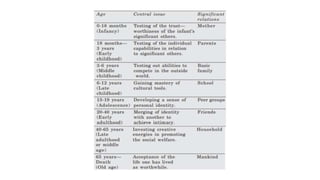
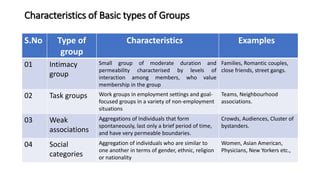
This document provides an overview of developmental psychology from infancy through late adulthood. It discusses the key stages of development, including infancy, early childhood, middle childhood, puberty/adolescence, and the various stages of adulthood. For each life stage, it outlines the typical physical, cognitive, social, and emotional milestones and changes that occur. It also discusses some of the potential adjustment problems that can arise during development. Additionally, it examines psychology related to vulnerable individuals, including those who are physically challenged or sick.