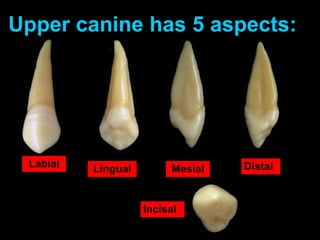
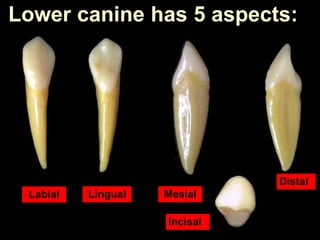
This document provides information about the anatomy and morphology of upper and lower canine teeth. It describes:
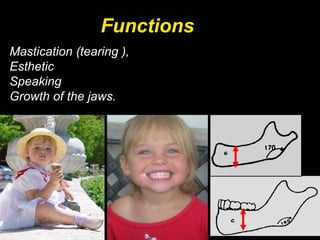
- The functions of canines as mastication and aesthetics.
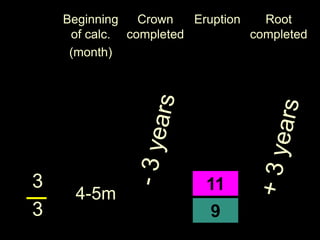
- Developmental stages from crown completion to root completion.
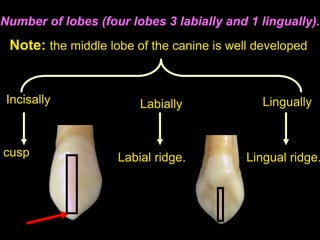
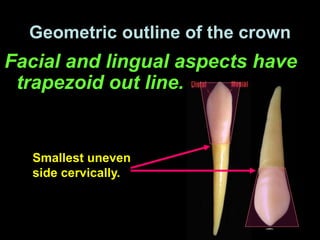
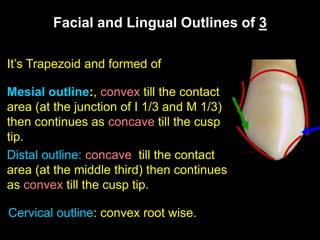
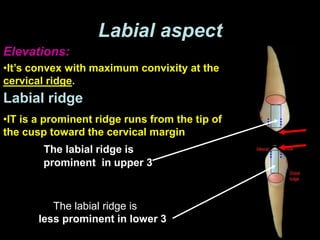
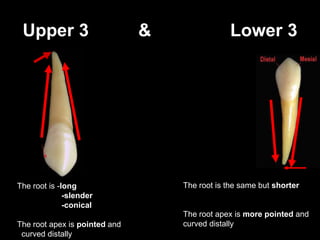
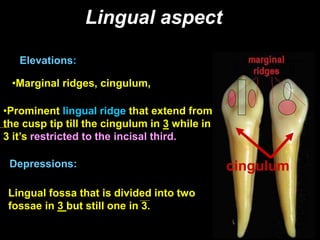
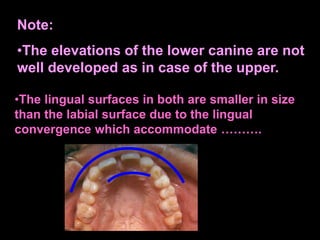
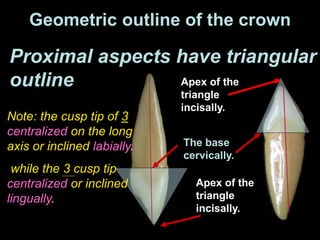
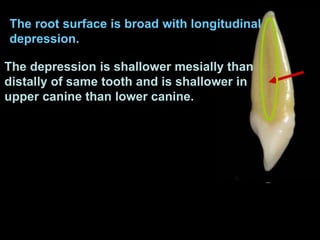
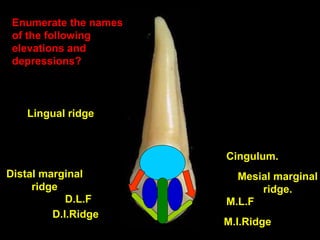
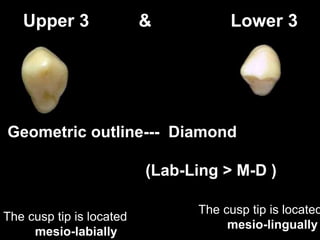
- Geometric outlines and surface anatomy features of the crowns and roots such as ridges, depressions, and outlines.
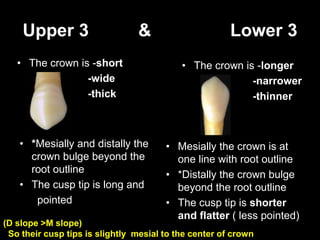
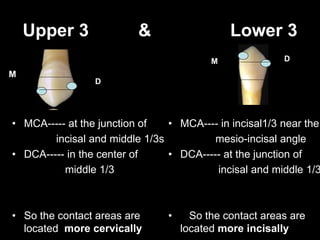
- Differences between upper and lower canines including size, shape of cusp tips, and location of contact areas.
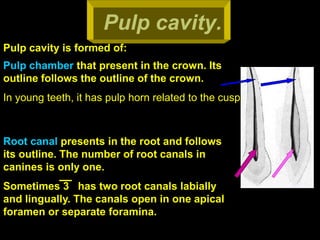
- Internal anatomy of the pulp cavity and root canals.