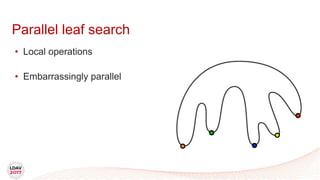
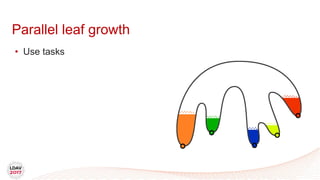
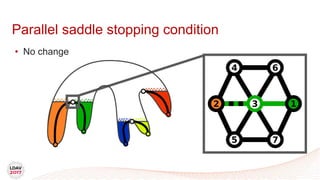
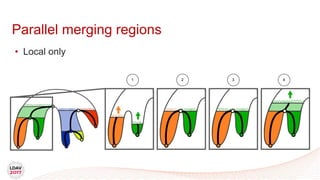
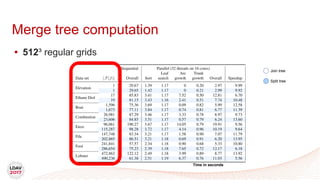
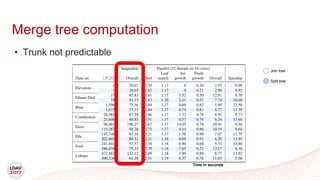
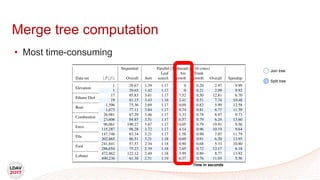
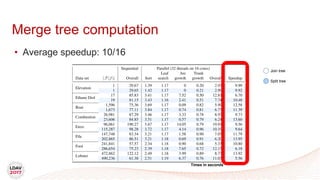
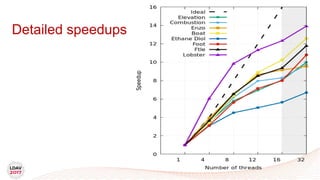
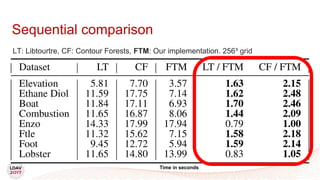
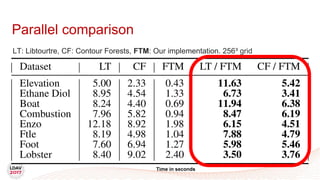
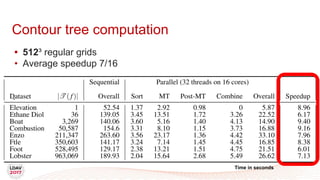
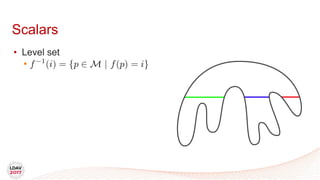
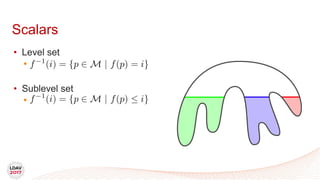
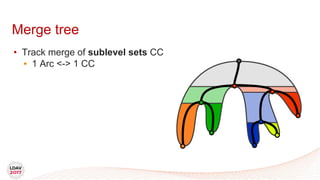
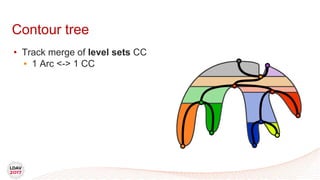
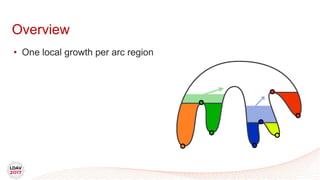
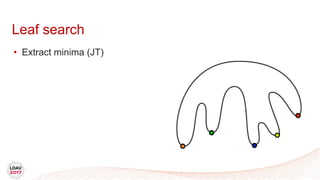
This document discusses a new algorithm for computing merge trees and contour trees in parallel using task-based parallelism. The algorithm uses Fibonacci heaps for efficient local computations and divides the work into asynchronous tasks for dynamic load balancing. It achieves good parallel speedups compared to other methods while maintaining the advantages of an augmented tree representation.
![Topological analysis
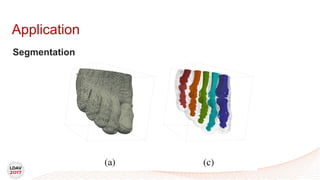
• Topological abstractions
• Segmentation
[Bock et al. 2017]
[Favelier et al. 2016]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ftmtreepres-180709113527/85/FTM-tree-2-320.jpg)
![Large data sets
● [512³]
● 2.4 GB
● Compute power through parallelism](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ftmtreepres-180709113527/85/FTM-tree-3-320.jpg)
![Related work
• Sequential
• Augmented tree
[Carr et al. 2000]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ftmtreepres-180709113527/85/FTM-tree-4-320.jpg)
![Related work
• Sequential
• Augmented tree
• Monotone path
[Chiang et al. 2005]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ftmtreepres-180709113527/85/FTM-tree-5-320.jpg)
![Related work
• Parallel
• Partitions:
• Load imbalance
• Redundant work
Partitions
V X
X
Shared memory:
● [Pascucci04]
● [Gueunet16]
Distributed:
● [Morozov13]
● [Landge14]
V
Monotonepath](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ftmtreepres-180709113527/85/FTM-tree-6-320.jpg)
![Related work
• Parallel
• Partitions:
• Load imbalance
• Redundant work
• Monotone path (MP):
• Not augmented
Partitions
V X
X
Shared memory:
● [Pascucci04]
● [Gueunet16]
Distributed:
● [Morozov13]
● [Landge14]
V ● [Natarajan15]
● [Maadasamy12]
● [Carr16]
Monotonepath](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ftmtreepres-180709113527/85/FTM-tree-7-320.jpg)
![Related work
• Parallel
• Partitions:
• Load imbalance
• Redundant work
• Monotone path (MP):
• Not augmented
Partitions
V X
X
Shared memory:
● [Pascucci04]
● [Gueunet16]
Distributed:
● [Morozov13]
● [Landge14]
Us!
V ● [Natarajan15]
● [Maadasamy12]
● [Carr16]
Monotonepath](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ftmtreepres-180709113527/85/FTM-tree-8-320.jpg)




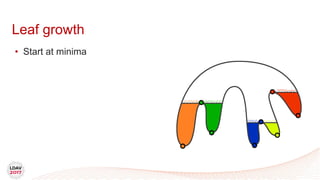
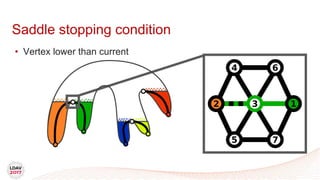
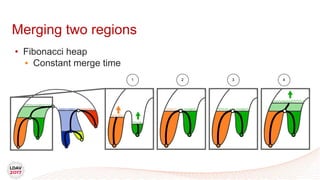
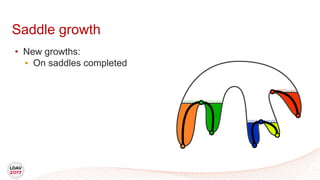
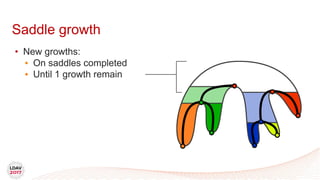
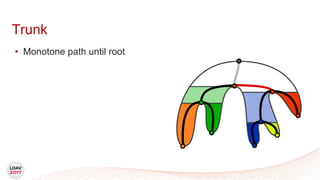
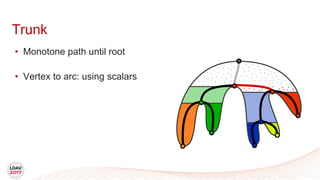
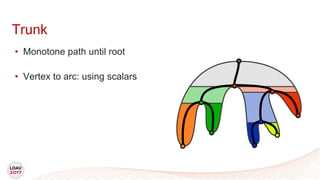

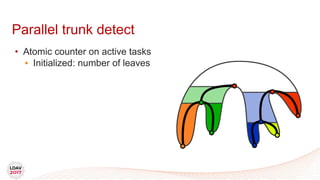
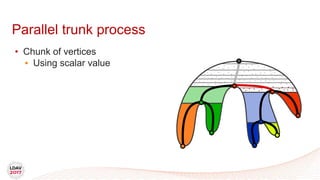
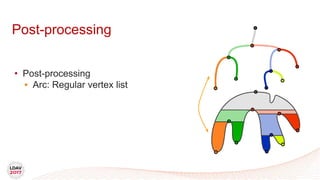
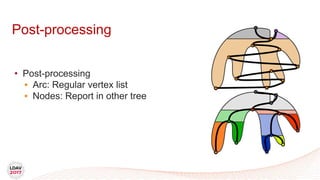
![Tasks
• Asynchronous work unit
• Dynamic load balancing
• Runtimes:
• OpenMP
• Intel TBB
• Intel Cilk Plus
[R. van der Pas, IWOMP 2009]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ftmtreepres-180709113527/85/FTM-tree-30-320.jpg)