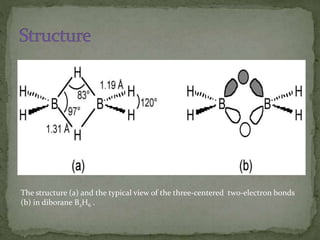
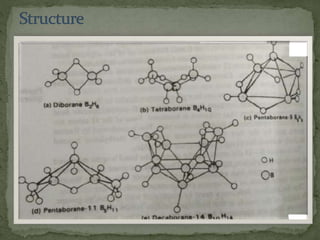
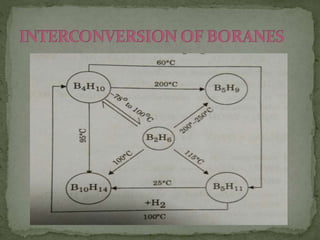
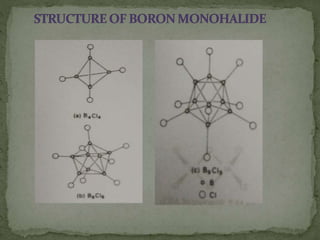
The document discusses the properties of elements in Group 13 of the periodic table, which includes boron, aluminium, gallium, indium, and thallium. It provides details on their electronic configuration, oxidation states, physical properties, and reactions. It also describes the molecular structure of diborane (B2H6) and discusses boranes, which are compounds composed of boron and hydrogen that are analogues of alkanes. Diborane has a unique three-centered two-electron bonding arrangement between its bridging hydrogen atoms.