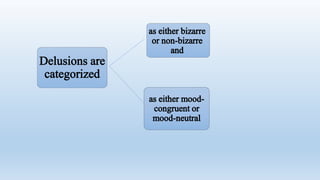
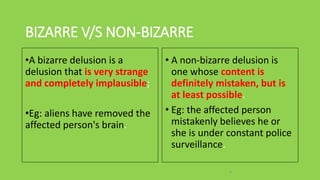
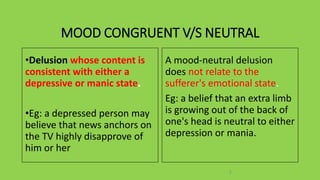
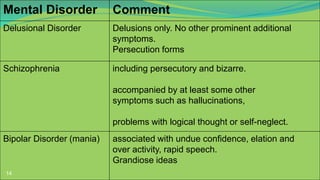
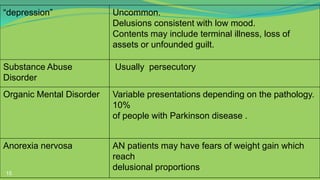
This document defines delusions and describes different types of delusions. It states that a delusion is a false, unshakeable belief that is not accepted by the person's culture. Delusions can be bizarre, non-bizarre, mood congruent, or neutral. Common themes of delusions include persecutory, jealous, erotomanic, somatic, and grandiose delusions. The document also notes that delusional disorder involves only delusions, while schizophrenia involves delusions and other symptoms.