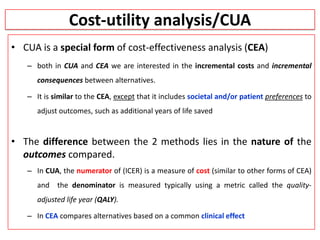
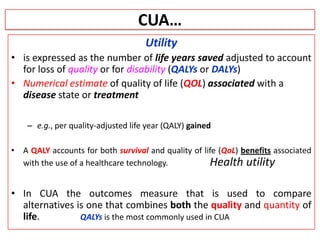
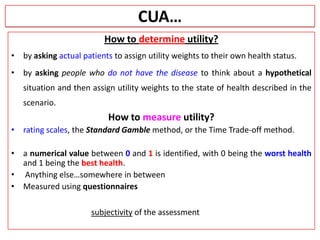
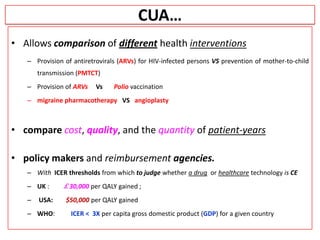
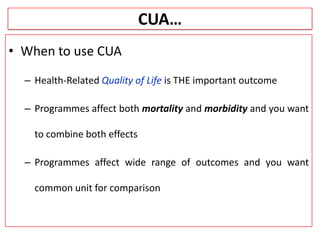
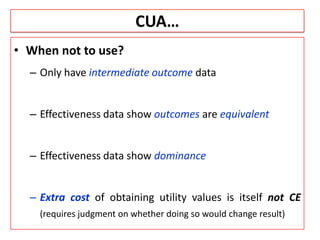
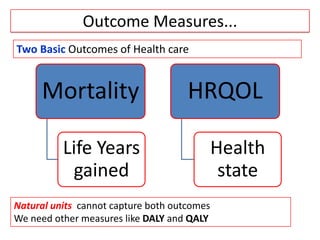
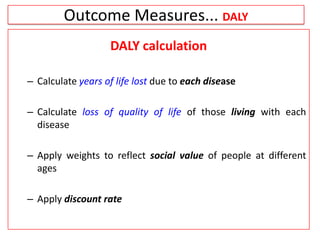
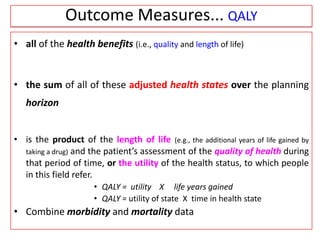
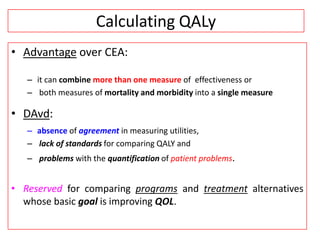
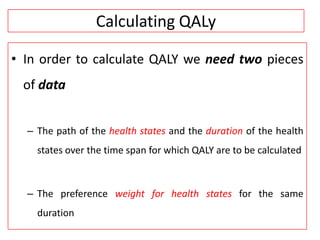
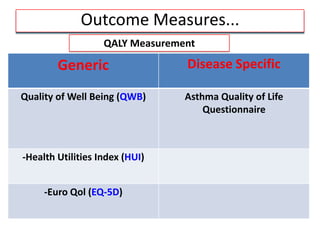
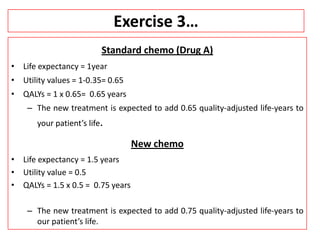
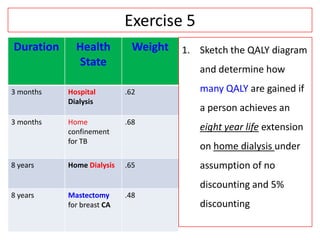
This document provides an overview of cost-utility analysis (CUA) as a form of pharmacoeconomic evaluation. It defines CUA and distinguishes it from cost-effectiveness analysis by noting that CUA compares outcomes in terms of quality-adjusted life years (QALYs). The document discusses how QALYs combine both survival time and health-related quality of life into a single metric. It also describes approaches to measuring health utility values and calculating QALYs. Finally, the document provides examples of when CUA would and would not be appropriate to use and outlines factors like incremental cost-utility ratios used to interpret CUA results.