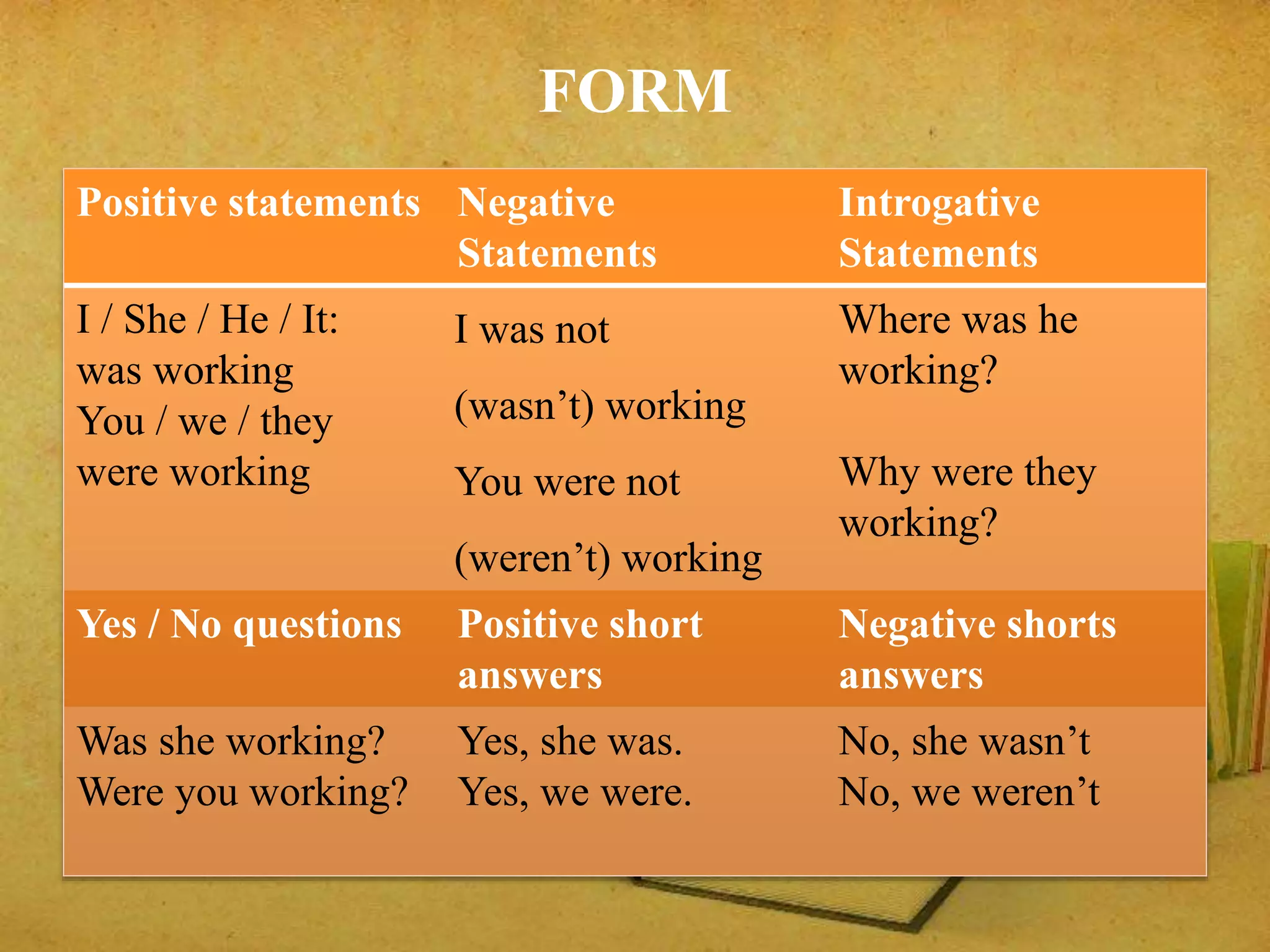
The document discusses the past continuous tense in English grammar. It explains that the past continuous is used to describe background activities or situations that were ongoing at a specific time in the past. It provides examples of using the past continuous to set the scene before describing events using the past simple tense. It also compares the past continuous and past simple. Additionally, it outlines the form, usage and structure of the past continuous tense, including positive and negative statements and questions. Finally, it discusses how nouns are related to the past continuous, including noun markers, endings and forming plurals.