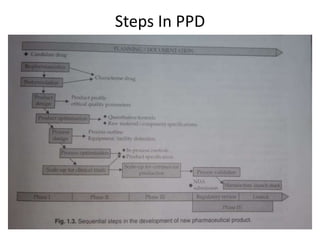
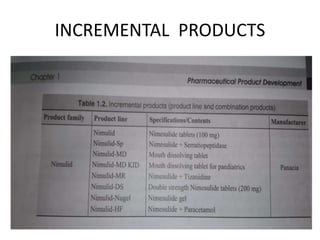
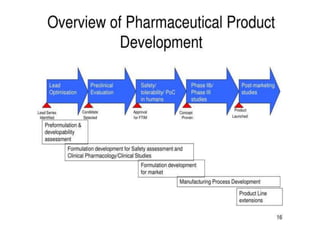
This document provides an overview of pharmaceutical product development, focusing on achieving predictable therapeutic responses and ensuring consistent product quality. It details the preformulation phase, highlighting its importance in characterizing new drug compounds, and outlines regulatory requirements for stability and quality testing. The guidelines mentioned pertain to both small molecules and herbal products, emphasizing the necessity of thorough testing to support safe and effective drug formulation.







![The general method of preparation is
provided under Sec312
•
The general method of preparation is provided under Sec
(a)(7)(iv)(a).
• The EMEA provides the following guidelines for herbal (botanical as
listed in United States) products:
• COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINE PRODUCTS
(CPMP)/QUALITY WORKING PARTY (QWP)/2819/00 [EUROPEAN
MEDICINES EVALUATION AGENCY (EMEA)/COMMITTEE ON
VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CVMP)/814/00] Note for
Guidance on Quality of Herbal Medicinal Products (CPMP/CVMP
adopted July 01).CPMP/QWP/2820/00 (EMEA/CVMP/815/00)
• Note for Guidance on Specifications: Test procedures and
Acceptance Criteria for Herbal Drugs, Herbal Drug Preparations and
Herbal Medicinal Products (CPMP/CVMP adopted July 01).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1-220406101233/85/PHARMACEUTICAL-PRODUCT-DEVELOPMENT-11-320.jpg)

