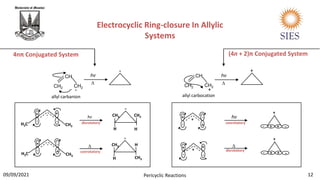
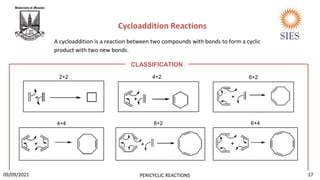
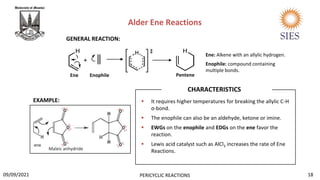
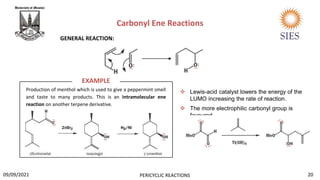
The document provides a comprehensive overview of pericyclic reactions, detailing their characteristics, types, and mechanisms such as electrocyclic, cycloaddition, and group transfer reactions. It explains the Woodward-Hoffmann rules that govern stereochemistry based on thermal or photochemical conditions, as well as real-world applications like the synthesis of vitamin D3 and beta-lactams. Additionally, the document covers specific reaction examples, including ene reactions and ketene cycloadditions, emphasizing their significance in organic synthesis.








![Woodward-Hoffmann Rules
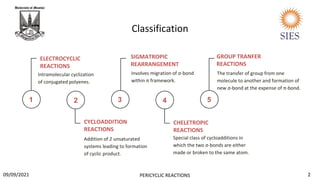
(4n)π
[Even Π Bonds]
Thermal
(4n+2)π
[Odd Π Bonds]
Photochemical
Conrotatory
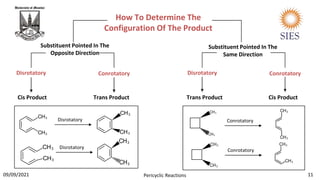
Reaction Conditions Allowed Mode Of Ring Closure
No. Of Π Electrons
Thermal
Photochemical
Disrotatory
Disrotatory
Conrotatory
9
PERICYCLIC REACTIONS
09/09/2021](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paper1-231105163340-ed5d68fc/85/Pericyclic-Reactions-pptx-11-320.jpg)


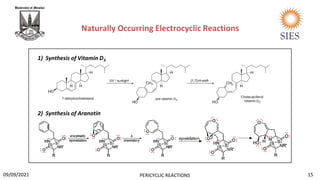
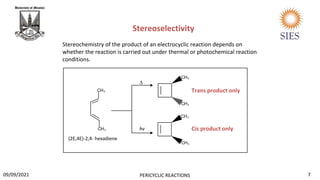
![ Biosynthesis of vitamin D3.
It is sub element of vitamin D which is essential for our bones. It is also called “sunshine vitamin” as
sunlight is a great source of vitamin D.
The first step involves a photochemically induced conrotatory ring opening of 7-dehydrocholesterol
to form pre vitamin D3, then a [1,7]-hydride shift then forms vitamin D3.
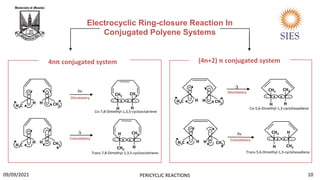
Biosynthesis of Aranotin.
Aranotin is an organic heterohexacyclic compound which is known for having antiviral and antibiotic
properties.
1st enzymatic epoxidation of the starting material takes place. In the 2nd step, disrotatory ring
opening electrocyclization reaction takes place containin 6pi e-. Then 2nd epoxidation of the ring
takes place and the nearby nucleophilic nitrogen attacks the electrophilic carbon, forming a five
membered ring. The resulting ring system is a common ring system found in aranotin and its
derivatives.
(Explaination)
16
PERICYCLIC REACTIONS
09/09/2021](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paper1-231105163340-ed5d68fc/85/Pericyclic-Reactions-pptx-18-320.jpg)


![Ketene [2 + 2] Cycloaddition
Preparation of dichloroketene follows E1cB elimination reaction.
The most e- rich end of alkene forms bond with e- deficient central Carbon atom of
Ketene.
Cl
Cl
Dichloroketene
EtO
+ C
O
Cl
Cl
O
Cl
Cl
EtO
Most electron
deficient
Most
electron rich
22
PERICYCLIC REACTIONS
09/09/2021
..
..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paper1-231105163340-ed5d68fc/85/Pericyclic-Reactions-pptx-24-320.jpg)









