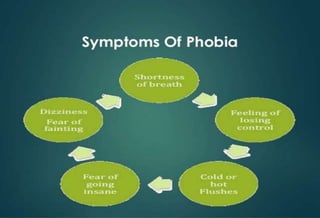
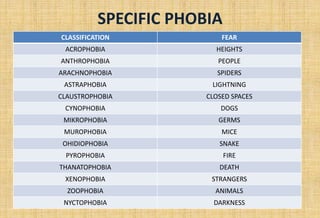
This document discusses phobias, including their symptoms, types, causes, and management. It defines phobia as an intense and irrational fear of a specific object, activity, or situation. The three major types of phobias are specific phobia, social phobia, and agoraphobia. Specific phobias involve irrational fears of things like animals, heights, and small spaces. Social phobia is a fear of social or performance situations where one may be scrutinized. Agoraphobia is a fear of public places or crowds. Phobias are thought to develop from conditioning, biological factors, and psychoanalytic theories. Treatment involves psychotherapy, behavior therapy, and homeopathic management.