Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX




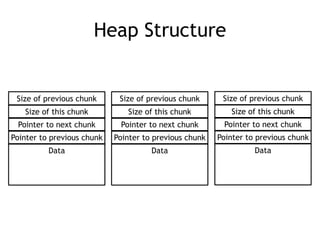


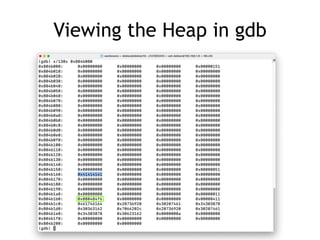
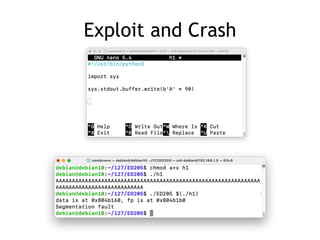
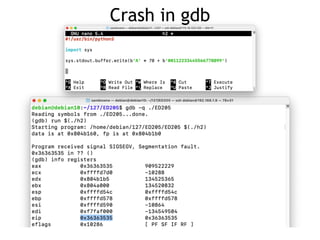



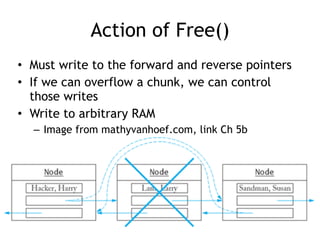




This document discusses heap overflows and exploit development. It explains that the heap is an area of memory used for dynamic allocation via malloc() and freed via free(). When free() is called, it must write to forward and backward pointers, allowing overflow data to potentially control those writes. This makes it possible to write to arbitrary RAM locations, such as the stack return address, global offset table, destructors table, or function pointers, in order to execute code and crash or exploit the program.
















