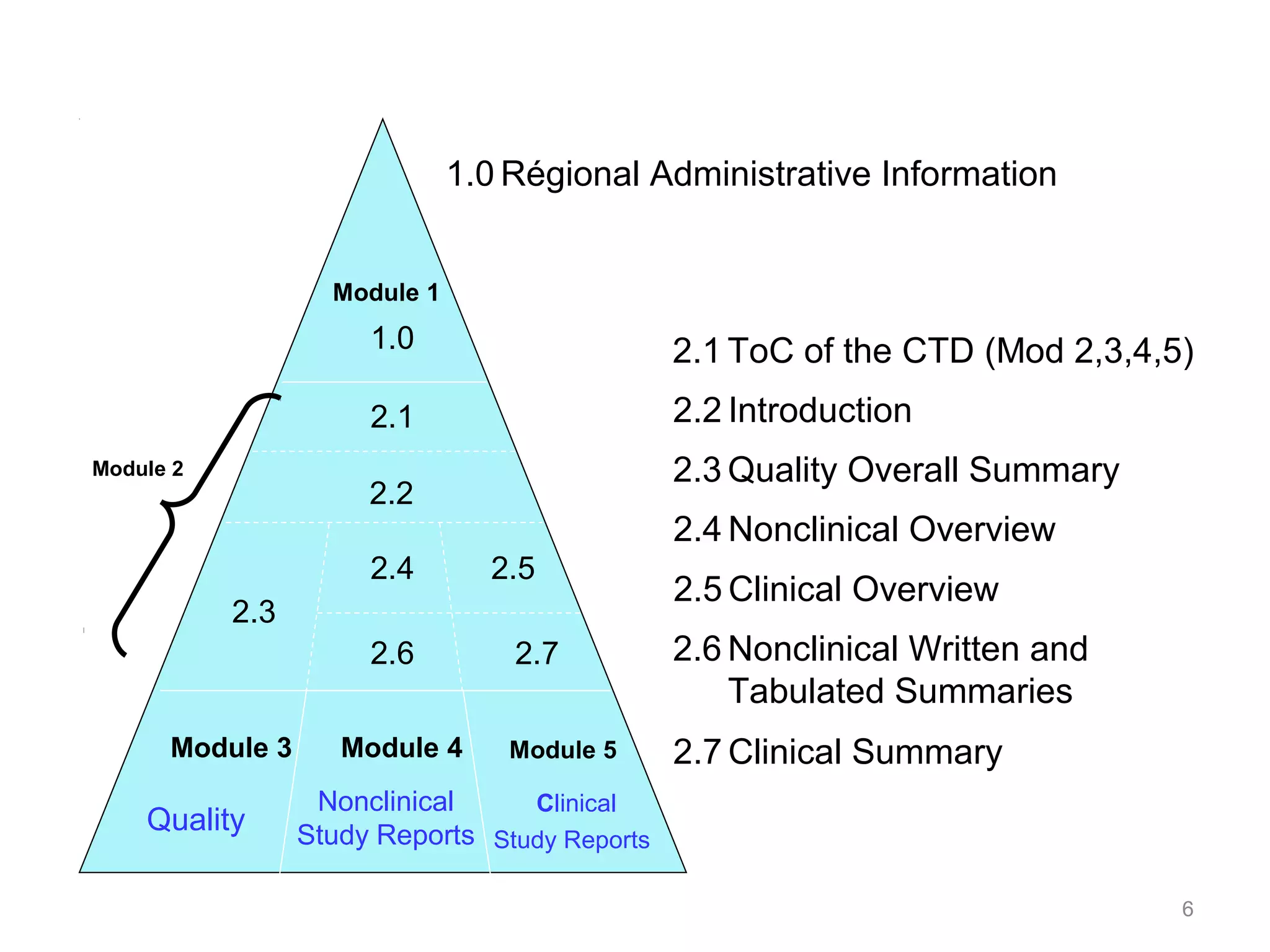
The document discusses the Common Technical Document (CTD), which provides a standardized format for new drug applications across Europe, Japan, and the US. The CTD is organized into 5 modules: Module 1 contains region-specific information; Modules 2-5 are common across regions. Module 2 provides overviews and summaries of quality, non-clinical, and clinical data in Modules 3-5. The CTD format aims to streamline drug approvals across major markets.