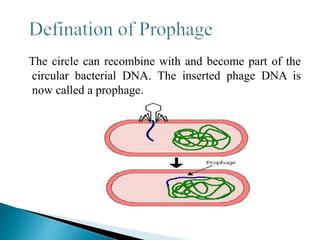
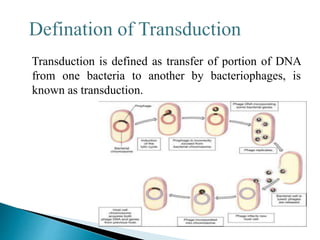
The document discusses bacteriophages, their role in lysogeny and the lytic cycle, and their use in genetic research. It explains the process of how bacteriophages integrate their DNA into host cells, leading to potential lysis and transduction. Key terms such as prophage, induction, and strain specificity of phages are also highlighted.