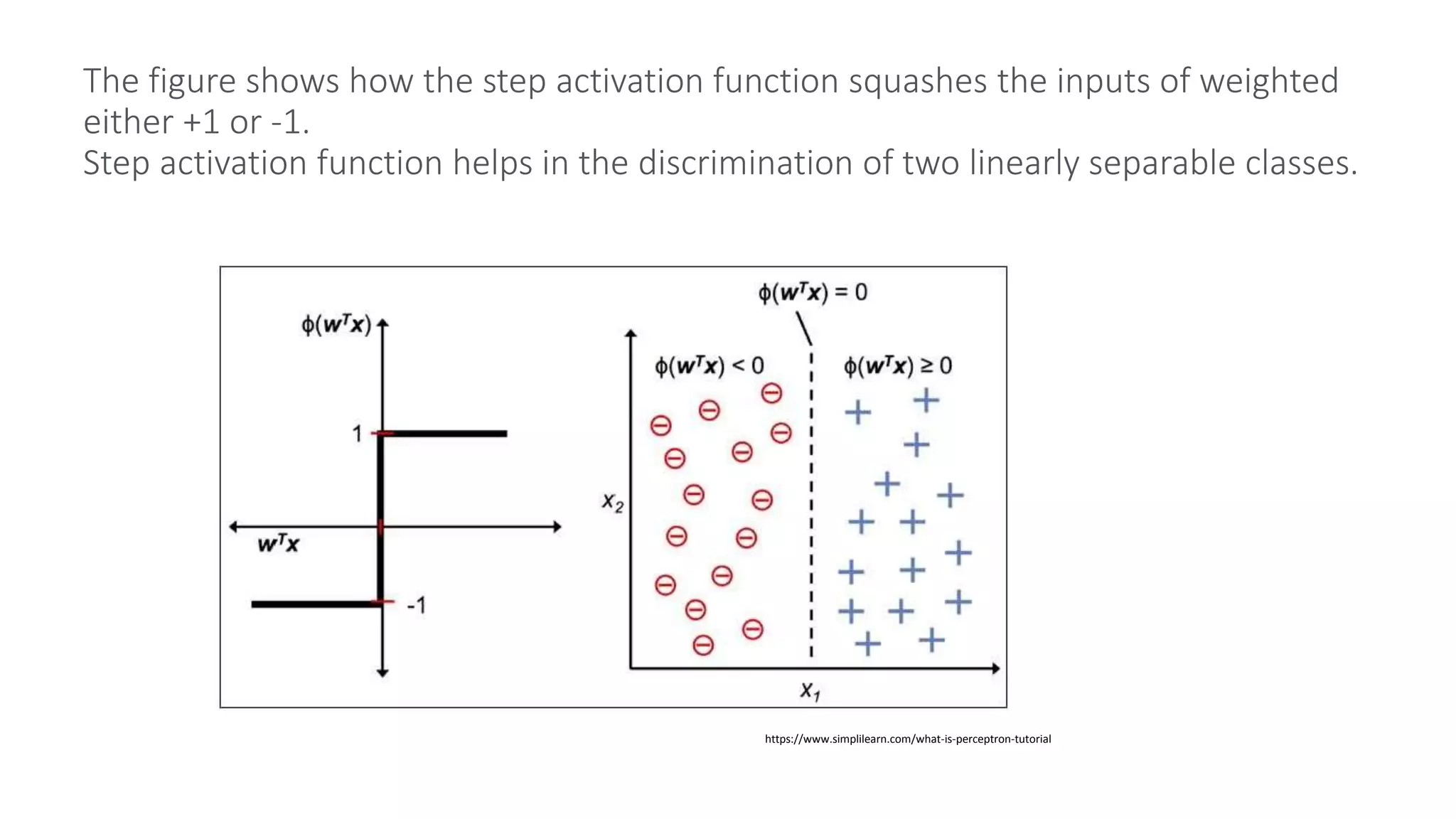
A perceptron is a basic model of an artificial neuron that can be used as a binary classifier. A single layer perceptron introduced by Rosenblatt in 1957 uses a step activation function to classify inputs into two classes. It can only handle linearly separable problems with a binary target. The bias helps shift the activation function and the weights are adjusted during training to correctly classify inputs. A multi-layer perceptron can handle non-linear problems using hidden layers between the input and output layers.










![Computation of final weights after the processing of
Training Set
Instance Target Weights
Weighted Sum
(∑W(i)X(i) ) Actual Target
Predicted Target
( if ∑W(i)X(i) >0 Then 1
Else 0 ) Delta Weight = old weight +η*(Actual Target - Predicted Target)
0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 [0 0 0 0] + 1*0 * [ 0 0 0 0] = [ 0 0 0 0]
1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 [1 1 1 1] + 1*1 * [ 0 0 0 0] = [ 1 1 1 1]
1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 1 1 [1 0 1 1] + 1*0 * [ 1 1 1 1 ] = [ 1 0 1 1]
0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 3 0 1 [1 1 1 1] + 1*(-1) * [ 1 1 1 1 ] = [ 1 0 0 0]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perceptronslideshare-200903114643/75/Perceptron-12-2048.jpg)

