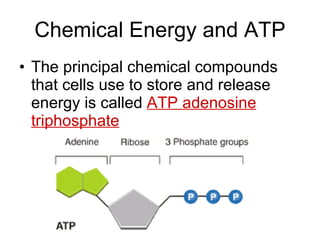
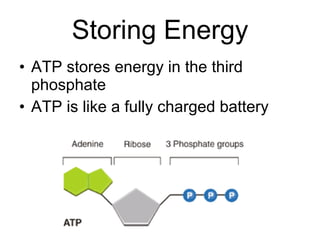
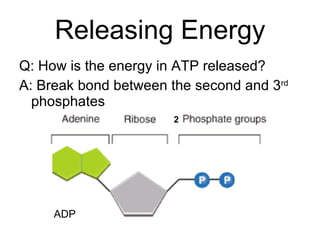
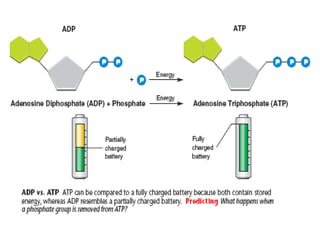
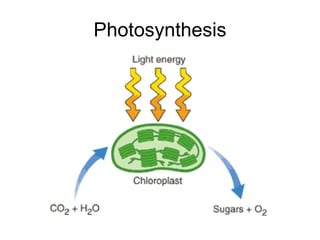
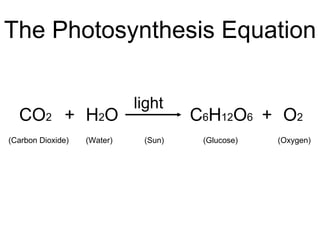
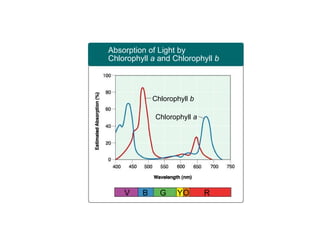
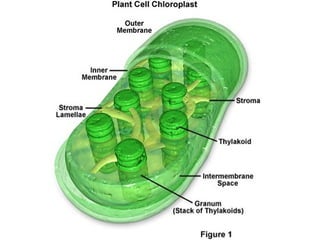
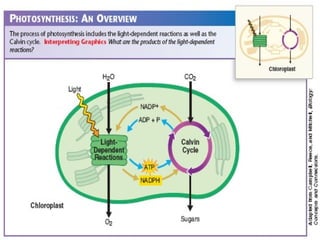
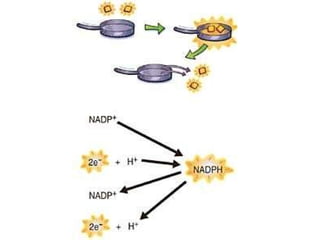
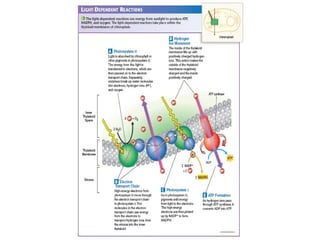
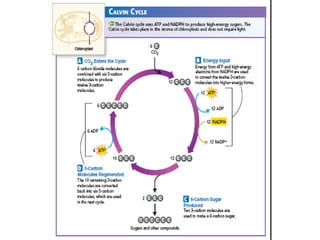
This document provides an overview of photosynthesis. It explains that plants get their energy from sunlight through the process of photosynthesis, where carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight are converted into glucose and oxygen. Chlorophyll is the pigment in plants that absorbs light energy. The reactions of photosynthesis are divided into light-dependent reactions, which take place in thylakoid membranes and produce ATP and NADPH, and light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, which use these products to produce sugars. Factors like water availability, temperature, and light intensity can affect photosynthesis.