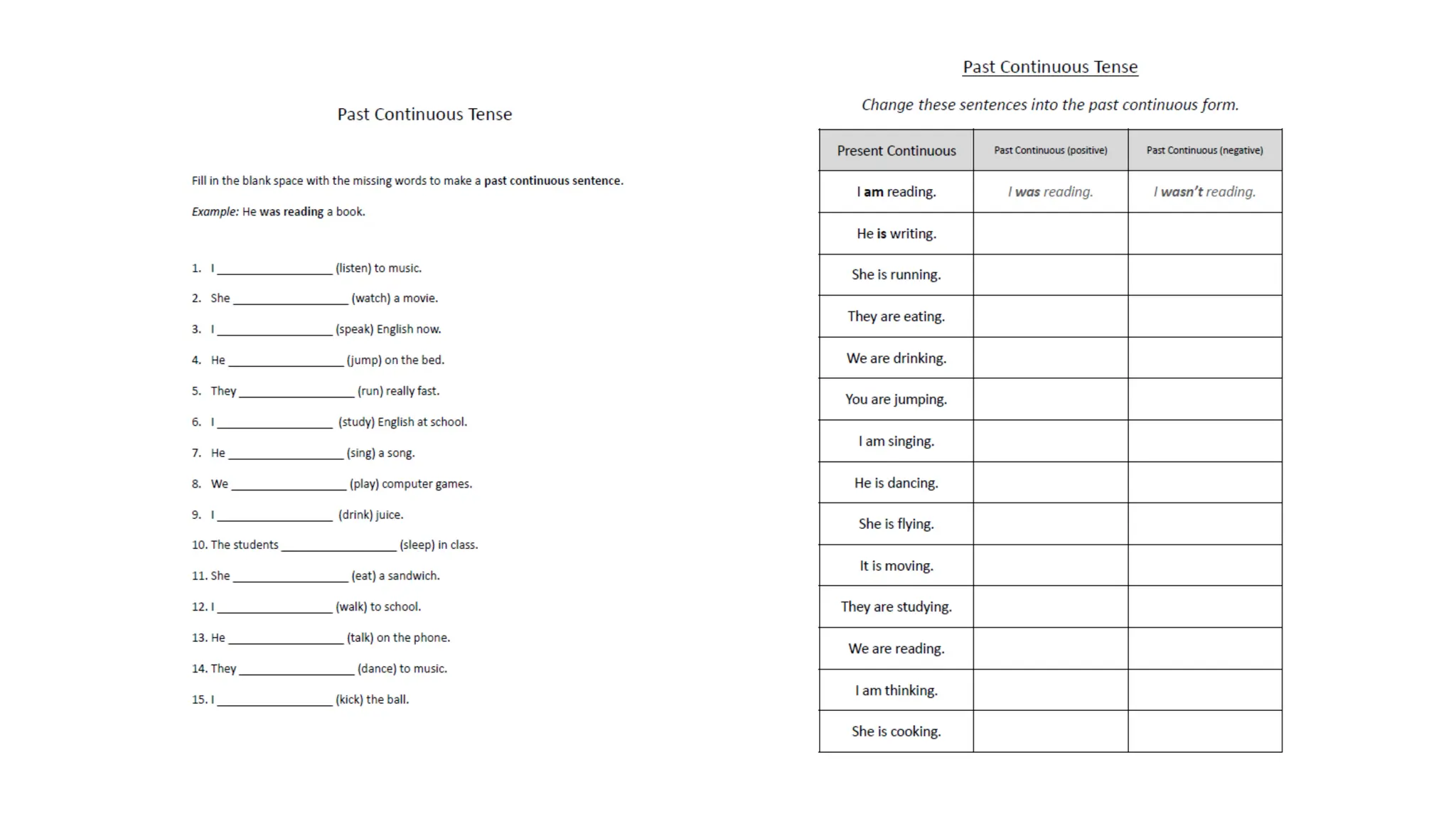
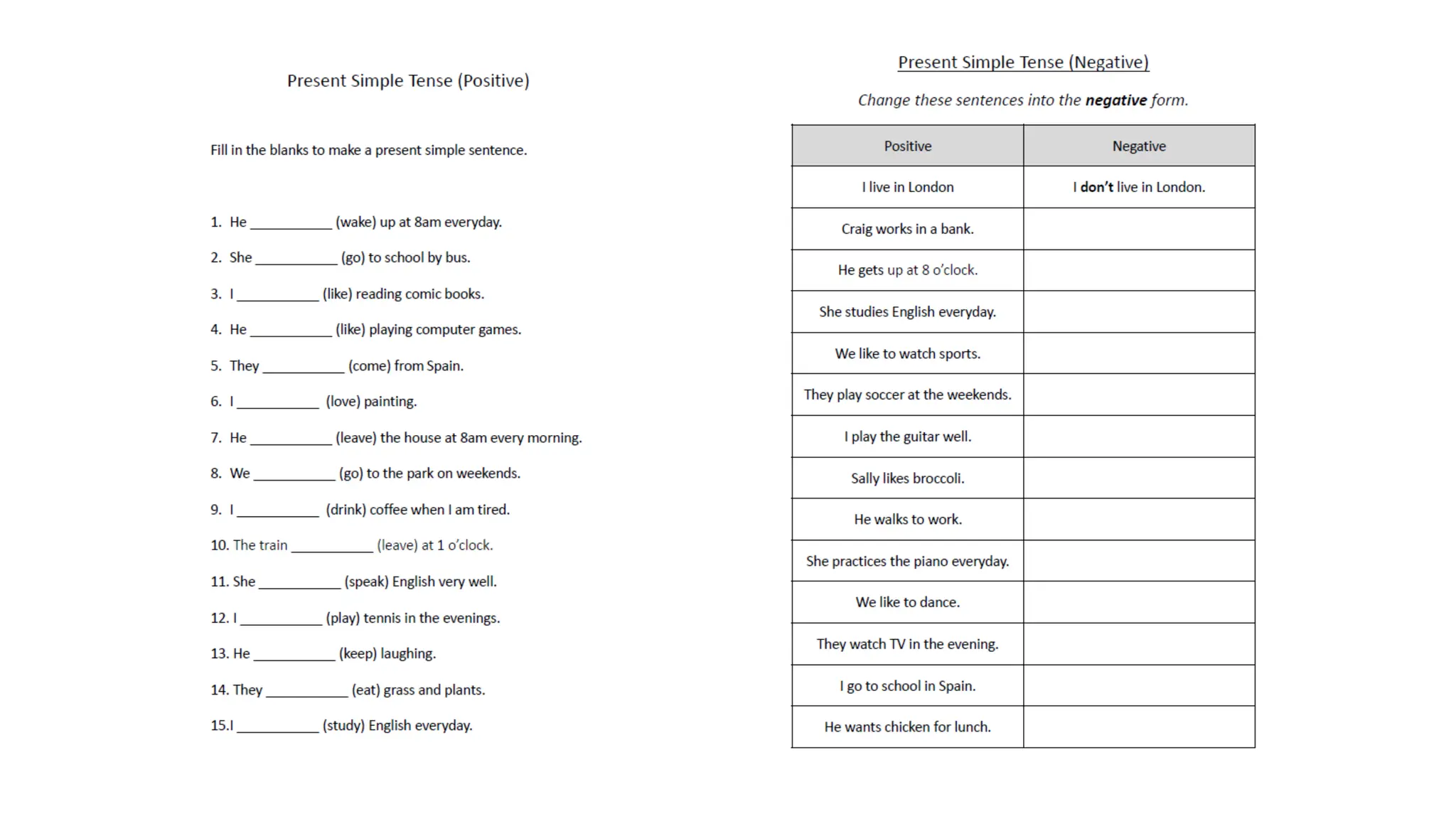
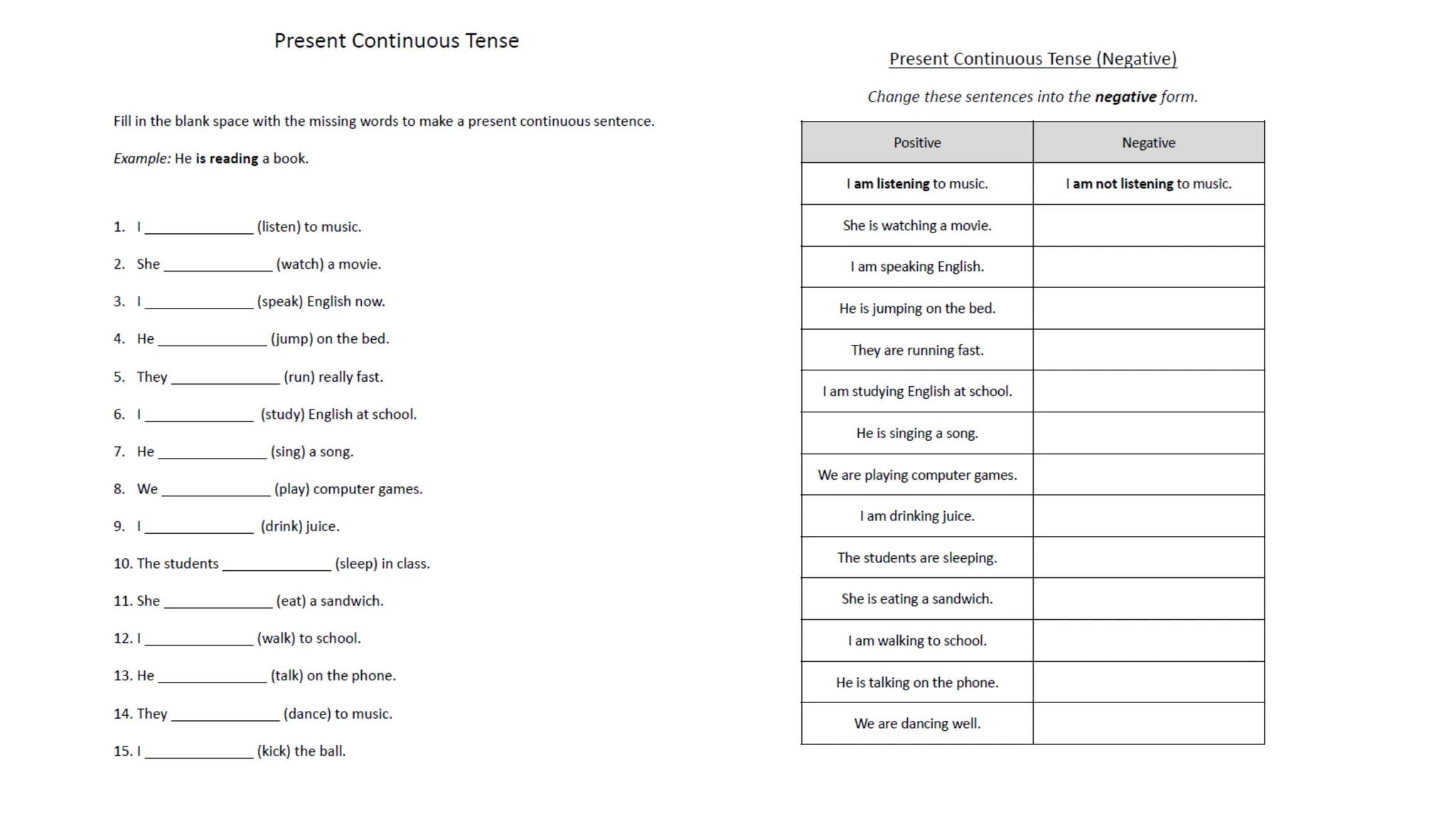
The document explains various verb tenses, including simple past, present, and future forms, and their specific uses in sentences. It details how to construct sentences in each tense, with examples provided for clarity, as well as exercises to practice each tense. Additionally, it discusses the difference between independent and dependent clauses in the context of past continuous tense.