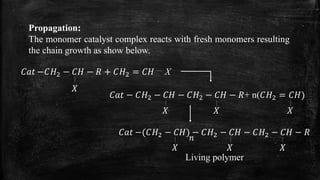
Ziegler-Natta polymerization is a coordination polymerization method discovered by Ziegler and Natta that requires a catalyst formed from transition metal halides and organometallic compounds. The process involves three steps: initiation, propagation, and termination, resulting in the production of various polymers such as polyethylene and polypropylene. However, it cannot be used to generate polyvinyl chloride or acrylates.