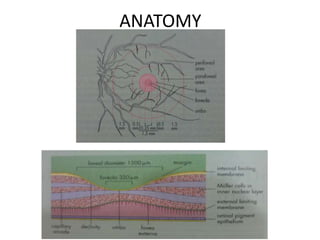
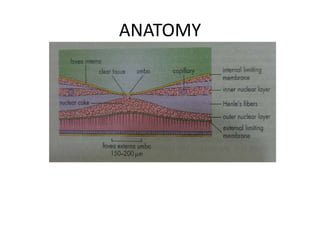
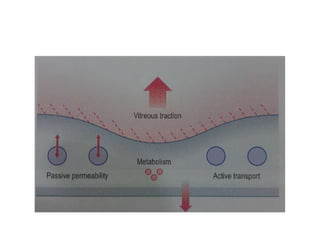
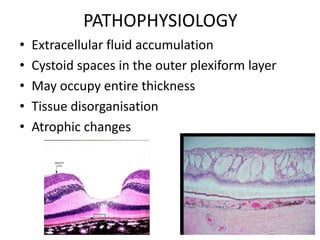
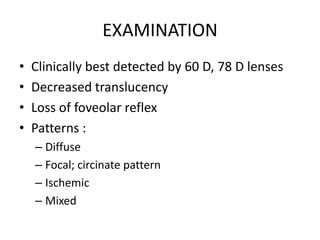
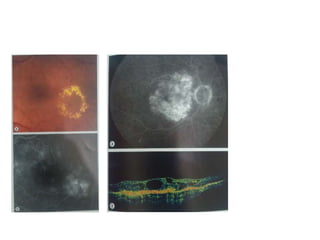
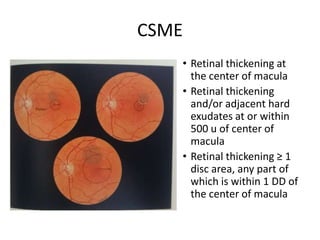
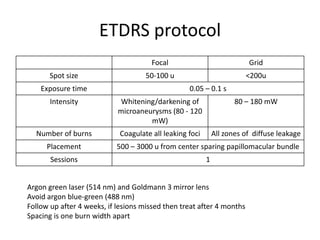
Diabetic macular edema (DME) is the leading cause of visual loss in diabetes, with various clinical associations including severity of diabetic retinopathy and glycemic control. The pathophysiology involves capillary damage, increased permeability, and fluid accumulation leading to progressive vision loss. Treatment options include laser photocoagulation, anti-VEGF therapy, and corticosteroids, each with specific protocols and potential complications.