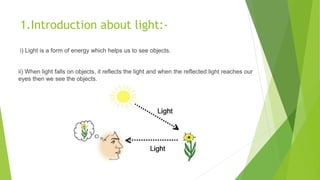
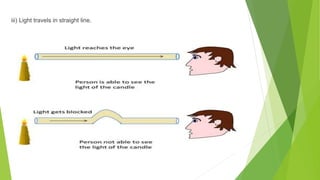
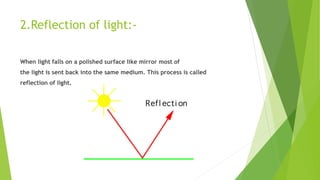
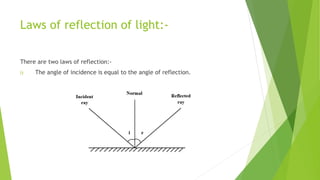
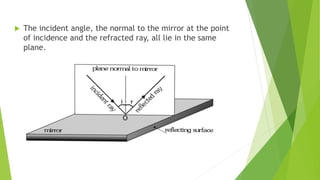
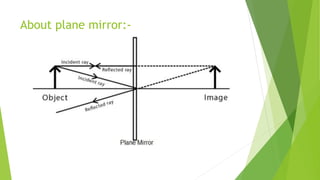
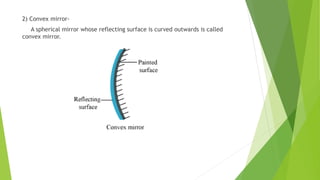
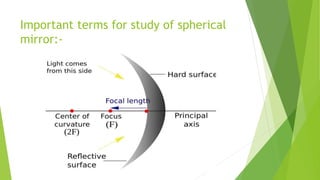
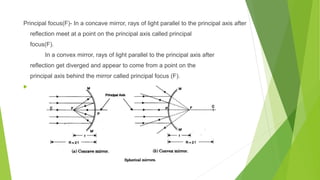
The document provides an overview of light as a form of energy essential for vision, emphasizing its behavior through various phenomena such as shadow formation and reflection. It describes the laws of reflection and the characteristics of plane and spherical mirrors, including their types (concave and convex) and important terms like pole, centre of curvature, and focal length. Additionally, it explains how light interacts with these mirrors, including image formation and the relationship between radius of curvature and focal length.