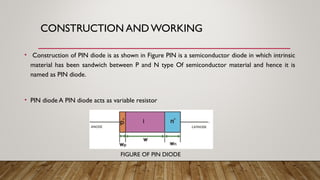
PIN diodes are semiconductor devices that can act as variable resistors at radio and microwave frequencies. They are controlled by forward bias current and can be used as attenuators, modulators, and switches. PIN diodes have a P-type semiconductor, an intrinsic semiconductor, and an N-type semiconductor sandwiched together. When forward biased, PIN diodes have a gradual increase in current flow through the intrinsic region, giving a variation in resistance. This property allows them to be used to control large RF signals with smaller DC excitation. Common applications of PIN diodes include RF switching, attenuation, and modulation.