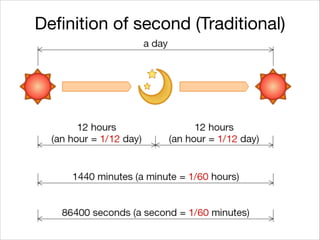
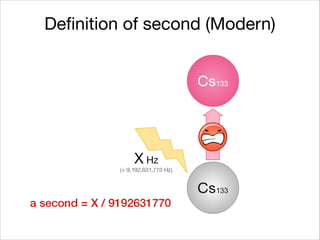
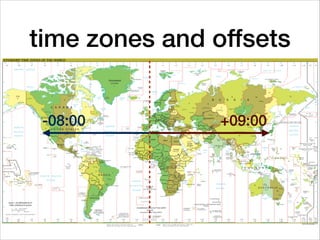
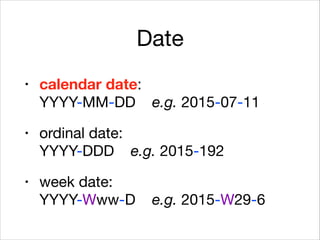
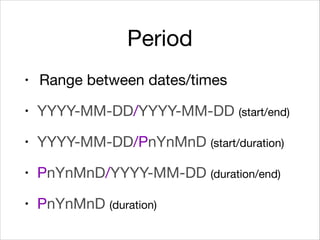
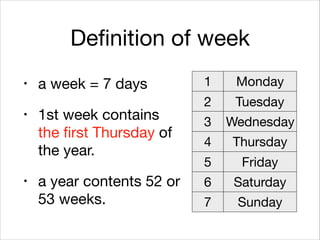
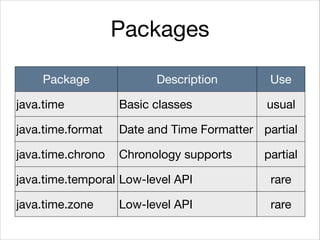
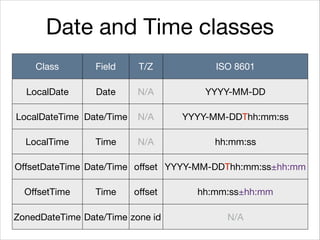
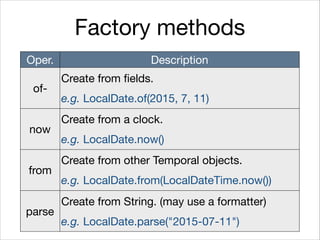
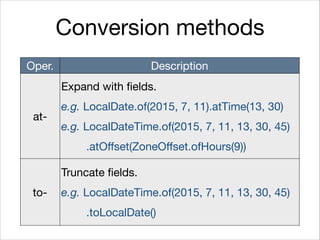
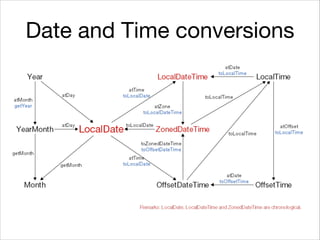
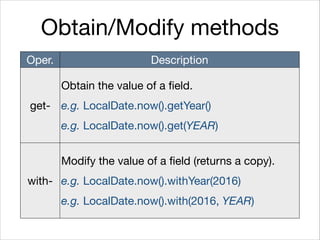
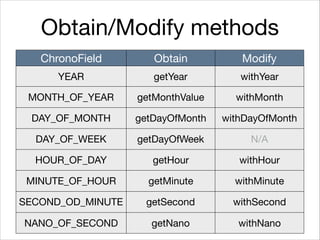
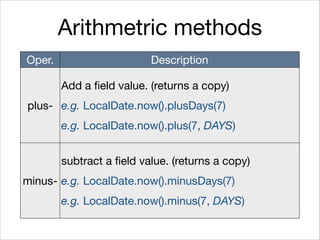
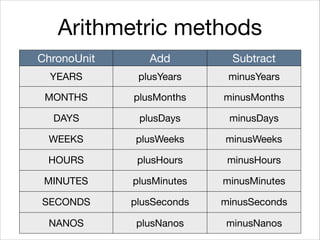
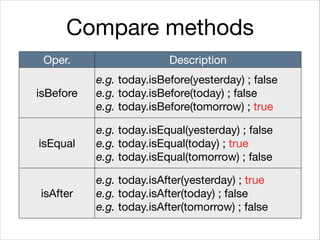
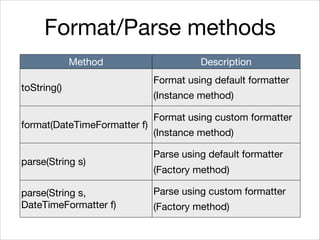
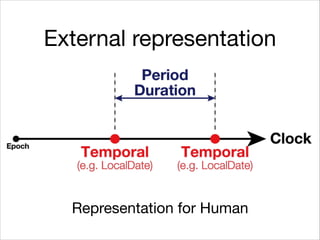
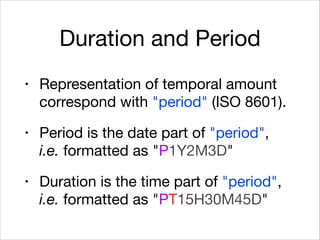
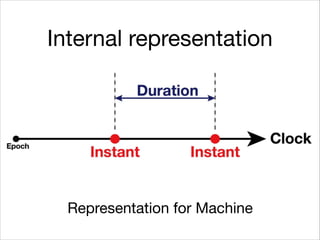
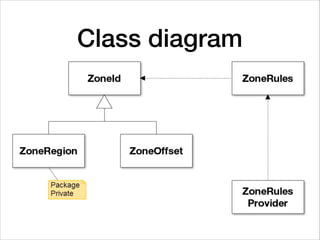
This document provides an introduction to Java's Date and Time API. It discusses key classes like LocalDate, LocalDateTime, and ZonedDateTime that represent dates, times, and timestamps. It also covers formatting and parsing dates and times using DateTimeFormatter, and manipulating dates and times using factory and conversion methods. The document concludes that the API provides a powerful way to perform date and time calculations while modeling the ISO 8601 standard.