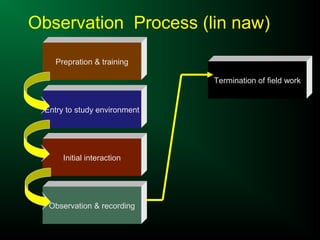
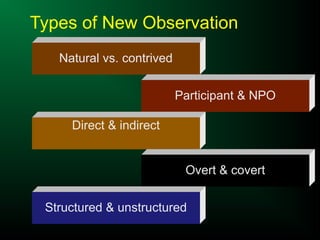
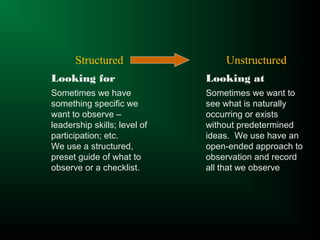
The document discusses different types of observation methods used in research. Observation involves systematically recording behaviors, occurrences, or processes without direct interaction. There are several key characteristics of observation, including it being a physical and mental activity that is purposeful, selective, and involves studying direct relationships. The document outlines different types of observation including natural vs. contrived, participant vs. non-participant, direct vs. indirect, overt vs. covert, and structured vs. unstructured. It provides examples of each type and discusses their advantages and disadvantages.