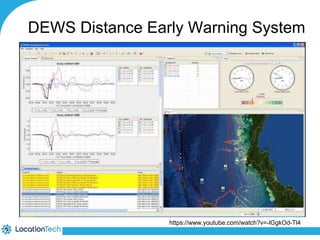
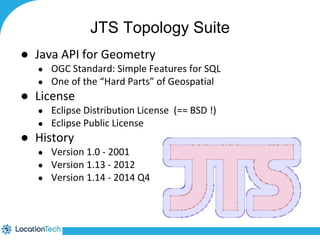
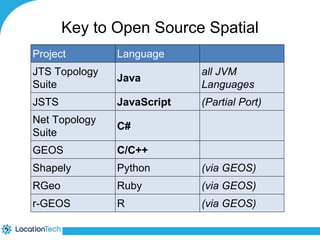
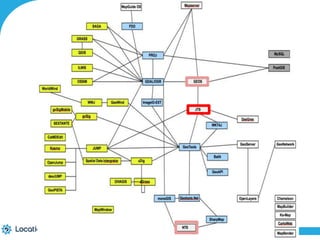
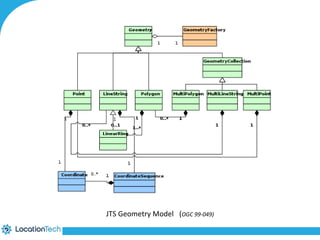
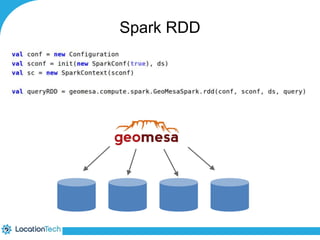
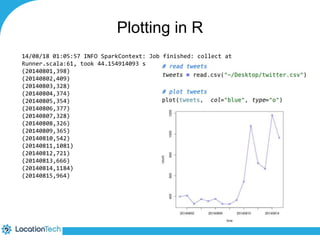
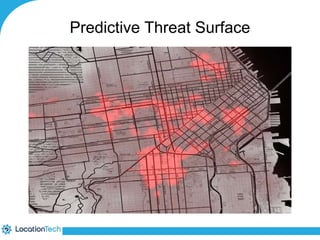
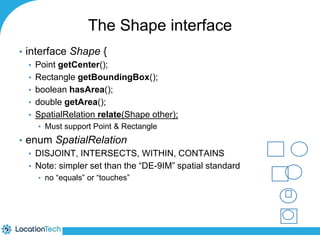
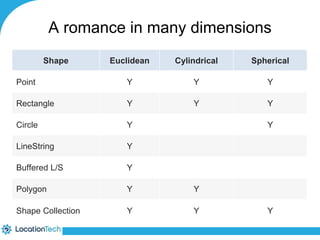
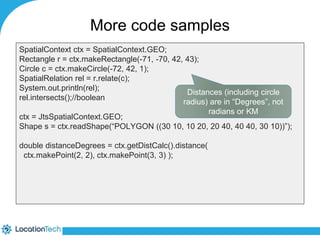
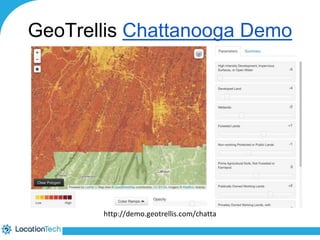
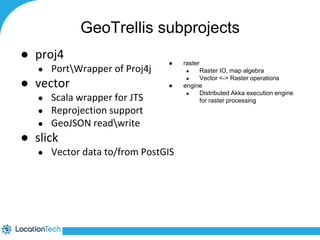
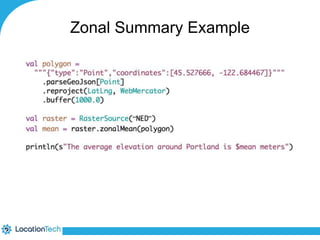
The document provides an introduction to LocationTech, detailing various projects focused on advanced location-aware technologies, including Geotools, GeoServer, and GeoMesa. It outlines the contributions of notable members, discusses technical aspects and capabilities of key projects, and highlights their applications in mobile mapping, geospatial data processing, and data storage. Additionally, it includes information on event opportunities and community engagement within the LocationTech ecosystem.




































![JavaScript
>> var geom = require("geoscript/geom");
>> var p = new geom.Point([-111.0, 45.7]);
>> p
<Point [-111, 45.7]>
>> var proj = require("geoscript/proj");
>> var p2 = proj.transform(p, "epsg:4326", "epsg:26912");
>> p2
<Point [500000, 5060716.31816507]>
>> var poly = p2.buffer(100);
>> poly.area
31214.451522458345](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/locationtechprojects-140911184841-phpapp01/85/LocationTech-Projects-67-320.jpg)