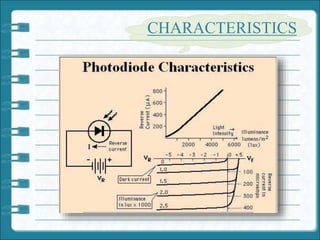
1) A photodiode is a type of photodetector that converts light into current or voltage depending on its mode of operation. It operates using the photoelectric effect when exposed to light in reverse bias mode.
2) Developed from PN junction diodes in the 1940s-50s, the PIN photodiode was developed in the late 1950s and uses a wide depletion area for increased light absorption. Silicon is commonly used but germanium can also be used.
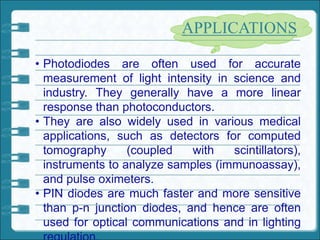
3) Photodiodes are used in applications like optical communications, camera light meters, smoke detectors, and CD players to convert light into electrical signals for various functions like power generation, circuit control, and signal processing.