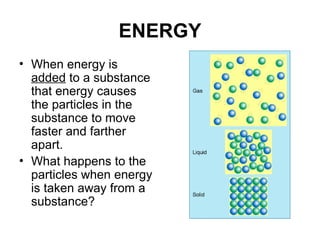
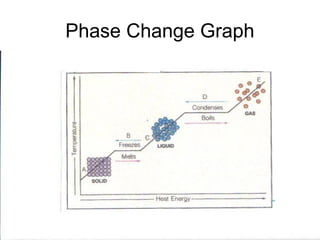
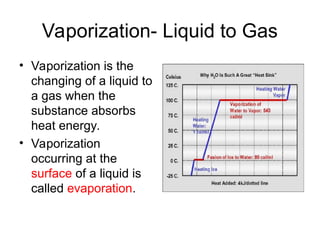
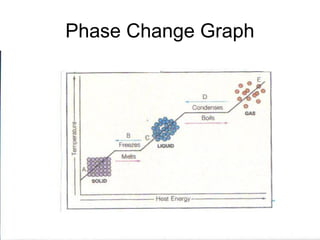
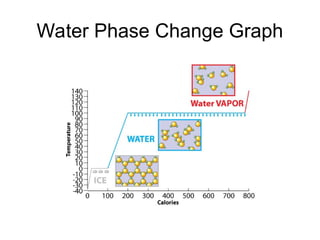
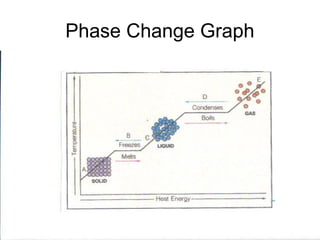
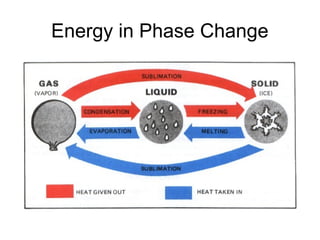
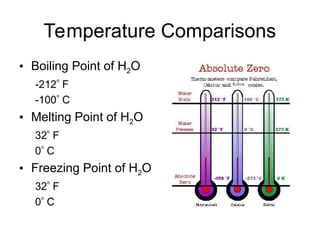
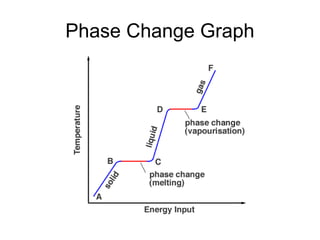
The document explains the three states of water: ice, liquid, and vapor, and describes how energy influences phase changes. It details endothermic changes that require energy input (melting, boiling, sublimation) and exothermic changes that release energy (freezing, condensation, deposition). Additionally, it outlines the phase change points for water and compares boiling and freezing points.