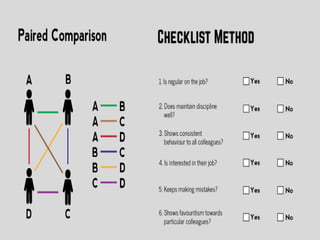
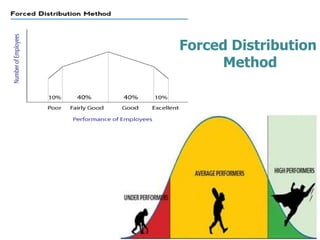
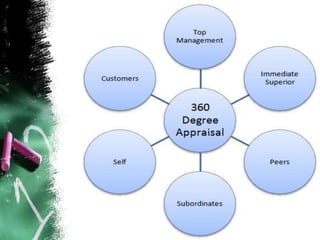
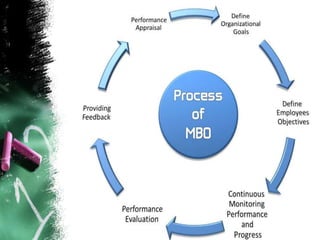
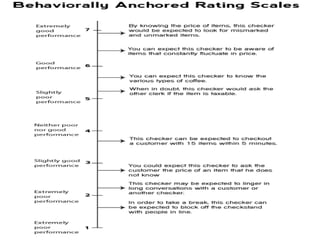
This document provides an overview of various performance appraisal methods, including traditional methods like paired comparison, checklist, critical incident, and forced distribution, as well as modern methods like graphic scale, confidential report, field review, essay, 360 degree, management by objectives, assessment centers, and behaviorally anchored rating scales. It describes the process and key aspects of each method.