Heap Property
MAXIMUM-HEAPIFY PROCEDURE
MAX-HEAPIFY(A,i )
1. l ← LEFT(i)
2. r ← RIGHT(i)
3. if l ≤ A.heap-size and A[l]>A[i]
4. largest ← l
5. else largest ← i
6. if r ≤ A.heap-size and A[r]>A[largest]
7. largest ← r
8. if largest ← i
9. exchange A[i] ↔ A[largest]
10. MAX-HEAPIFY(A, largest)
9 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heapsort-160101105129/85/Heap-sort-21-320.jpg)




![Problems
• What is the effect of calling MAX-HEAPIFY(A, i) when the
element A[i] is larger than its children?
• What is the effect of calling MAX-HEAPIFY(A, i) for
i>A.heap-size/2?
• Show that the worst-case running time of MAX-HEAPIFY on a
heap of size n is Ω(lgn).
12 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heapsort-160101105129/85/Heap-sort-26-320.jpg)
![Building a heap
Building Max Heap PROCEDURE
BuildMaxHeap(A)
1. heap-size[A] ← length[A]
2. for i ← length[A]/2 downto 1
3. do MaxHeapify(A, i)
13 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heapsort-160101105129/85/Heap-sort-27-320.jpg)






![HEAP SORT PROCEDURE
• Sort by maintaining the as yet unsorted elements as a max-heap.
• Start by building a max-heap on all elements in A.
Maximum element is in the root, A[1].
17 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heapsort-160101105129/85/Heap-sort-34-320.jpg)
![HEAP SORT PROCEDURE
• Sort by maintaining the as yet unsorted elements as a max-heap.
• Start by building a max-heap on all elements in A.
Maximum element is in the root, A[1].
• Move the maximum element to its correct final position.
Exchange A[1] with A[n].
17 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heapsort-160101105129/85/Heap-sort-35-320.jpg)
![HEAP SORT PROCEDURE
• Sort by maintaining the as yet unsorted elements as a max-heap.
• Start by building a max-heap on all elements in A.
Maximum element is in the root, A[1].
• Move the maximum element to its correct final position.
Exchange A[1] with A[n].
• Discard A[n] it is now sorted.
Decrement heap-size[A].
17 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heapsort-160101105129/85/Heap-sort-36-320.jpg)
![HEAP SORT PROCEDURE
• Sort by maintaining the as yet unsorted elements as a max-heap.
• Start by building a max-heap on all elements in A.
Maximum element is in the root, A[1].
• Move the maximum element to its correct final position.
Exchange A[1] with A[n].
• Discard A[n] it is now sorted.
Decrement heap-size[A].
• Restore the max-heap property on A[1..n1].
Call MaxHeapify(A, 1).
17 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heapsort-160101105129/85/Heap-sort-37-320.jpg)
![HEAP SORT PROCEDURE
• Sort by maintaining the as yet unsorted elements as a max-heap.
• Start by building a max-heap on all elements in A.
Maximum element is in the root, A[1].
• Move the maximum element to its correct final position.
Exchange A[1] with A[n].
• Discard A[n] it is now sorted.
Decrement heap-size[A].
• Restore the max-heap property on A[1..n1].
Call MaxHeapify(A, 1).
• Repeat until heap-size[A] is reduced to 2.
17 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heapsort-160101105129/85/Heap-sort-38-320.jpg)
![HEAP SORT
// Input: A: an (unsorted) array
// Output: A modifed to be sorted from smallest to largest
// Running Time: O(nlogn) where n = length[A]
HeapSort(A)
1. Build-Max-Heap(A)
2. for i ← length[A] downto 2
3. do exchange A[1] ↔ A[i]
4. heap-size[A] ← heap-size[A] 1
5. MaxHeapify(A, 1)
18 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heapsort-160101105129/85/Heap-sort-39-320.jpg)