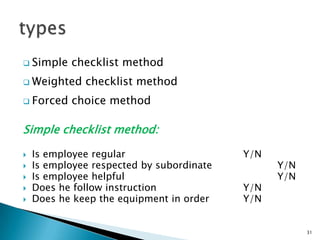
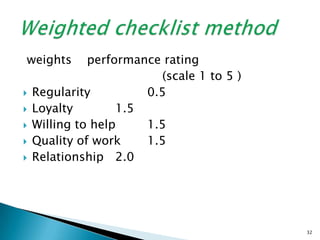
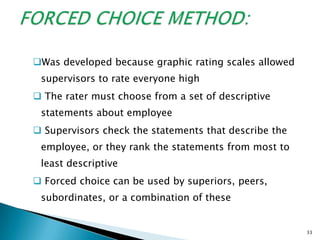
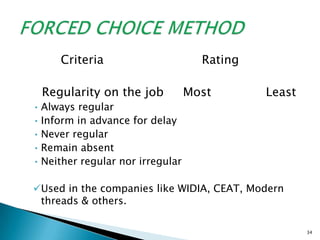
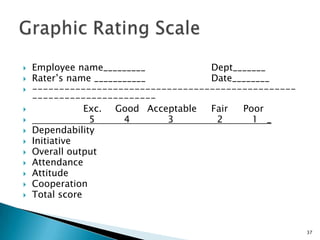
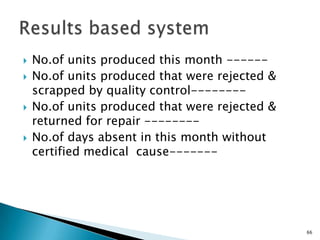
The document discusses various methods used for performance appraisal. It describes traditional methods like graphic rating scales, forced distribution and essay evaluation. It also covers modern techniques such as behavioral anchored rating scales, management by objectives and assessment centers. The benefits, limitations and process of different appraisal methods are explained.