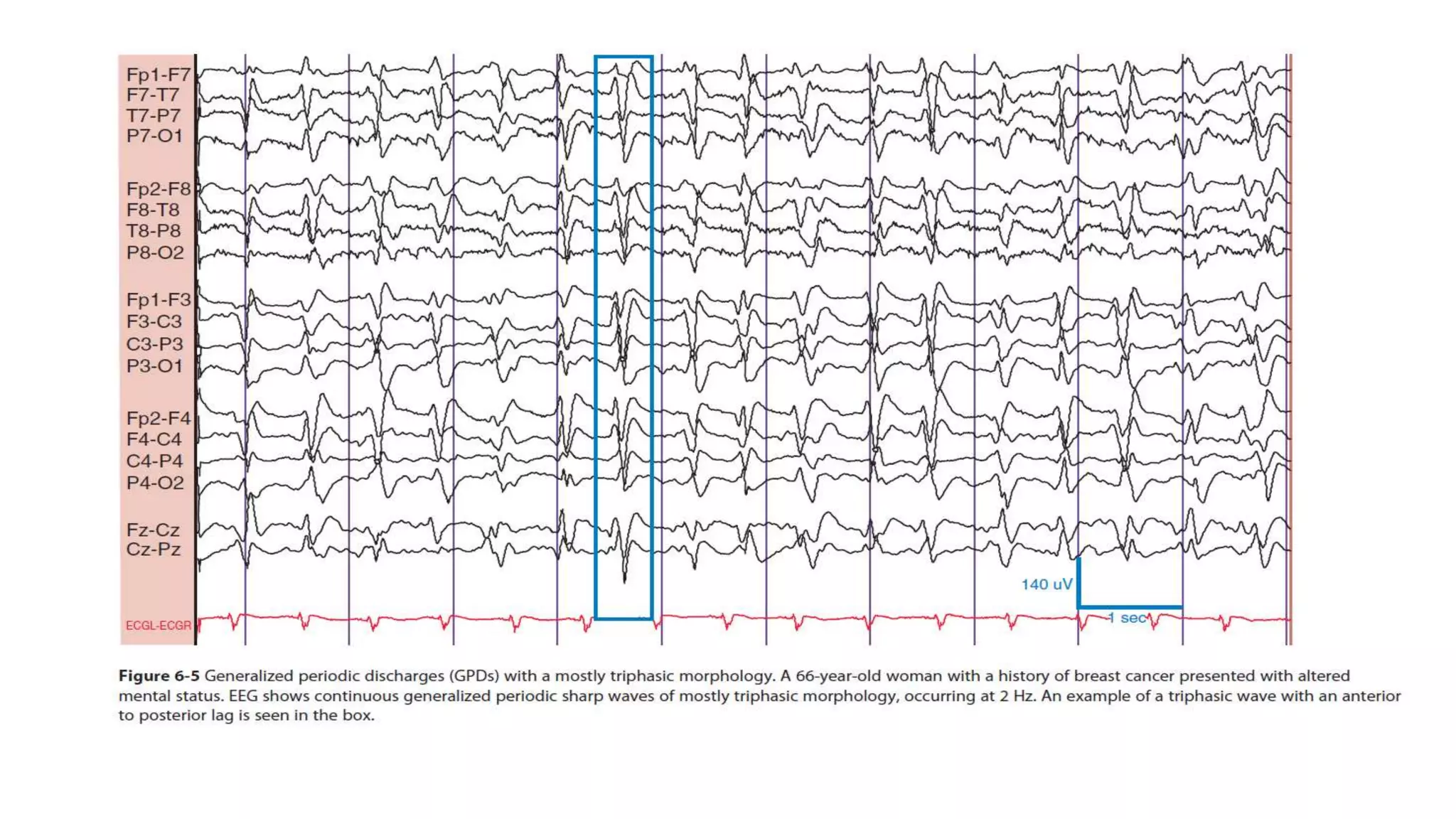
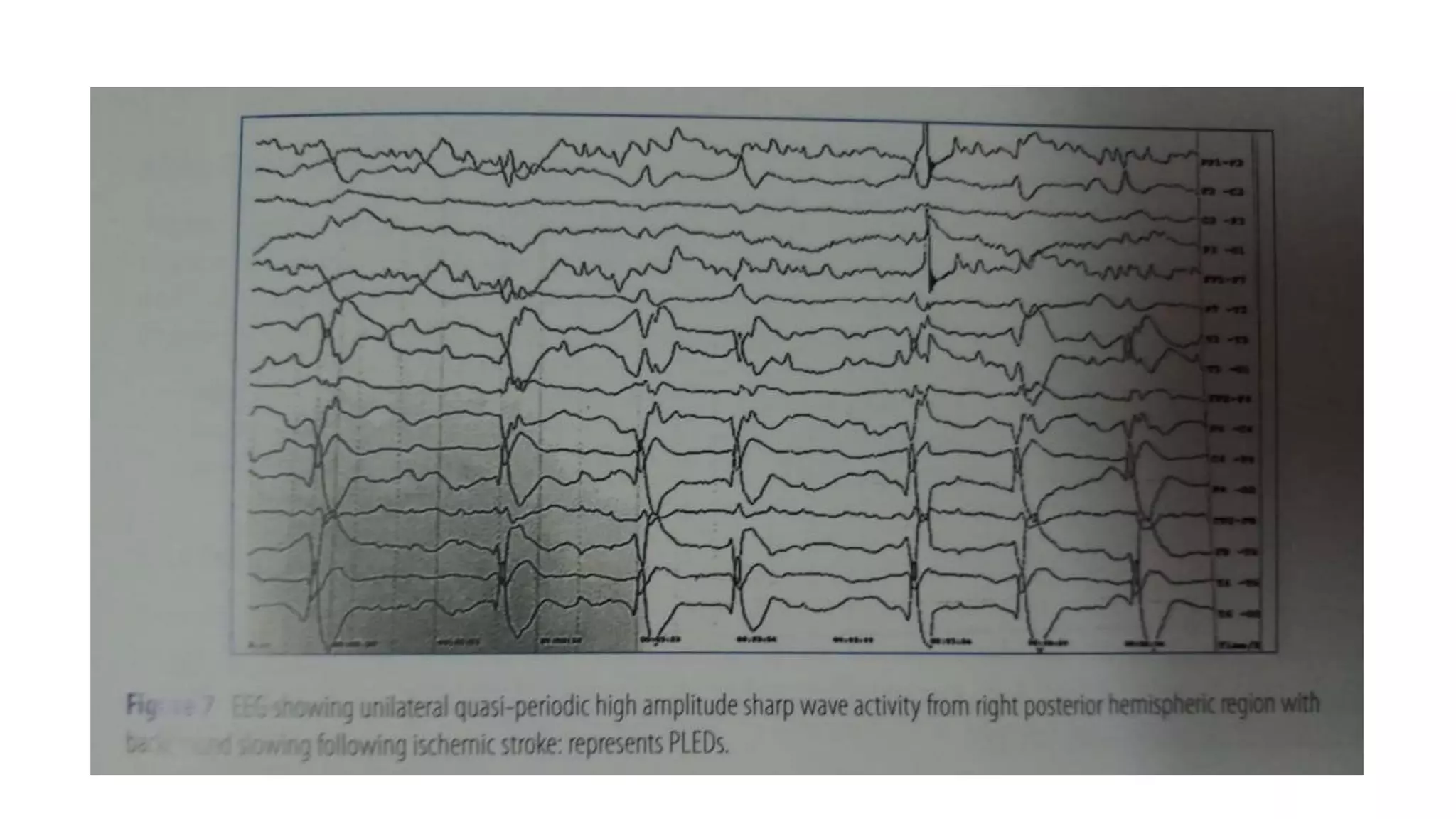
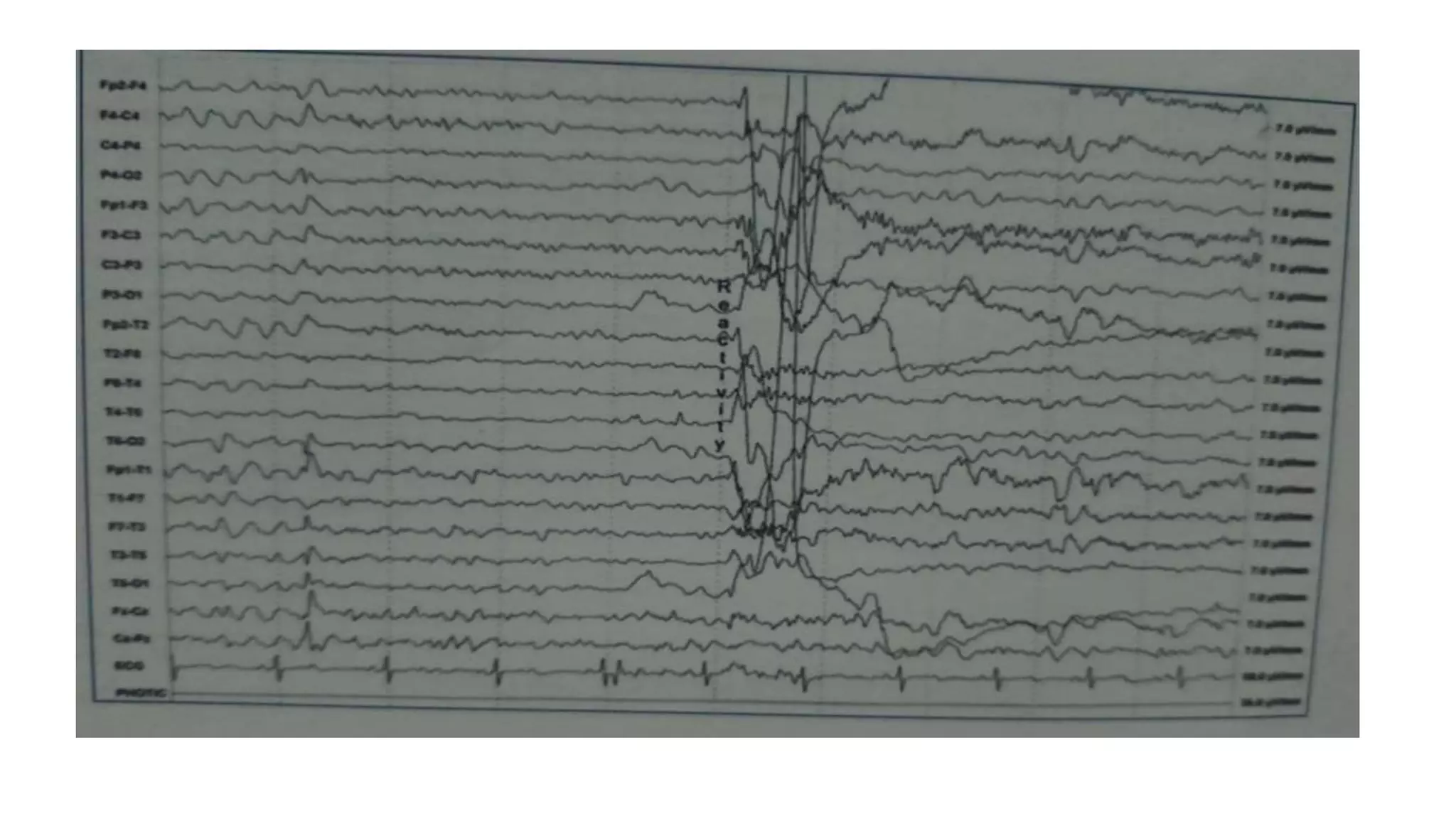
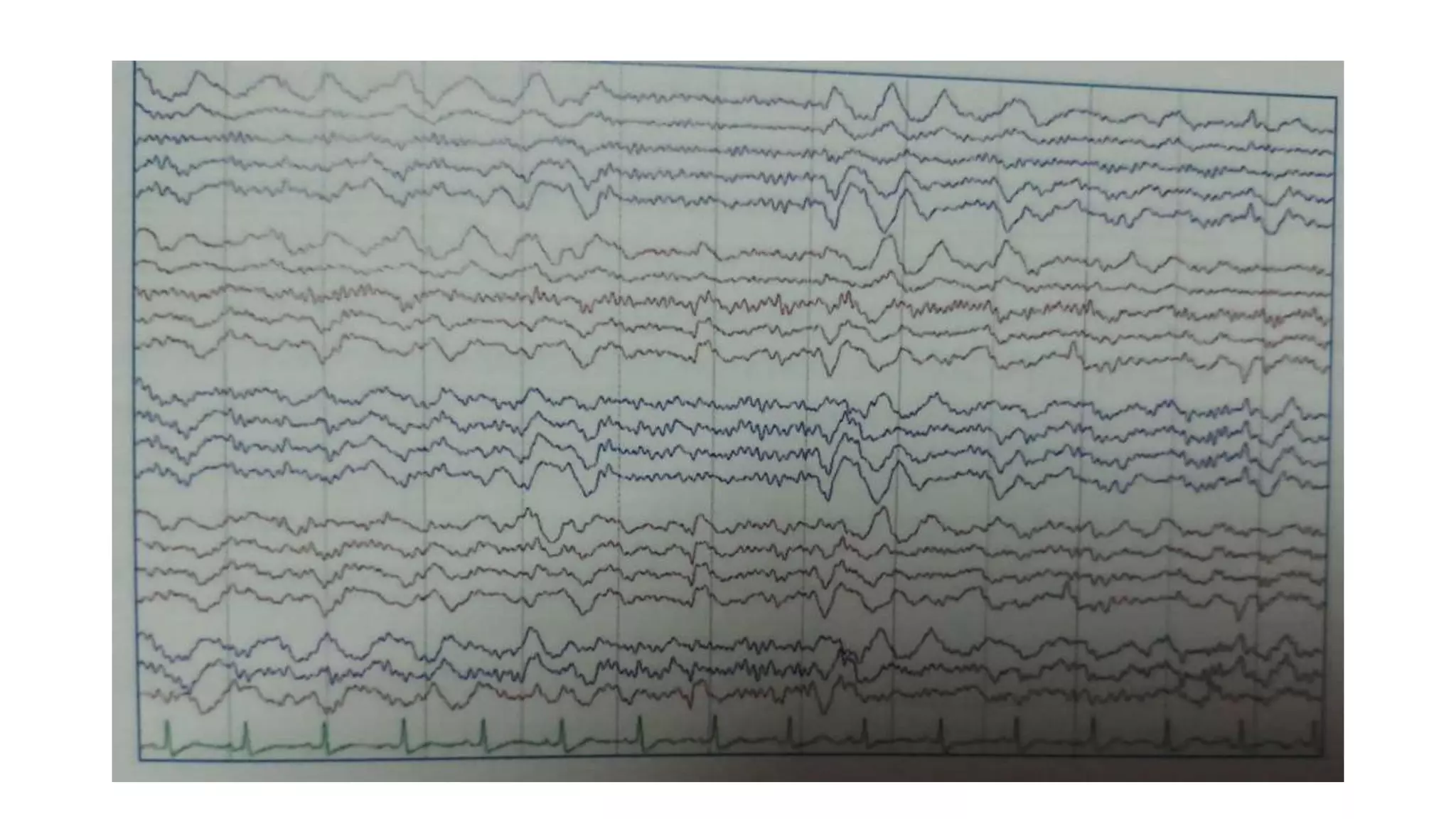
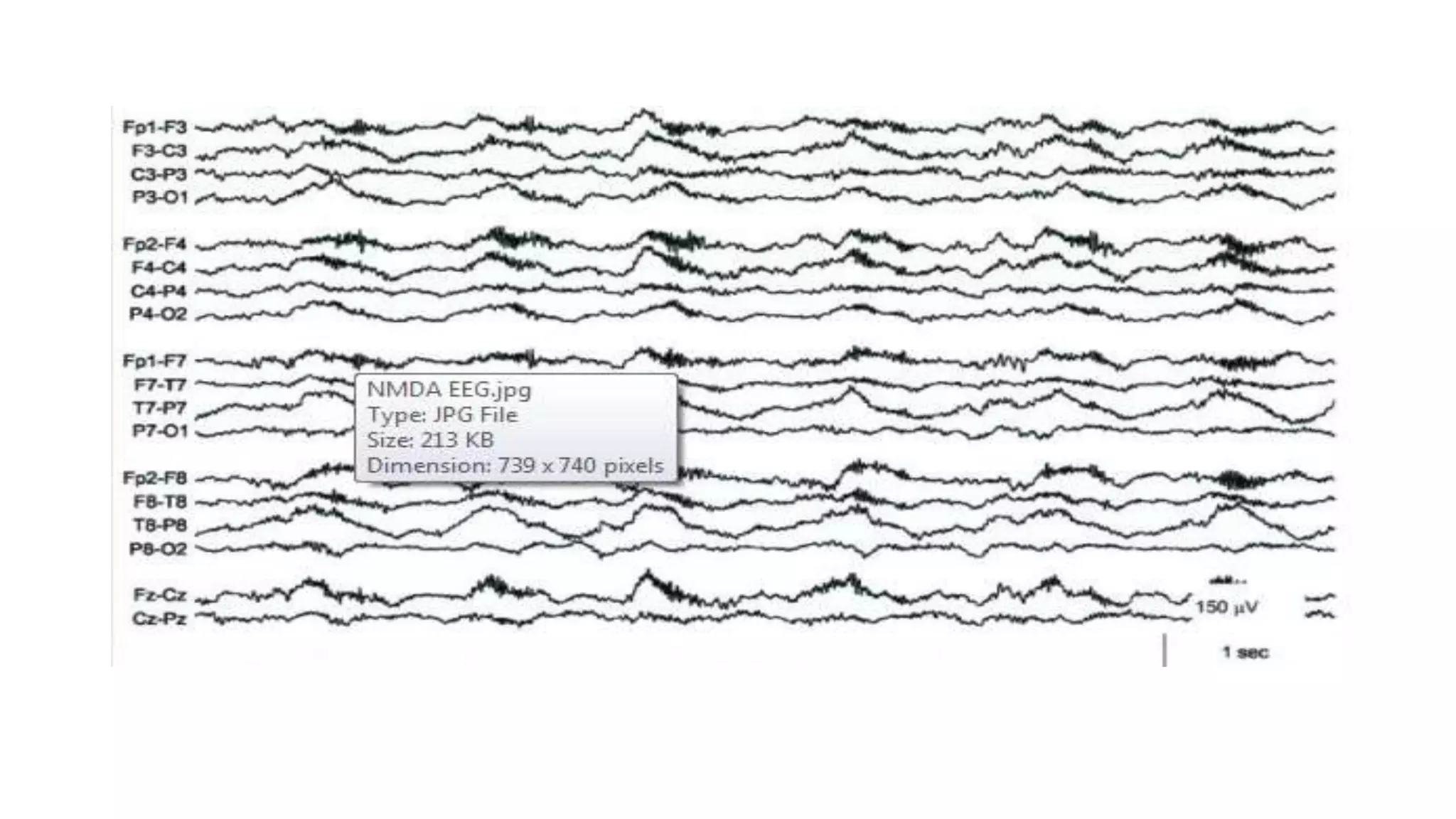
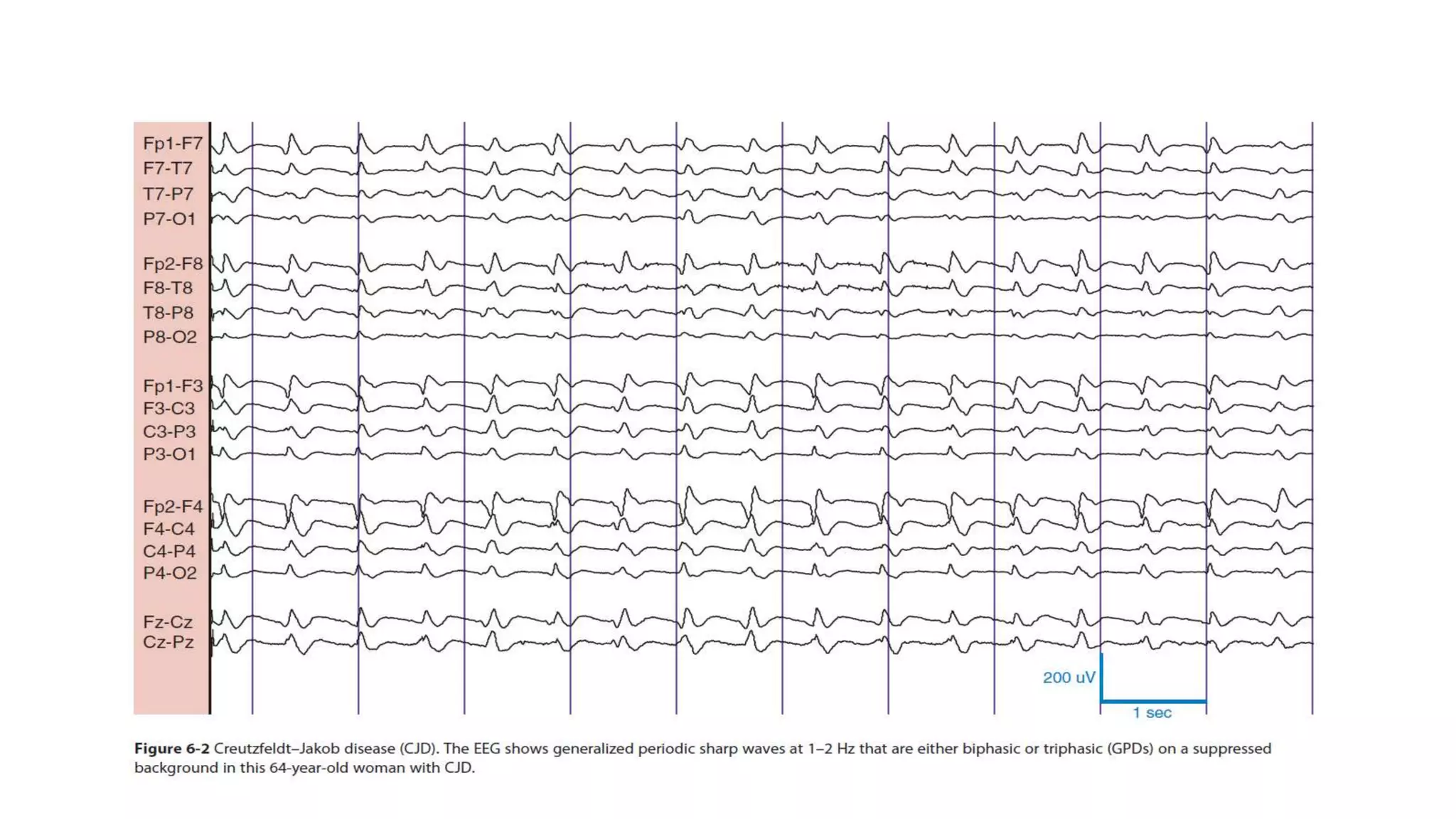
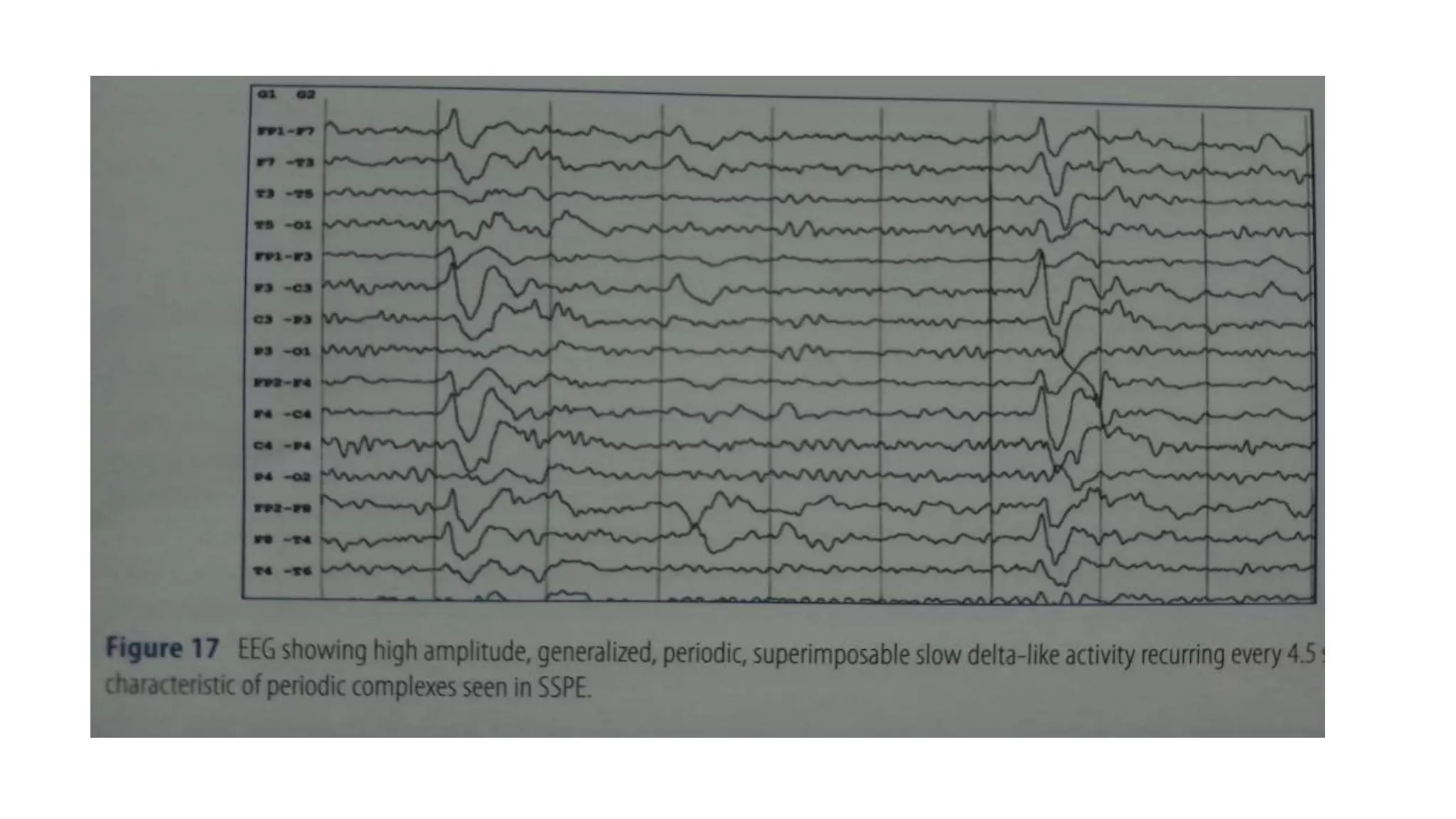
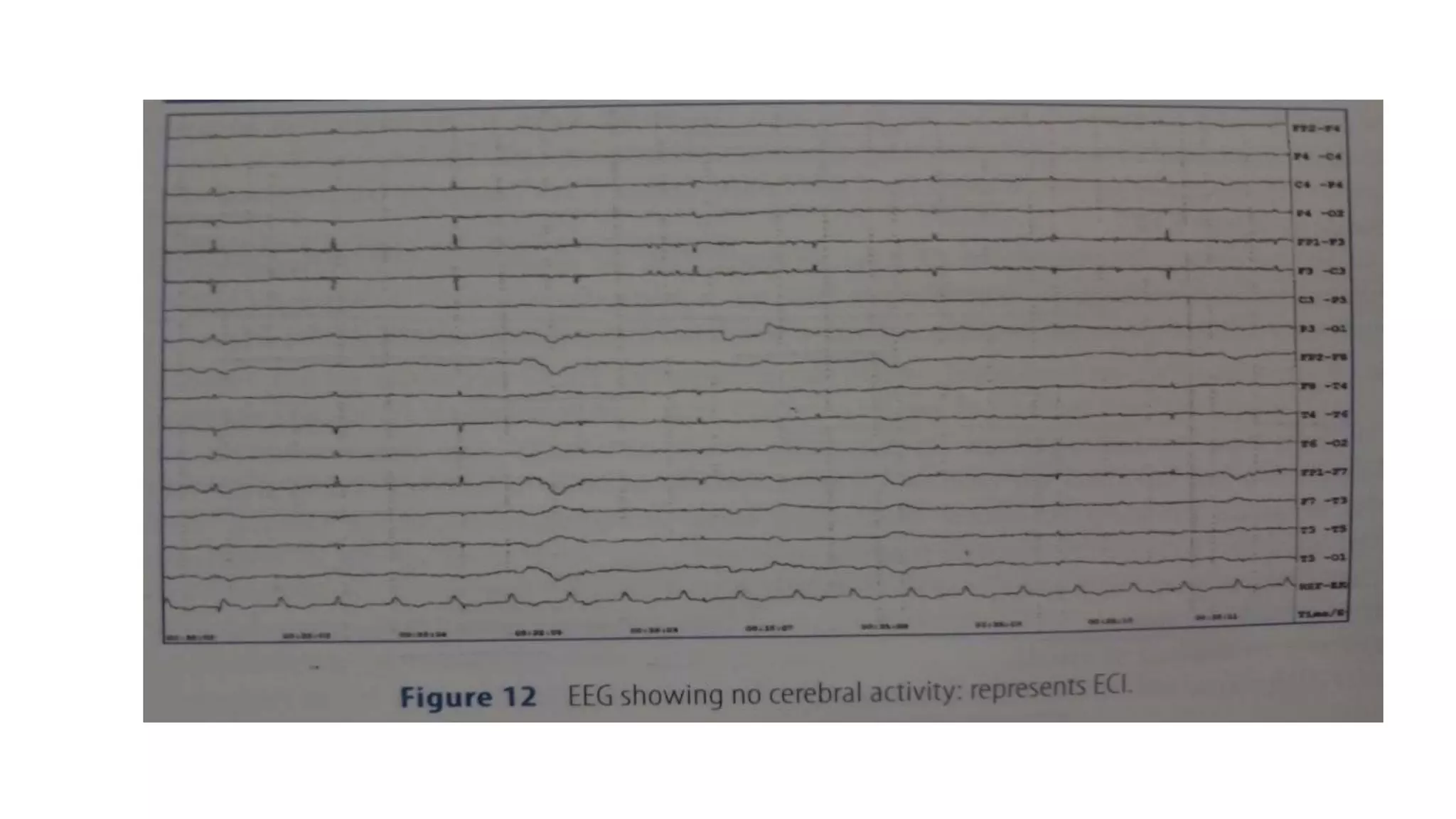
The document summarizes EEG patterns seen in various encephalopathies. It describes diffuse slowing, triphasic waves, burst suppression, periodic epileptiform discharges (PLEDs, BIPLEDs, GPEDs), alpha coma, spindle coma and beta coma patterns. Specific patterns are seen in hepatic encephalopathy, uremia, Hashimoto's encephalopathy, NMDAR encephalitis, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Criteria for periodic discharges and electrocerebral inactivity seen in brain death are also outlined.