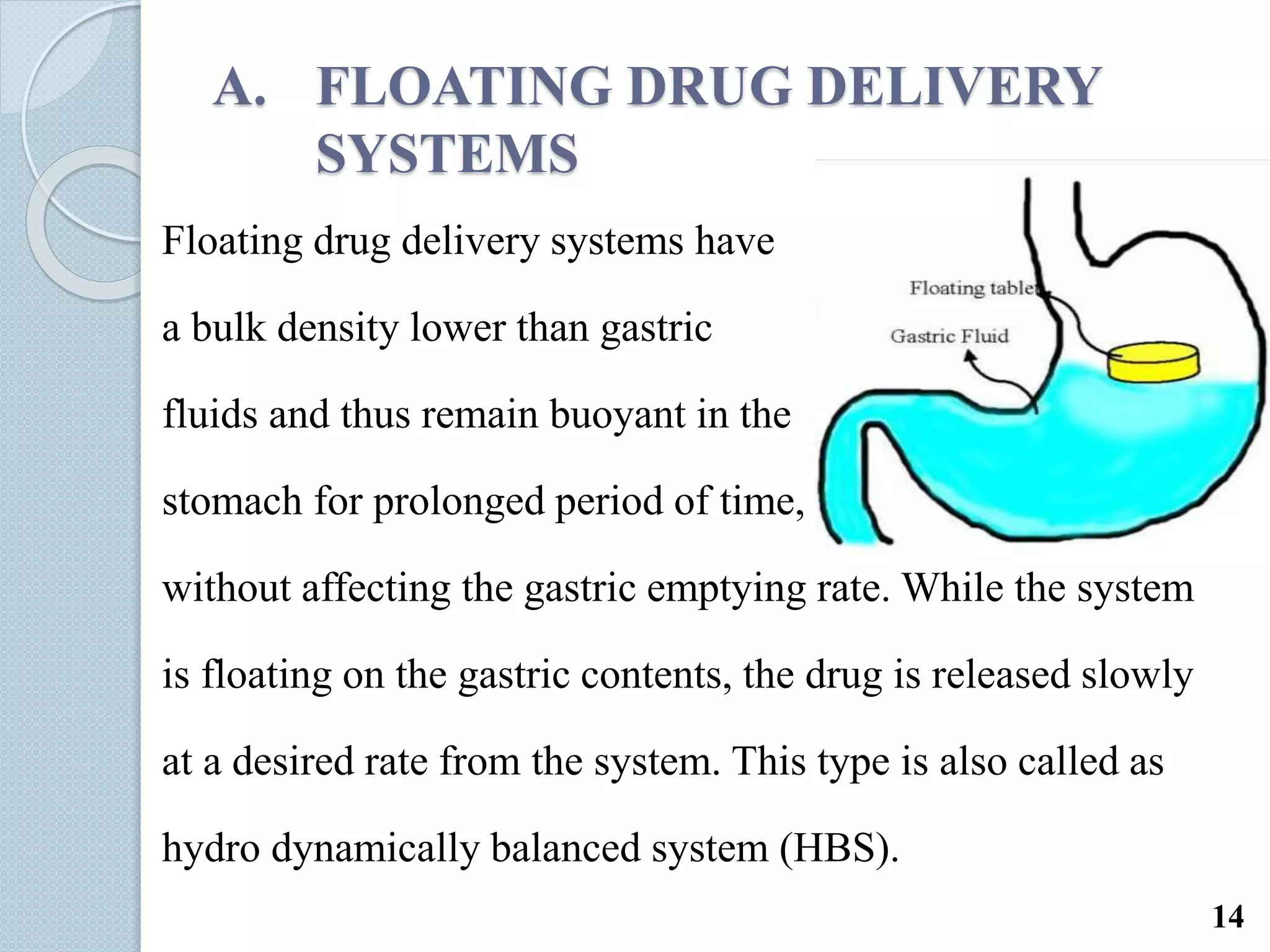
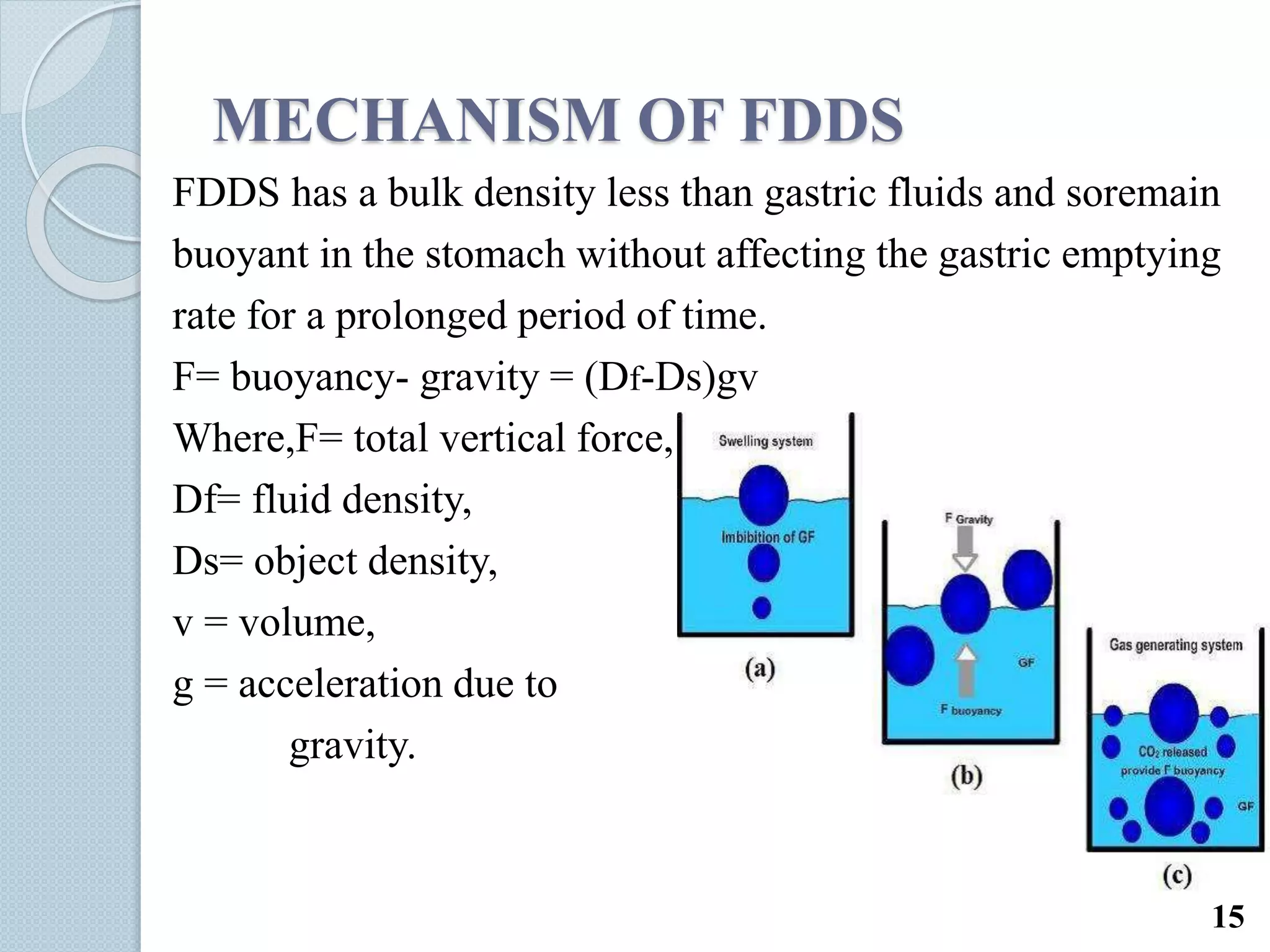
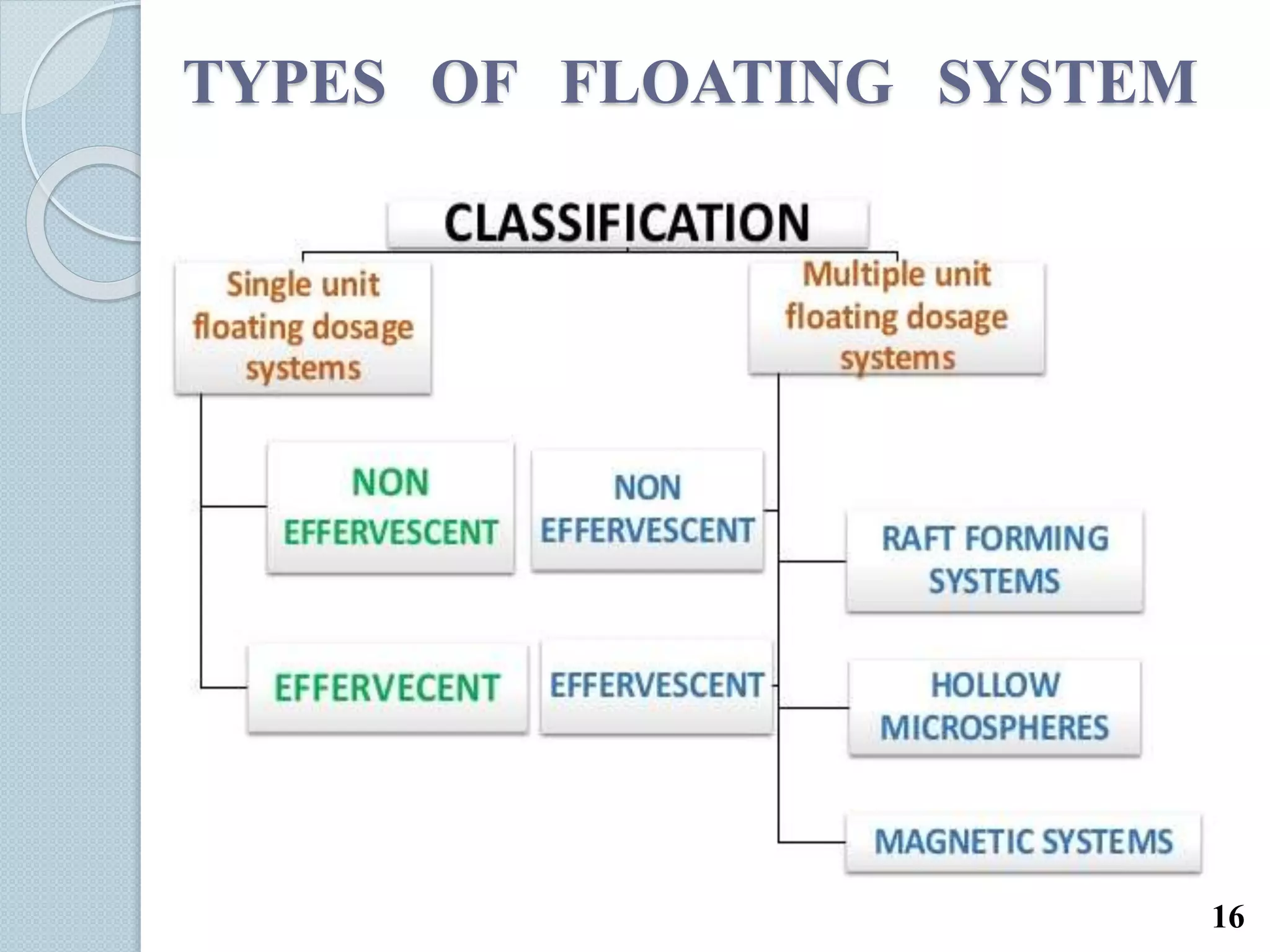
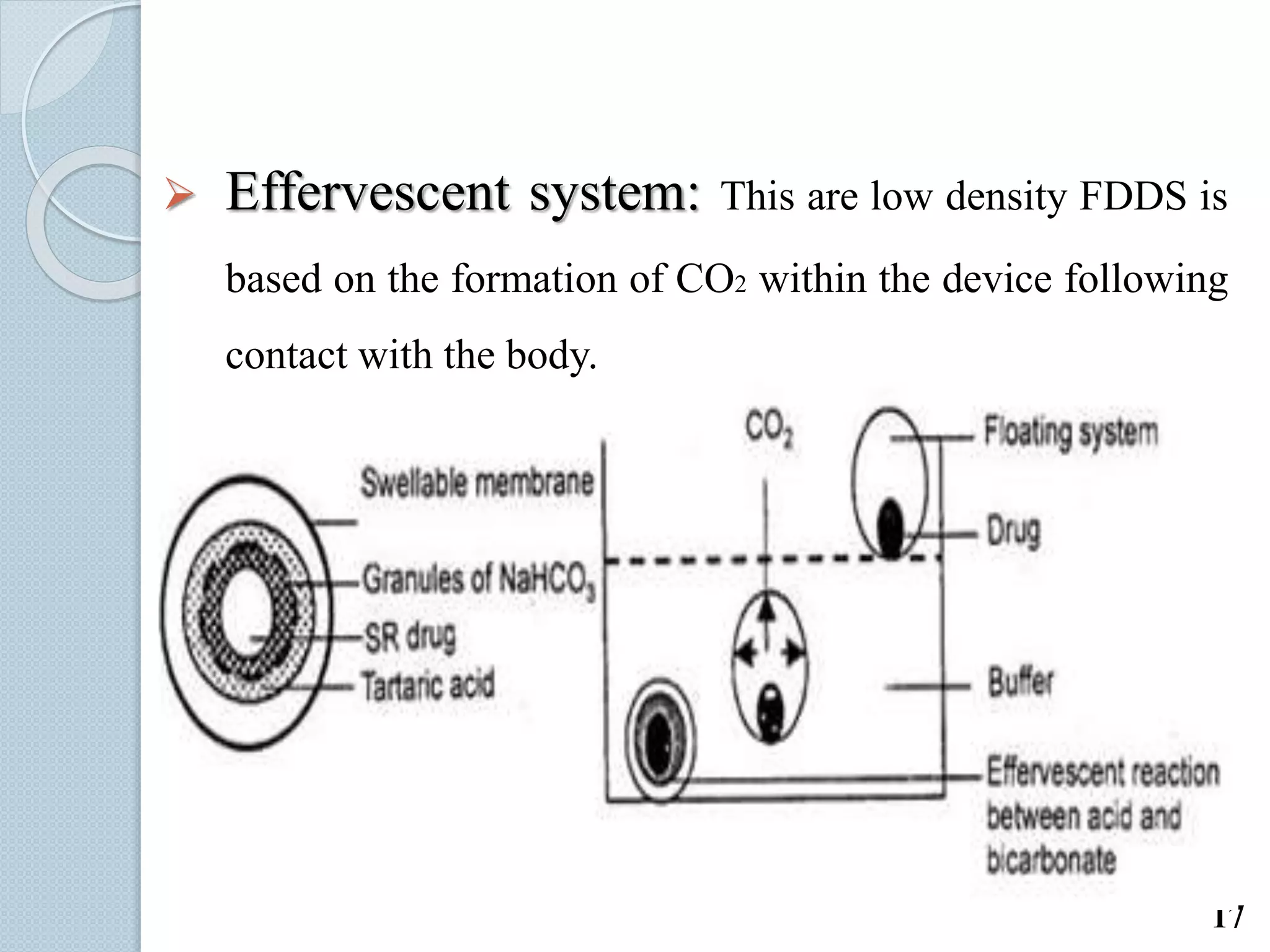
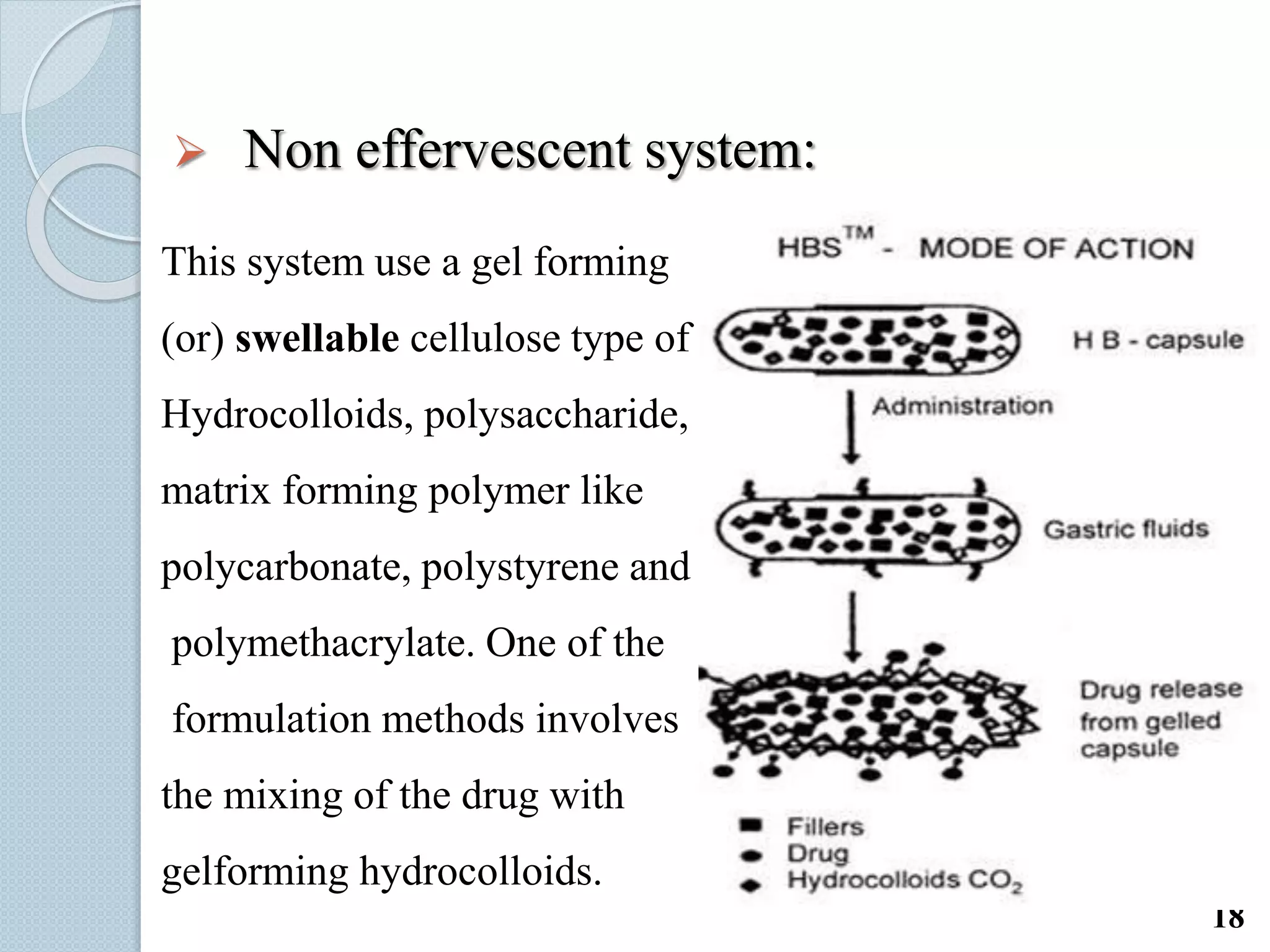
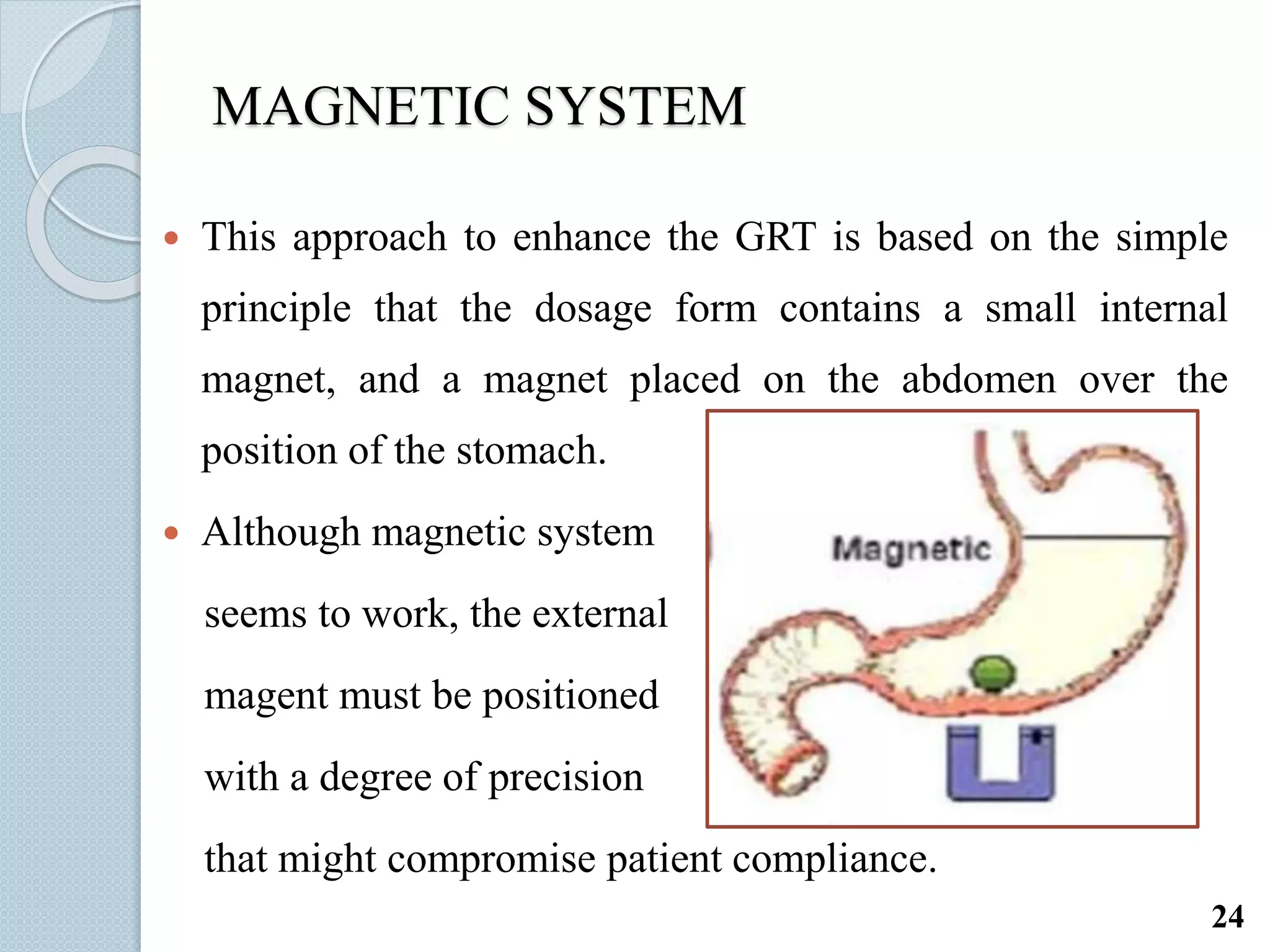
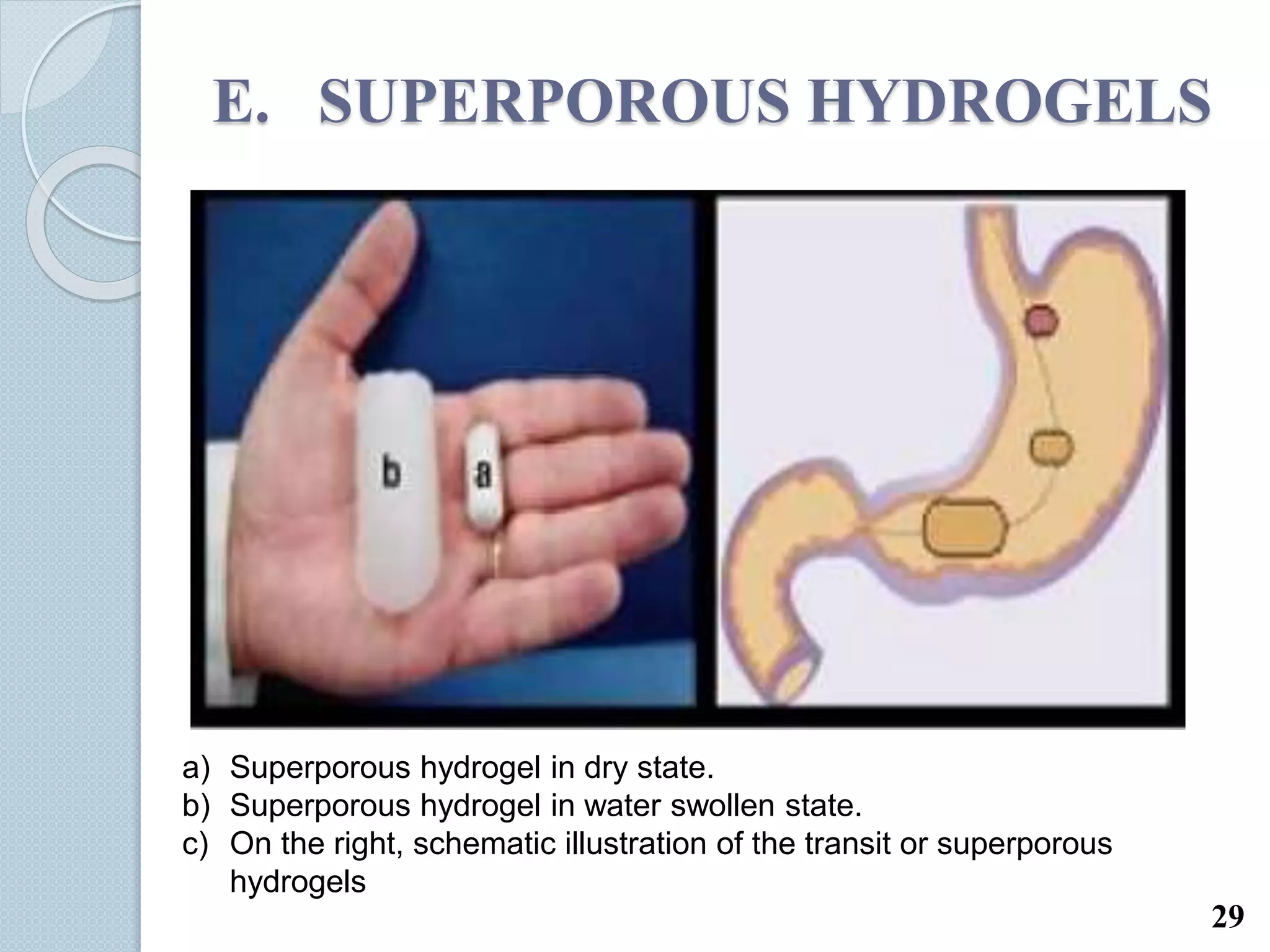
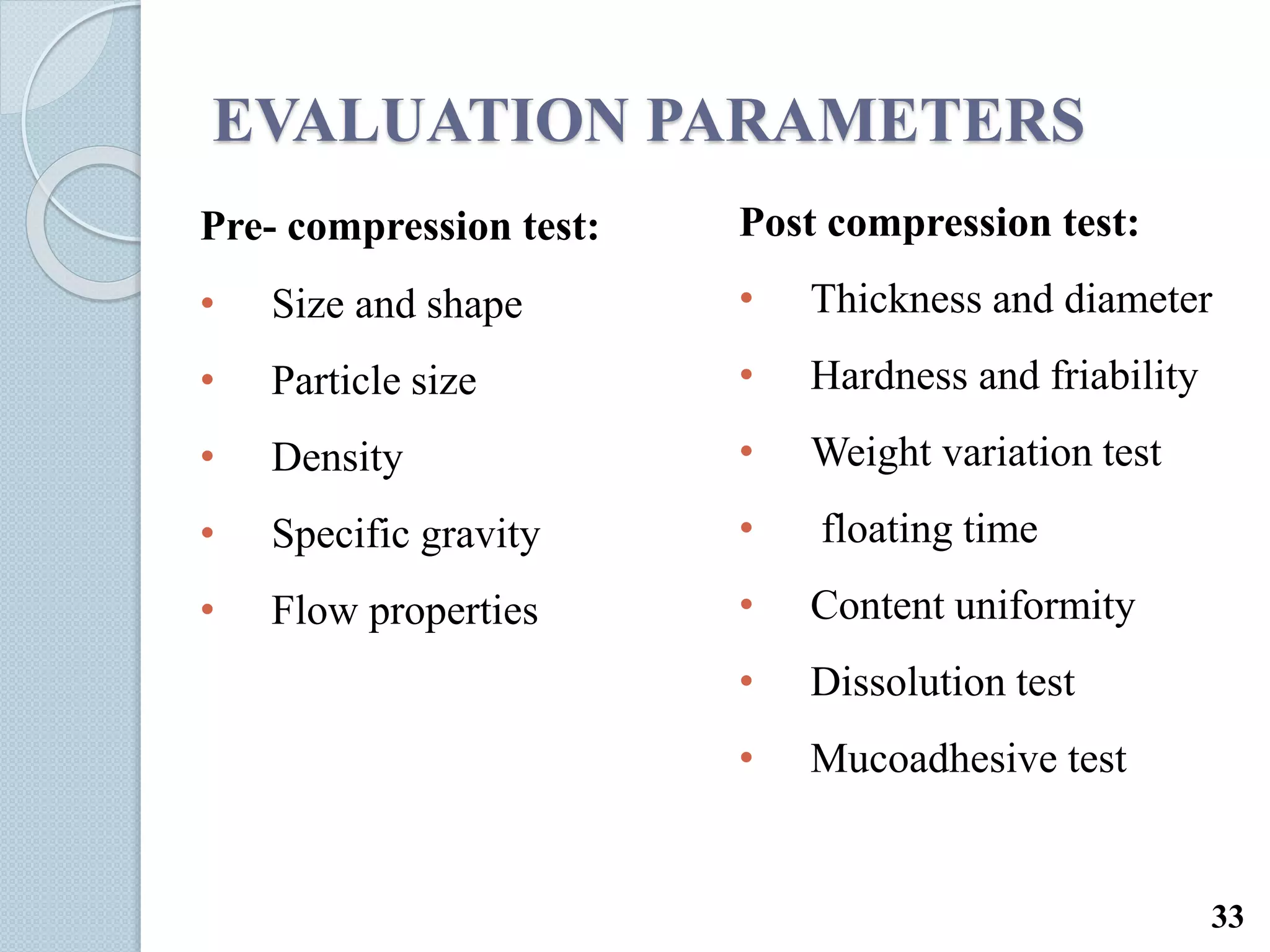
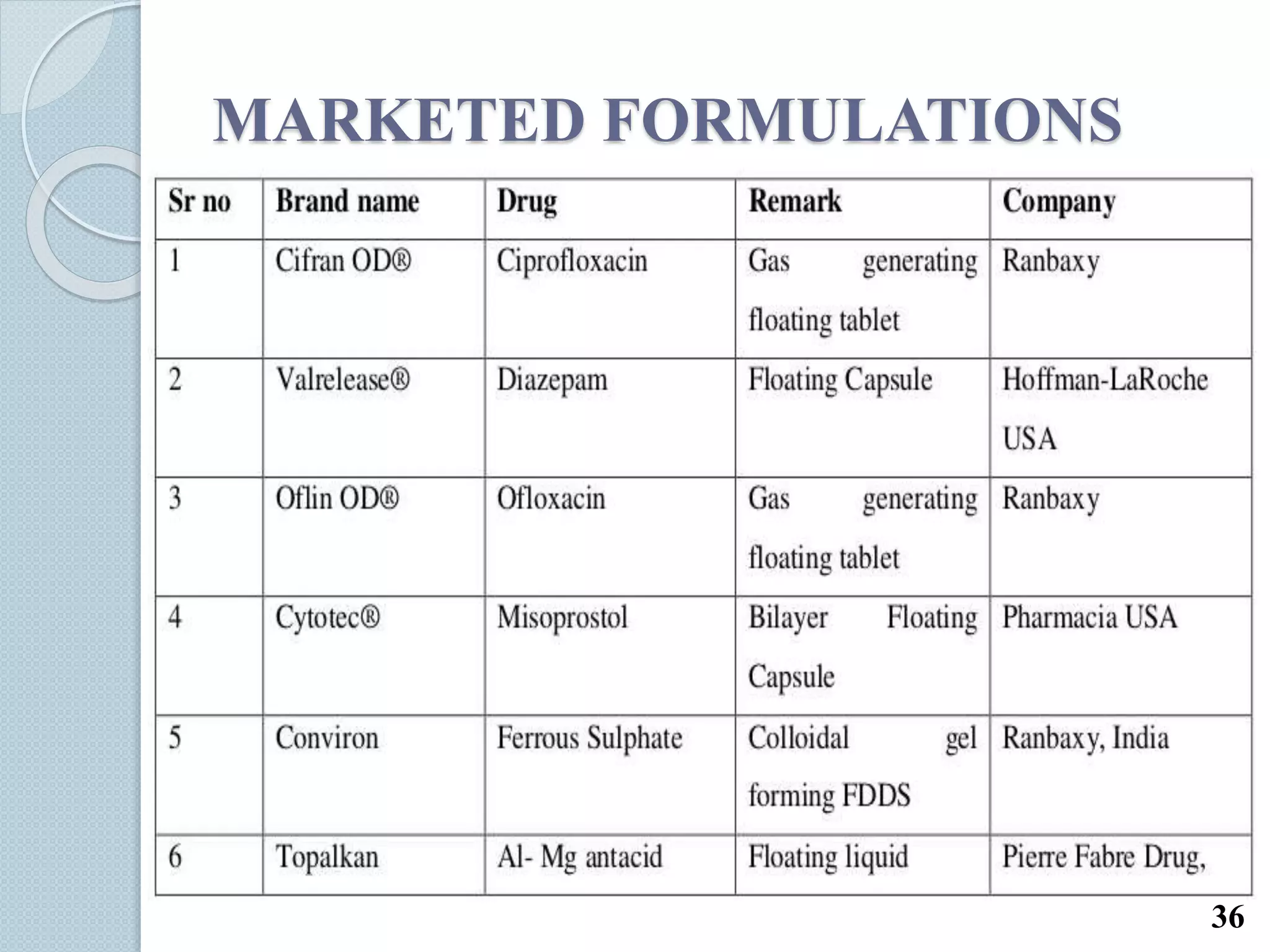
This document discusses gastro-retentive drug delivery systems (GRDDS), which aim to prolong the gastric residence time of drugs and target drug release in the upper gastrointestinal tract. It describes the physiology of the gastrointestinal tract and potential drug candidates for GRDDS. Various approaches for GRDDS are covered, including floating, high density, bioadhesive, swelling, and superporous hydrogel systems. Evaluation parameters, applications, marketed formulations, and conclusions about GRDDS are also summarized.