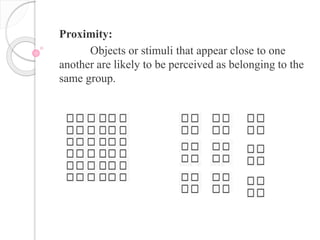
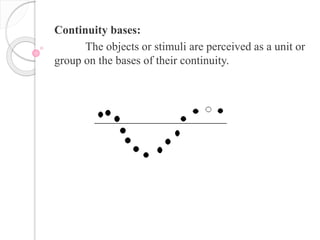
Perception is the process of interpreting sensory information to produce meaningful objects and relationships. It involves identifying objects, events, or relationships by extracting information from sensations. The organization of perception depends on principles like figure-ground relationship, closure, similarity, proximity, and continuity. Perception can be influenced by factors like sense organ function, brain function, previous experience, psychological state, frequency of exposure, interest, and motives. Errors in perception include illusions, which are false perceptions caused by changes in sensory or brain function, and hallucinations, which are false perceptions without external stimuli.