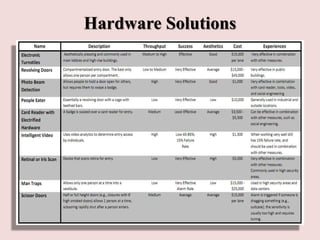
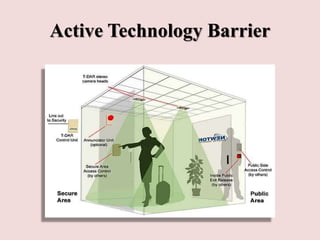
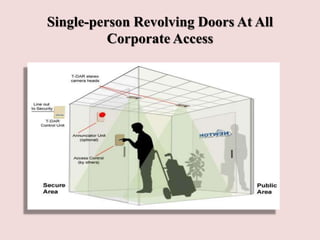
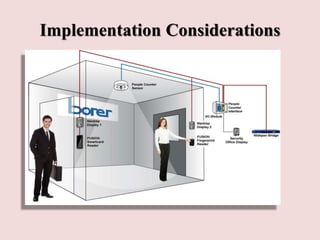
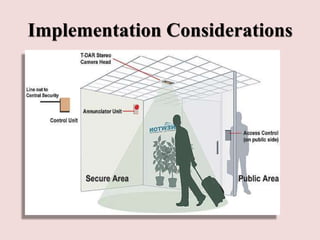
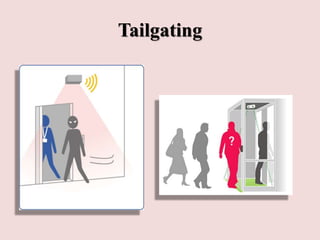
This document discusses piggybacking and tailgating as security risks. Piggybacking refers to when an unauthorized person gains entry by following an authorized person, while tailgating implies the unauthorized person follows without consent. The document outlines various methods used for piggybacking, like surreptitiously following others or blending into large crowds. Tailgating is a security and compliance issue that can result in costs from theft, data breaches, and loss of productivity. The document recommends both physical security measures and social engineering or policy solutions to address tailgating risks.