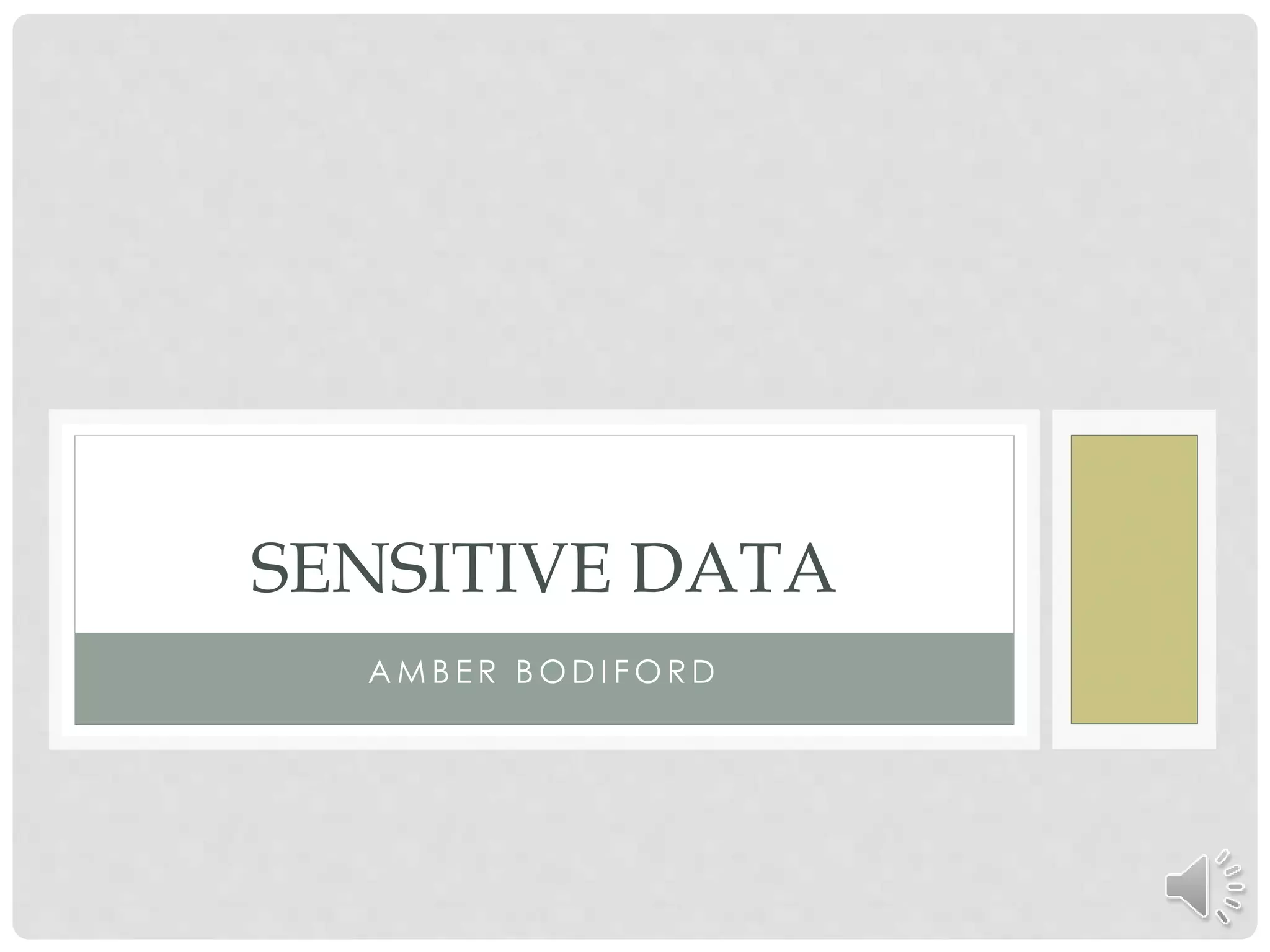
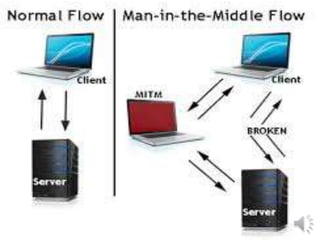
This document discusses the importance of protecting sensitive data and minimizing exposure. It defines sensitive data as information that must be safeguarded from unauthorized access, such as passwords, addresses, social security numbers, and credit card information. The document outlines laws and regulations that govern sensitive data protection and explains how data is often exposed through security flaws, intrusions, phishing, or social engineering. It recommends encrypting sensitive data, restricting access to authorized individuals only, and learning from past security incidents to strengthen protections.