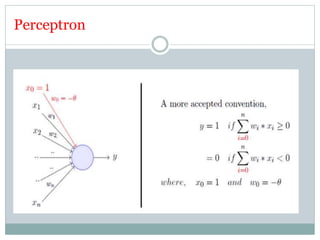
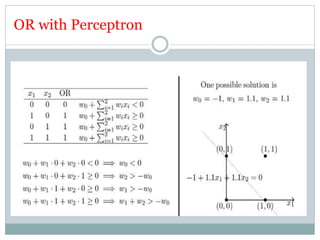
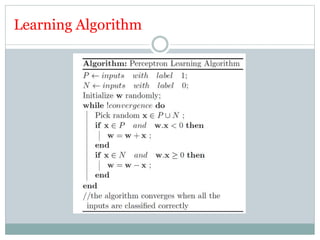
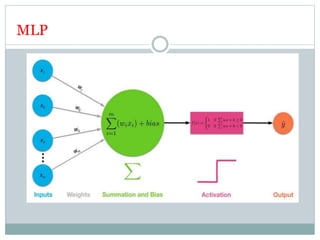
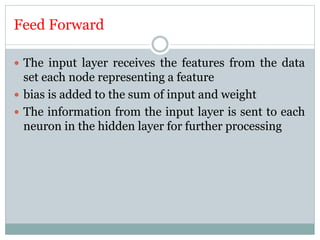
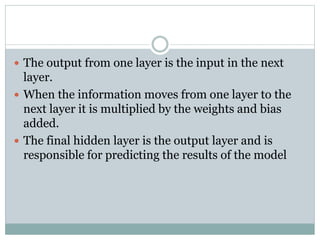
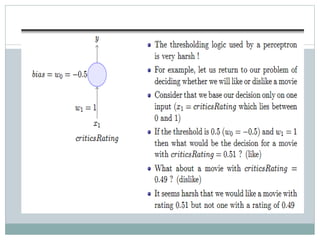
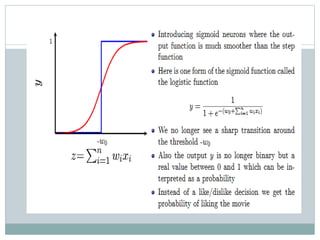
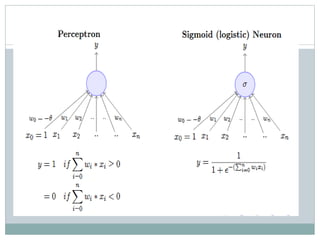
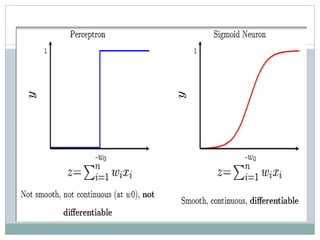
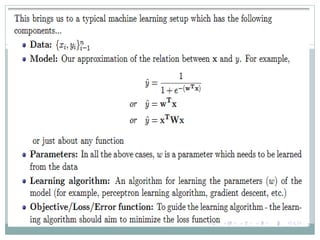
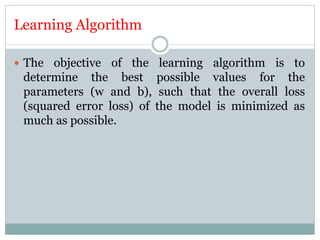
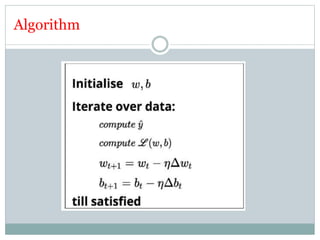
This document discusses perceptron and sigmoid neurons. It defines perceptrons as computational models that take real-valued inputs, aggregate them using weighted sums, and output binary values based on a threshold. Perceptrons are linear classifiers. Sigmoid neurons are then introduced to address limitations of perceptrons by having real-valued inputs and outputs between 0-1. Multi-layer perceptrons are described as neural networks with multiple hidden layers that use backpropagation to train the network weights to minimize error between predicted and actual outputs.