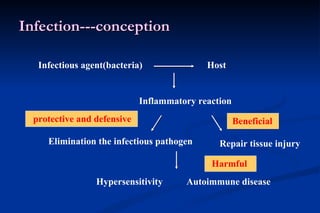
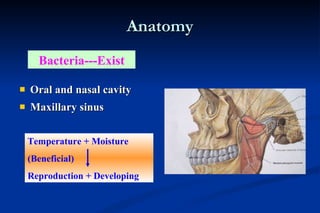
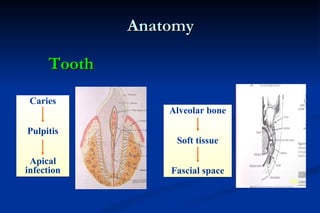
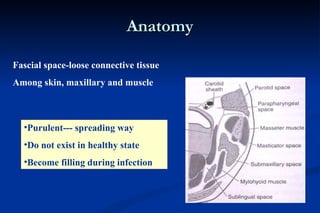
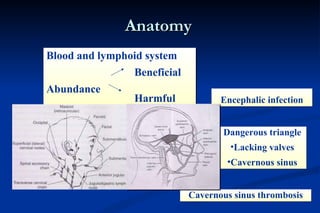
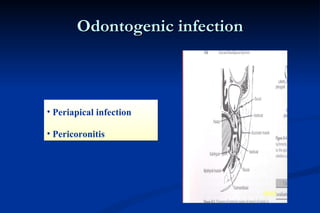
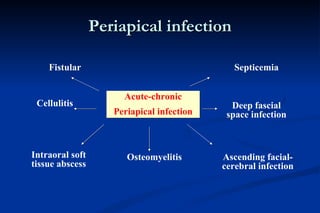
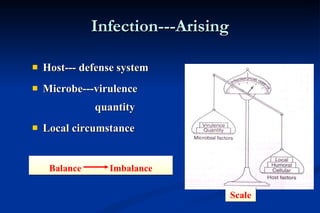
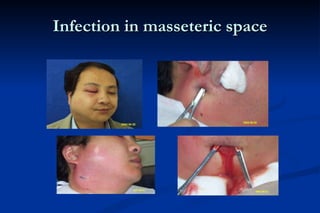
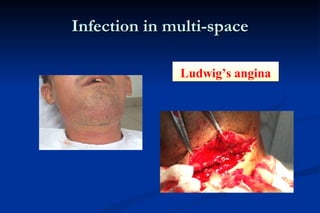
1. Infection in the oral and maxillofacial region can arise due to a balance between the host's defense system, microbial virulence and quantity, and local circumstances. Common routes of infection include odontogenic, traumatic, hematogenous, and iatrogenic causes.
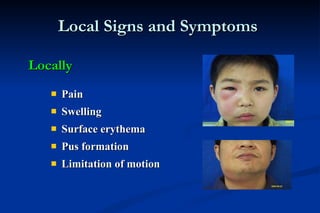
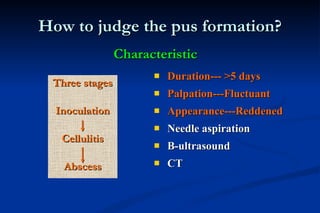
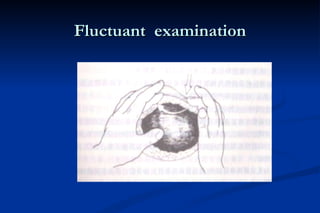
2. Diagnosis involves identifying local signs like pain, swelling and pus formation as well as systemic symptoms such as fever and lymphadenopathy. Imaging may also be used.
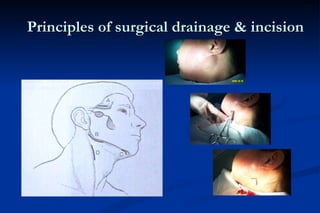
3. Treatment of acute infections focuses on supporting the host's defense system with antibiotics and surgical drainage or incision of abscesses when pus has formed. For chronic infections, surgical removal of the infection source is often needed in addition to antibiotics and drainage.