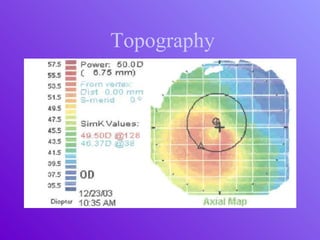
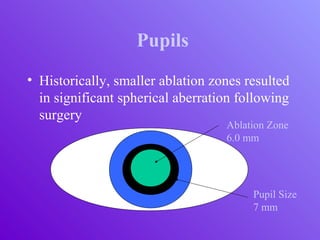
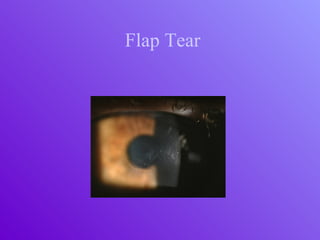
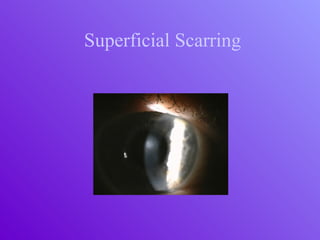
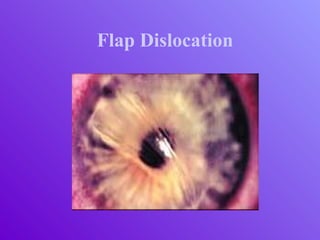
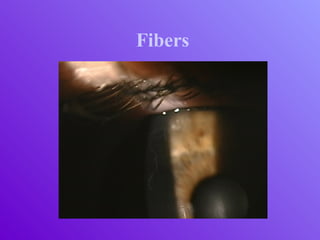
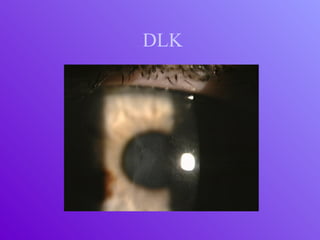
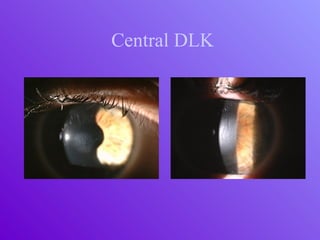
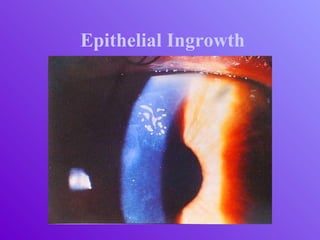
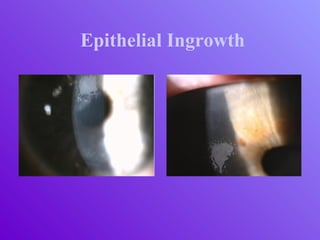
The document outlines essential aspects of refractive surgery, including preoperative evaluations and the surgical procedure using both traditional microkeratomes and the all-laser intralase method. It highlights the importance of assessing individual patient needs, managing potential complications, and ensuring proper postoperative care. Key considerations include pupil size, ablation zone, and the management of various eye health issues and systemic diseases that could affect surgical outcomes.