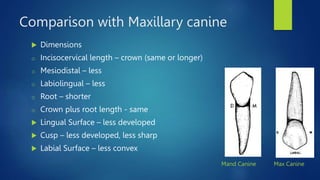
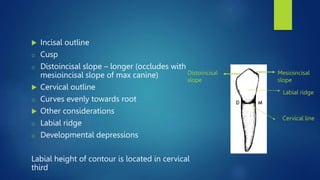
The document details the characteristics of permanent mandibular canines, including their arch position, universal numbering, dimensions, and general form. It highlights differences in the form and function of mandibular canines compared to maxillary canines, particularly in terms of cusp development and outline dimensions. Additional considerations regarding labial and lingual aspects, as well as root features, are also discussed.