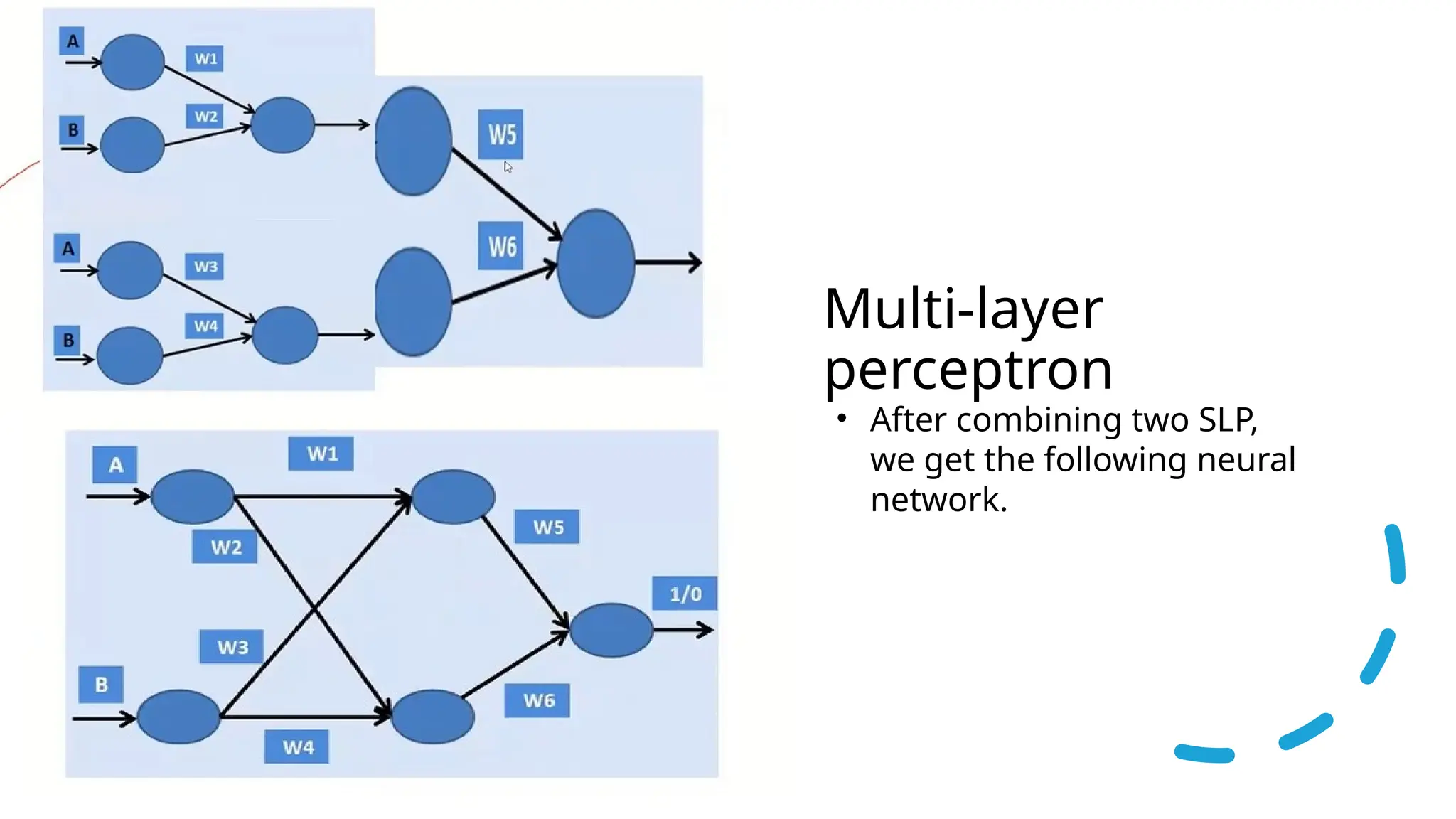
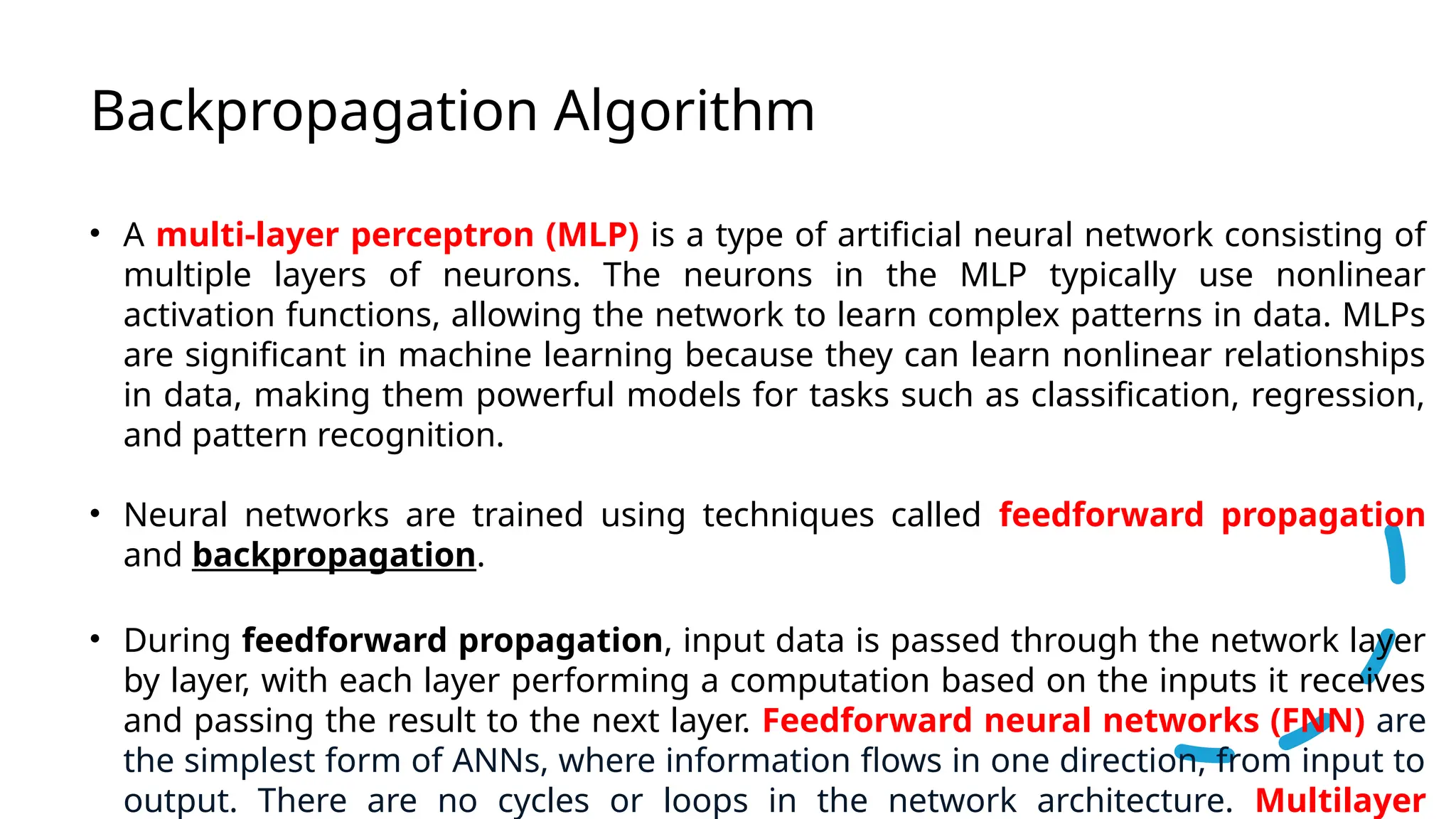
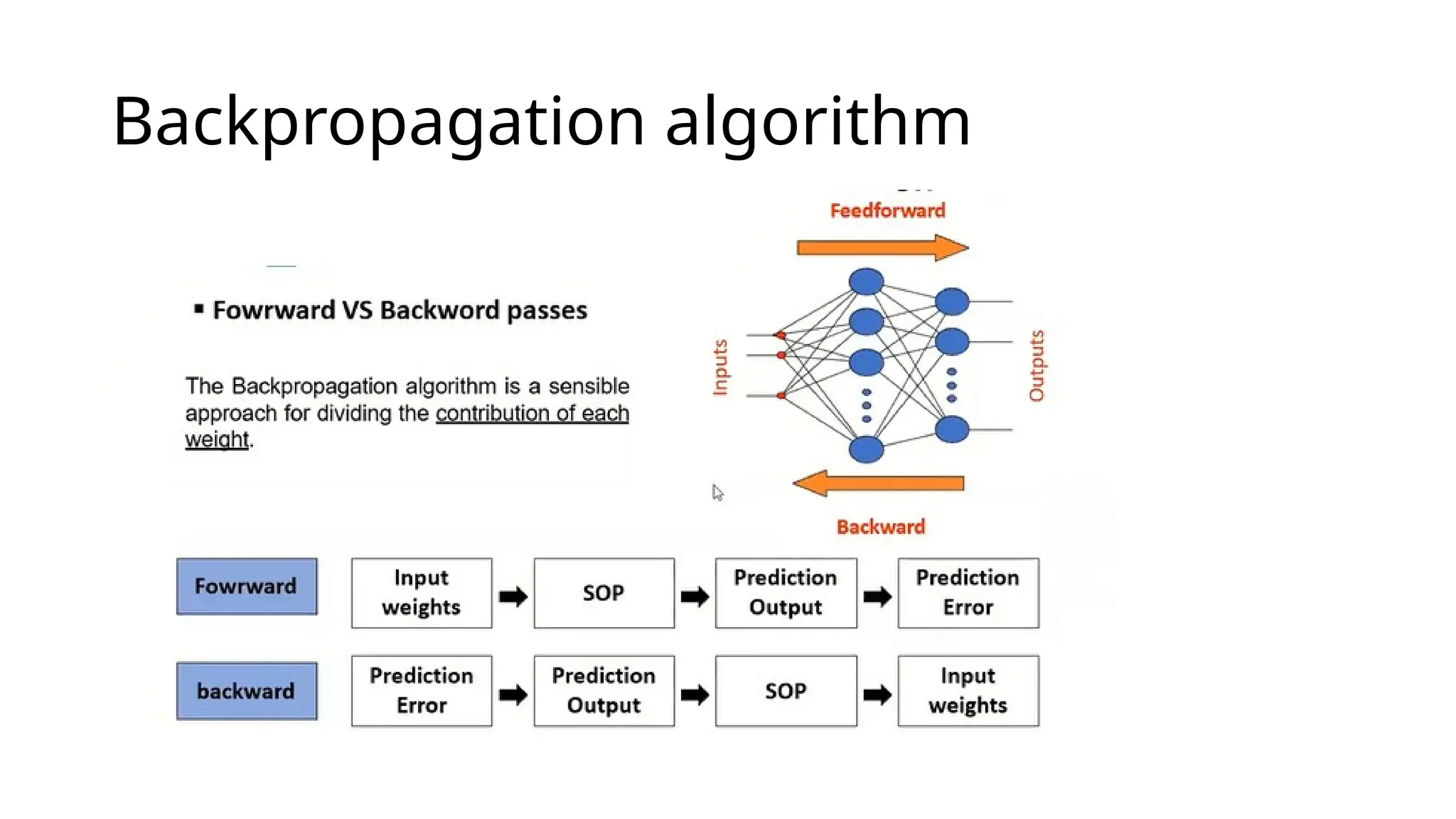
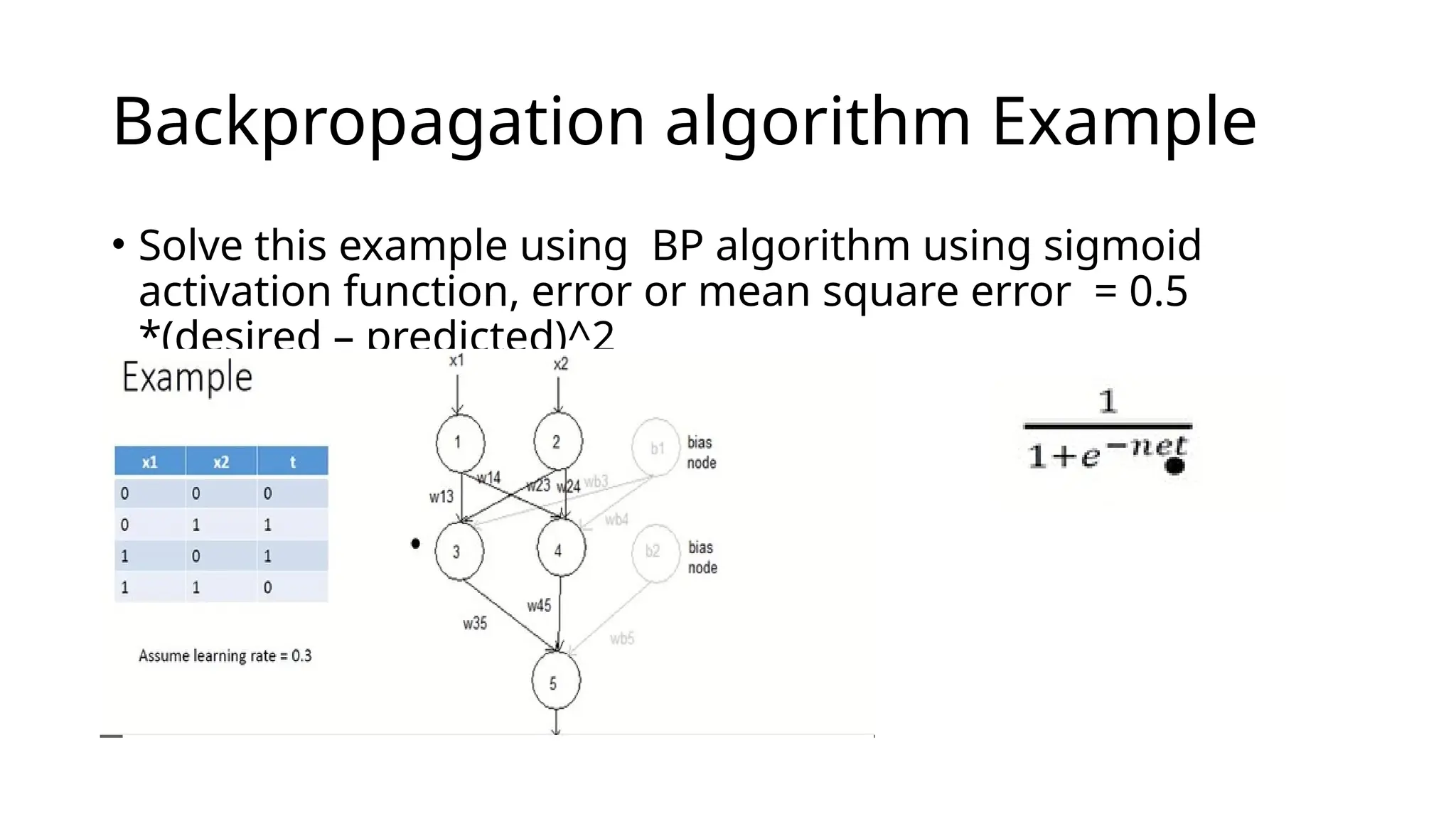
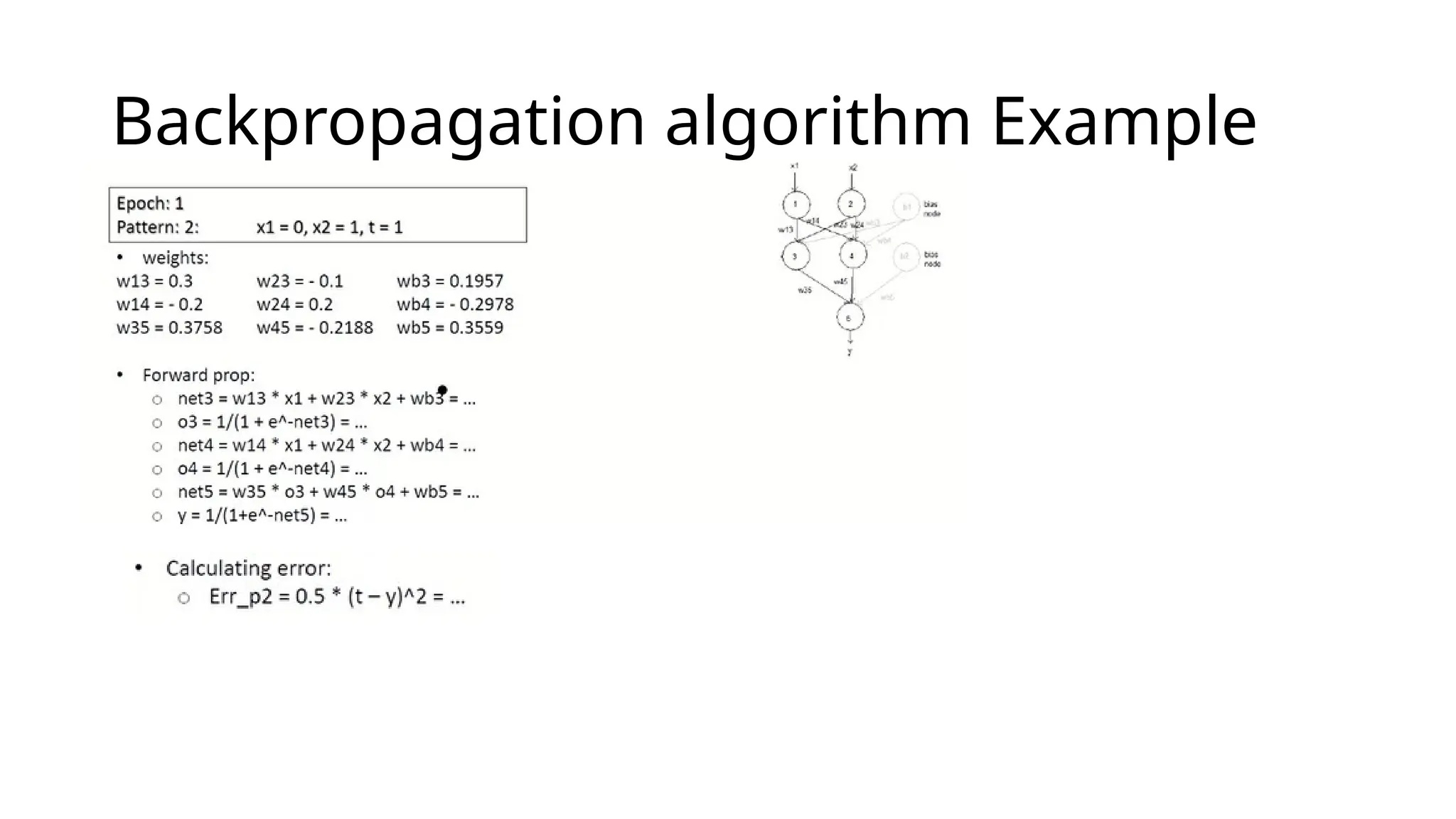
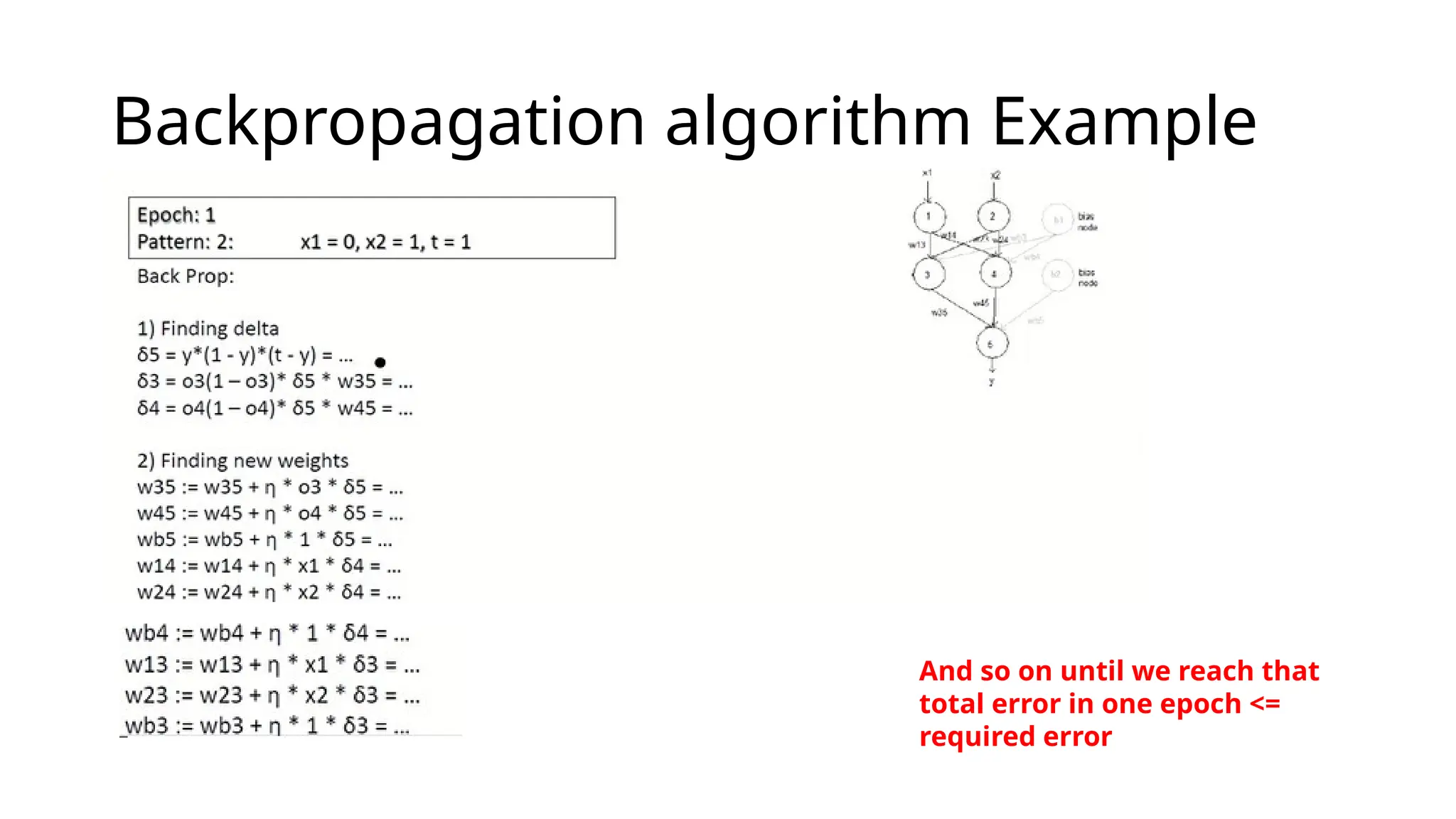
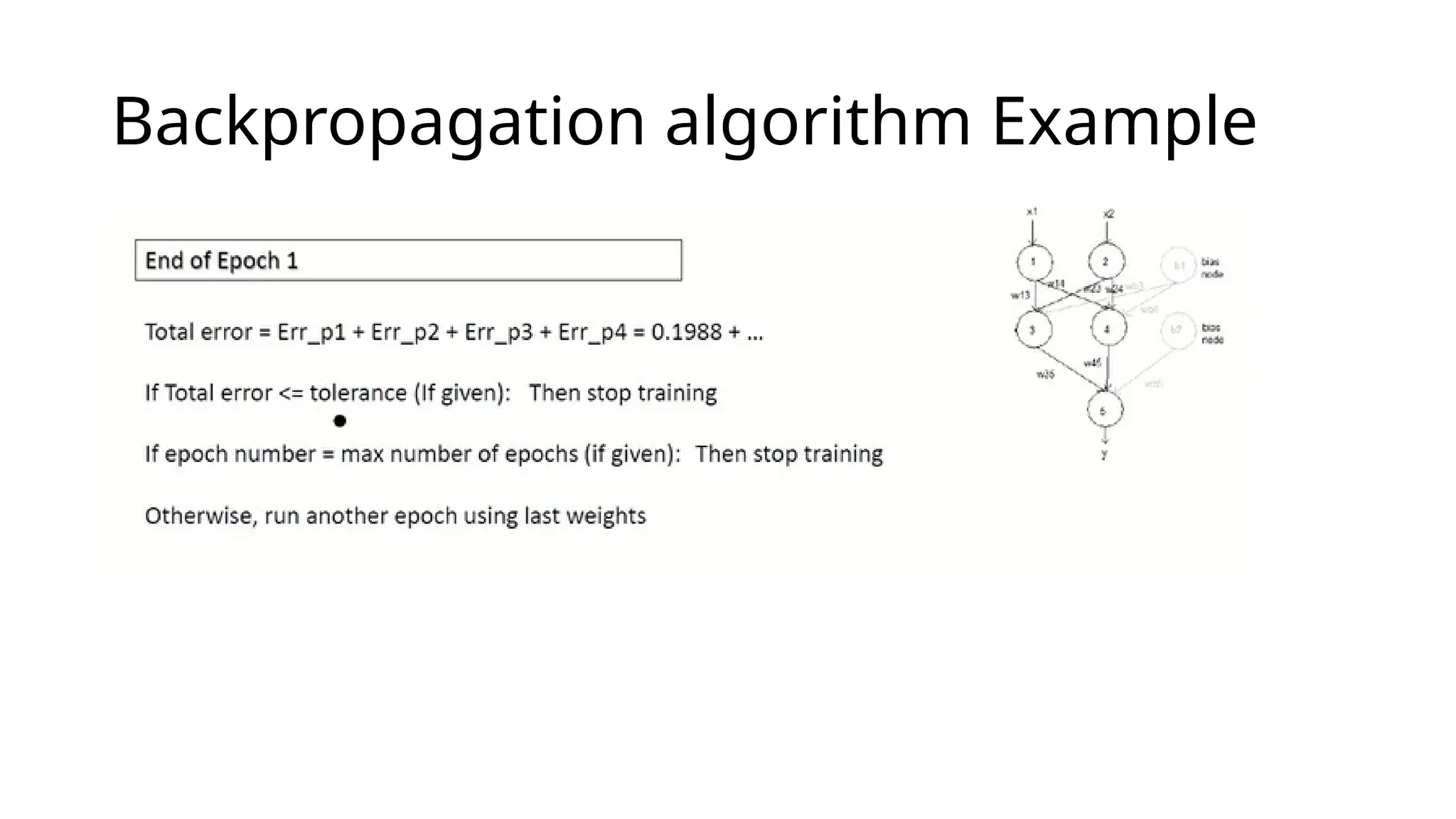
This document discusses multi-layer perceptrons (MLPs), which are types of artificial neural networks capable of learning complex, non-linear patterns in data through layers of neurons and using non-linear activation functions. It explains the processes involved in training MLPs, specifically focusing on the backpropagation algorithm, which optimizes the network by adjusting weights and biases to minimize a loss function. The document further elaborates on gradient descent methods for finding optimal model parameters and outlines steps for applying the backpropagation algorithm.