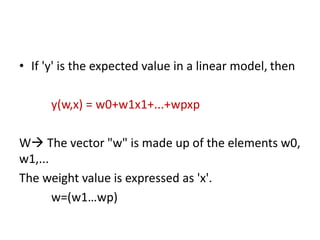
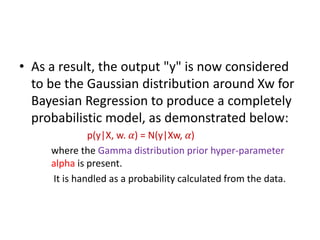
Bayesian linear regression models the relationship between variables by characterizing the mean of one parameter as a weighted sum of other variables. It determines prior distributions for the regressors and finds the posterior distribution, which is the likelihood function multiplied by the prior, normalized. This allows the model to produce probabilistic outputs and account for uncertainty. Bayesian linear regression is useful when datasets are small but becomes less efficient than other approaches as data size increases.