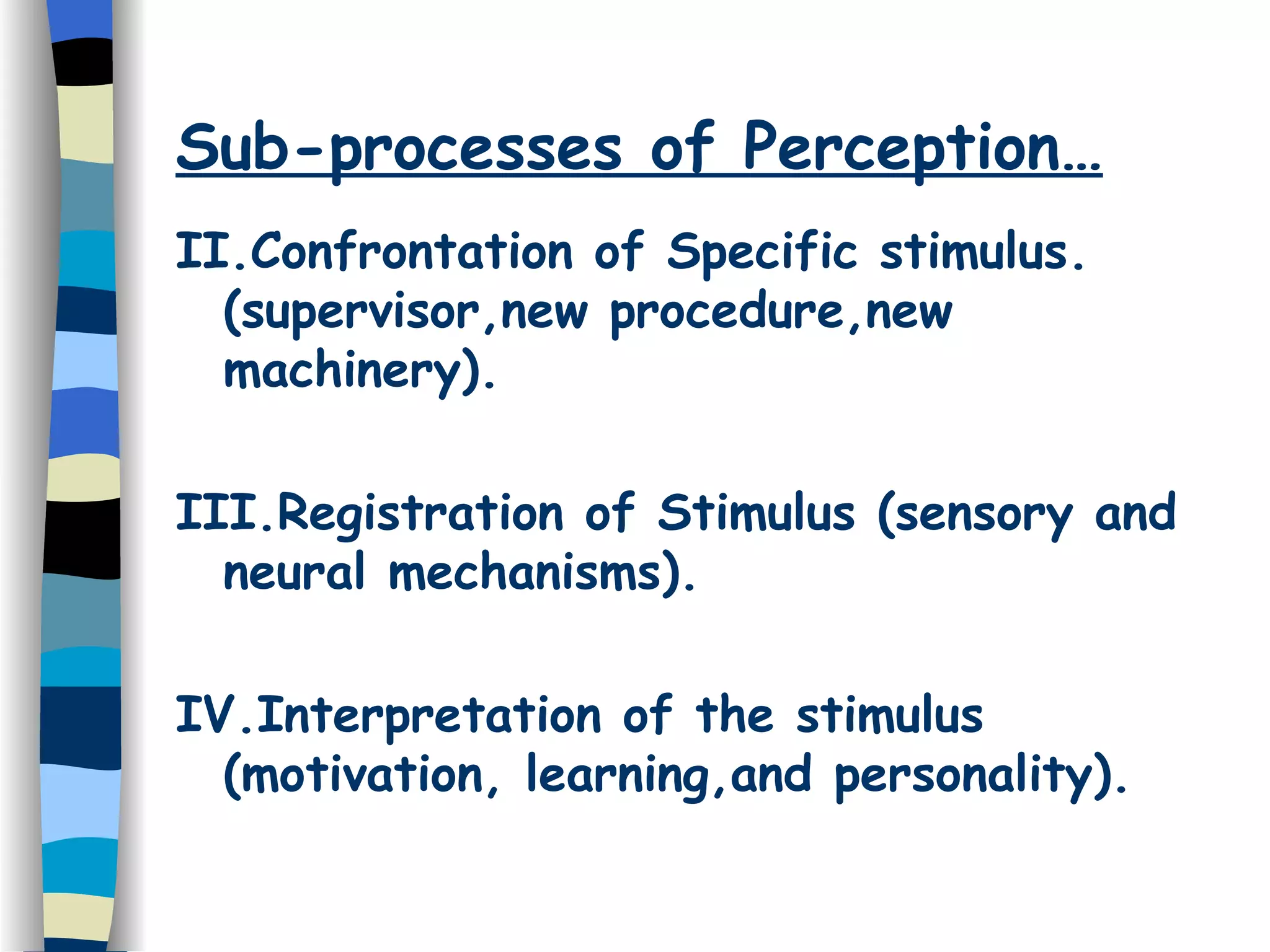
The perceptual process involves the active selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory information to make sense of the external environment. It has several sub-processes including confronting a specific stimulus, registering the stimulus through sensory and neural mechanisms, and interpreting the stimulus based on motivation, learning, and personality. Individual perception also involves selectivity of external and internal factors as well as organizational processes like figure-ground perception and constancy. Social perception depends on characteristics of the perceiver and perceived, and can involve biases like stereotyping. Impression management strategies can be used to prevent negative impressions or promote positive ones.