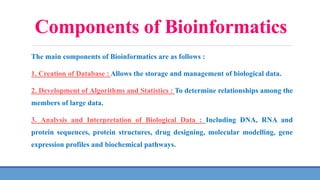
Bioinformatics, coined by Paulien Hogeweg and Ben Hesper, is an interdisciplinary field that merges biology, computer science, and statistics to analyze biological data. Key components include database creation, algorithm development, and data analysis for areas like gene identification, genome mapping, and drug design. Its global importance lies in facilitating data management and sharing for research, aiding in understanding biological processes and potential applications in various fields.