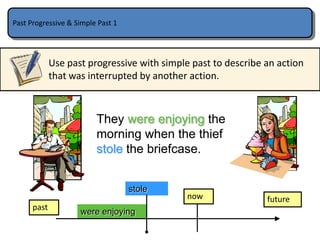
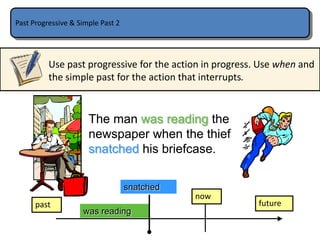
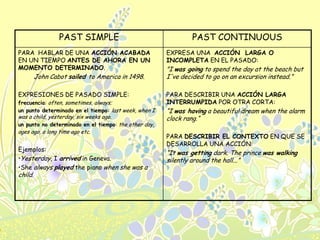
The document provides information on the difference between using the simple past and past continuous tenses in English. The simple past is used for actions that were completed in the past, while the past continuous is used for actions that were ongoing or in progress at a specific time in the past. Examples are given of how to form the past continuous using was/were + verb+ing. It notes some verbs like want or know are usually not used in the continuous form. The past continuous can also be used to describe an ongoing action that was interrupted by another shorter action using time expressions like "while" or "when".