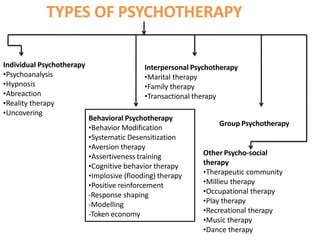
This document discusses psychotherapy, including its objectives, classification, and treatment modes. Psychotherapy aims to help patients relieve symptoms, resolve problems, and promote personal growth through a structured relationship with a trained therapist. It can help patients accept themselves, empower life changes, and cope more effectively, though it cannot change their environment. Psychotherapy classifications include individual, group, couple, and family therapies. Therapies also differ in content and methods, such as analytic, interpersonal, cognitive, behavioral, and cognitive-behavioral approaches. Psychotherapy provides a safe setting, working alliance, and confidential therapeutic relationship to help patients identify and change unhelpful behaviors/thoughts, improve relationships, learn problem-solving skills, and set realistic goals